Download
https://archive.apache.org/dist/kafka/2.6.0/
Make sure to download the binaries otherwise you would get the following error
Classpath is empty. Please build the project first e.g. by running ‘gradlew jarAll’

Install

Unzip it in C:\ drive and rename the folder to shorter name (ex: kafka)
You may get following error, if not installed in c:\ drive
input line is too long when starting kafka
Create two folders kafka-logs and zookeeper under KAFKA_HOME

Update config\server.properties as follows
log.dirs=C:/kafka/kafka-logs
Update config\zookeeper.properties as follows
dataDir=C:/kafka/zookeeper
Create file bin\windows\start-kafka.bat
Note : Line #1 (Setting Java home correctly) is required otherwise you would get the following error
The system cannot find the path specified
set JAVA_HOME=%ProgramFiles%\Java\jdk1.8.0_261
start zookeeper-server-start.bat ..\..\config\zookeeper.properties
TIMEOUT 10
start kafka-server-start.bat ..\..\config\server.properties
Add KAFKA_HOME\bin\windows to PATH environment variables
In Admin mode start command prompt, and execute the following
start-kafka.bat

Zookeeper and kafka started

List The Topics
kafka-topics --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --list

Create Topic
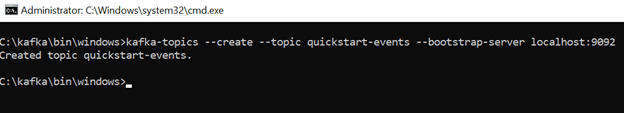
Lets create topic quickstart-events
kafka-topics --create --topic quickstart-events --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
Describe Topic
kafka-topics --describe --topic quickstart-events --bootstrap-server localhost:9092

Produce Events
kafka-console-producer --topic quickstart-events --bootstrap-server localhost:9092

Consume Events
kafka-console-consumer --topic quickstart-events --from-beginning --bootstrap-server localhost:9092

Delete Topic
The following command will have no effect if in the Kafka server.properties file, delete.topic.enable is not set to be true
kafka-topics --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --delete --topic quickstart-events
Java Client
Refer the examples for Java Client
For more information on the APIs, see Apache documentation on the Producer API and Consumer API.


