Basic Authentication - Django REST Framework
Last Updated :
14 Sep, 2021
Authentication is a mechanism that provides access control based on the credentials associated with incoming requests. Django REST Framework provides several authentication schemes. In this section, let's look at the Basic Authentication in Django rest framework, i.e., authenticated against a user's username and password.
Basic Authentication in Django REST Framework uses HTTP Basic Authentication. It is generally appropriate for testing. The REST framework will attempt to authenticate the Basic Authentication class and set the returned values to request.user and request.auth. If successfully authenticated, BasicAuthentication provides the following credentials.
- request.user will be a Django User instance.
- request.auth will be None.
if not, the value of request.user will be set to as an instance of django.contrib.auth.models.AnonymousUser, and request.auth will be set to None. To make of BasicAuthentication scheme, we need to set it to the default authentication scheme. You can either set it globally or you can set the authentication scheme on a per-view basis.
Setting the authentication scheme globally
You can set the authentication globally by using the DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES setting.
Python3
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication',
]
}
Setting the authentication scheme per-view basis
Setting the authentication scheme on a per-view basis differs in function-based views and class-based views.
Function-based views
We can make use of @authentication_classes and @permission_classes decorators to set the authentication scheme in function-based views that use @api_view decorator. The sample code is as follows:
Python3
@api_view(['GET'])
@authentication_classes([BasicAuthentication])
@permission_classes([IsAuthenticated])
def function_based_view(request, format=None):
content = {
# `django.contrib.auth.User` instance
'user': str(request.user),
# None
'auth': str(request.auth),
}
return Response(content)
Class-based views
By using the APIView class, we can set the authentication scheme in class-based views. The sample code is as follows:
Python3
from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication, BasicAuthentication
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.views import APIView
class ClassBasedView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [BasicAuthentication]
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated]
def get(self, request, format=None):
content = {
# `django.contrib.auth.User` instance
'user': str(request.user),
# None
'auth': str(request.auth),
}
return Response(content)
Note: Here, we will use the simplest style of permission that allows access to any authenticated user, and deny access to any unauthenticated user. This corresponds to the 'IsAuthenticated' class in REST framework. If not set to 'IsAuthenticated' class, it uses the default class 'AllowAny', which allows unrestricted access.
Including BasicAuthentication to Restful Webservice
Let's set the BasicAuthentication scheme globally. You can open the settings.py file of our restful web service and add the below code.
Python3
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES':(
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication',
)
}
Note: You can refer The Browsable API section for Models, Serializers, and Views of Project used in the article
Here we set the BasicAuthentication scheme globally, so we don't need to set it for each view. But we need to set the permission class since, by default, the permission class is set to AllowAny, which allows unrestricted access. To make use IsAuthenticated class we need to import it from rest_framework.permissions.
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
Now, let's set the permission class to 'IsAuthenticated' for RobotDetail and RobotList class. The code is as follows:
Python3
class RobotDetail(generics.RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView):
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated]
queryset = Robot.objects.all()
serializer_class = RobotSerializer
name = 'robot-detail'
class RobotList(generics.ListCreateAPIView):
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated]
queryset = Robot.objects.all()
serializer_class = RobotSerializer
name = 'robot-list'
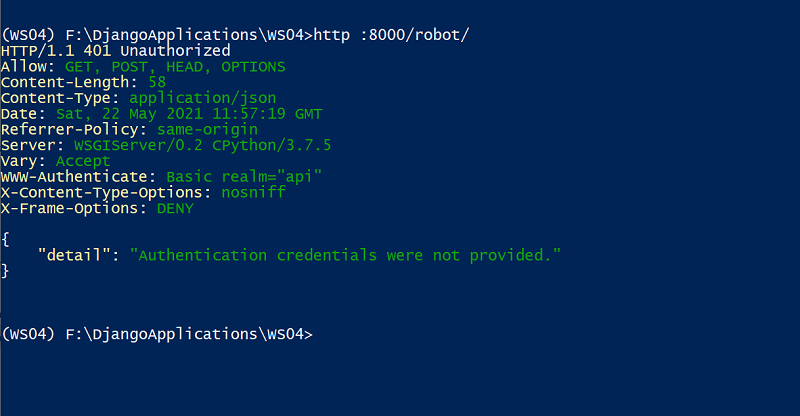
Let's try to retrieve robots without providing any credentials. The HTTPie command is
http :8000/robot/
Output
Now we will create a superuser and provide the credentials to retrieve robots. You can follow How to create superuser in Django? to create a superuser.
Let's try the HTTPie command with credentials to retrieve the robots.
http -a "admin":"admin@123" :8000/robot/
Output

Let's try an HTTPie command that creates a new robot entry.
http -a "admin":"admin@123" POST :8000/robot/ name="SR-3iA" robot_category="SCARA Robots" currency="USD" price=25000 manufacturer="Fanuc" manufacturing_date="2020-05-10 00:00:00+00:00"
Output

Note: If you use BasicAuthentication in production, you should ensure your API is available only for HTTPS and always re-request the credentials. If you are deploying to Apache using mod_wsgi, you need to explicitly configure mod_wsgi to pass the required headers through to the application by setting the WSGIPassAuthorization to 'On'.
Similar Reads
JWT Authentication with Django REST Framework JSON Web Token is an open standard for securely transferring data within parties using a JSON object. JWT is used for stateless authentication mechanisms for users and providers, this means maintaining session is on the client-side instead of storing sessions on the server. Here, we will implement t
2 min read
Implement Token Authentication using Django REST Framework Token authentication refers to exchanging username and password for a token that will be used in all subsequent requests so to identify the user on the server side.This article revolves about implementing token authentication using Django REST Framework to make an API. The token authentication works
2 min read
Django Authentication Project with Firebase Django is a Python-based web framework that allows you to quickly create efficient web applications.. When we are building any website, we will need a set of components: how to handle user authentication (signing up, signing in, signing out), a management panel for managing our website, how to uploa
7 min read
Browsable API in Django REST Framework The browsable API feature in the Django REST framework generates HTML output for different resources. It facilitates interaction with RESTful web service through any web browser. To enable this feature, we should specify text/html for the Content-Type key in the request header. It helps us to use we
8 min read
Class based views - Django Rest Framework Class-based views help in composing reusable bits of behavior. Django REST Framework provides several pre-built views that allow us to reuse common functionality and keep our code DRY. In this section, we will dig deep into the different class-based views in Django REST Framework. This article assum
12 min read
How to Create a basic API using Django Rest Framework ? Django REST Framework (DRF) is a powerful extension of Django that helps you build APIs quickly and easily. It simplifies exposing your Django models as RESTfulAPIs, which can be consumed by frontend apps, mobile clients or other services.Before creating an API, there are three main steps to underst
4 min read
Filter data in Django Rest Framework Django REST Framework's generic list view, by default, returns the entire query sets for a model manager. For real-world applications, it is necessary to filter the queryset to retrieve the relevant results based on the need. Â So, let's discuss how to create a RESTful Web Service that provides filte
4 min read
Adding Permission in API - Django REST Framework There are many different scenarios to consider when it comes to access control. Allowing unauthorized access to risky operations or restricted areas results in a massive vulnerability. This highlights the importance of adding permissions in APIs. Â Django REST framework allows us to leverage permissi
7 min read
Creating and Using Serializers - Django REST Framework In Django REST Framework the very concept of Serializing is to convert DB data to a datatype that can be used by javascript. Serializers allow complex data such as querysets and model instances to be converted to native Python datatypes that can then be easily rendered into JSON, XML or other conten
3 min read
Function based Views - Django Rest Framework Django REST Framework allows us to work with regular Django views. It facilitates processing the HTTP requests and providing appropriate HTTP responses. In this section, you will understand how to implement Django views for the Restful Web service. We also make use of the @api_view decorator. Before
13 min read