Create a Correlation Matrix using Python
Correlation matrix is a table that shows how different variables are related to each other. Each cell in the table displays a number i.e. correlation coefficient which tells us how strongly two variables are together. It helps in quickly spotting patterns, understand relationships and making better decisions based on data.
A correlation matrix can be created using two libraries:
1. Using NumPy Library
NumPy provides a simple way to create a correlation matrix. We can use the np.corrcoef() function to find the correlation between two or more variables.
Example: A daily sales and temperature record is kept by an ice cream store. To find the relationship between sales and temperature, we can utilize the NumPy library where x is sales in dollars and y is the daily temperature.
import numpy as np
x = [215, 325, 185, 332, 406, 522, 412,
614, 544, 421, 445, 408],
y = [14.2, 16.4, 11.9, 15.2, 18.5, 22.1,
19.4, 25.1, 23.4, 18.1, 22.6, 17.2]
matrix = np.corrcoef(x, y)
print(matrix)
Output:
[[1. 0.95750662]
[0.95750662 1. ]]
2. Using Pandas library
Pandas is used to create a correlation matrix using its built-in corr() method. It helps in analyzing and interpreting relationships between different variables in a dataset.
Example: Let's create a simple DataFrame with three variables and calculate correlation matrix.
import pandas as pd
data = {
'x': [45, 37, 42, 35, 39],
'y': [38, 31, 26, 28, 33],
'z': [10, 15, 17, 21, 12]
}
dataframe = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['x', 'y', 'z'])
print("Dataframe is : ")
print(dataframe)
matrix = dataframe.corr()
print("Correlation matrix is : ")
print(matrix)
import pandas as pddata = { 'x': [45, 37, 42, 35, 39], 'y': [38, 31, 26, 28, 33], 'z': [10, 15, 17, 21, 12]}dataframe = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['x', 'y', 'z'])print("Dataframe is : ")print(dataframe)matrix = dataframe.corr()print("Correlation matrix is : ")print(matrix)Output:

3. Using Matplotlib and Seaborn for Visualization
In addition to creating a correlation matrix, it is useful to visualize it. Using libraries like Matplotlib and Seaborn, we can generate heatmaps that provide a clear visual representation of how strongly variables are correlated.
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
matrix = dataframe.corr()
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
sns.heatmap(matrix, annot=True, cmap="coolwarm", fmt=".2f", linewidths=0.5)
plt.title("Correlation Heatmap")
plt.show()
import seaborn as snsimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltmatrix = dataframe.corr()plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))sns.heatmap(matrix, annot=True, cmap="coolwarm", fmt=".2f", linewidths=0.5)plt.title("Correlation Heatmap")plt.show()Output:

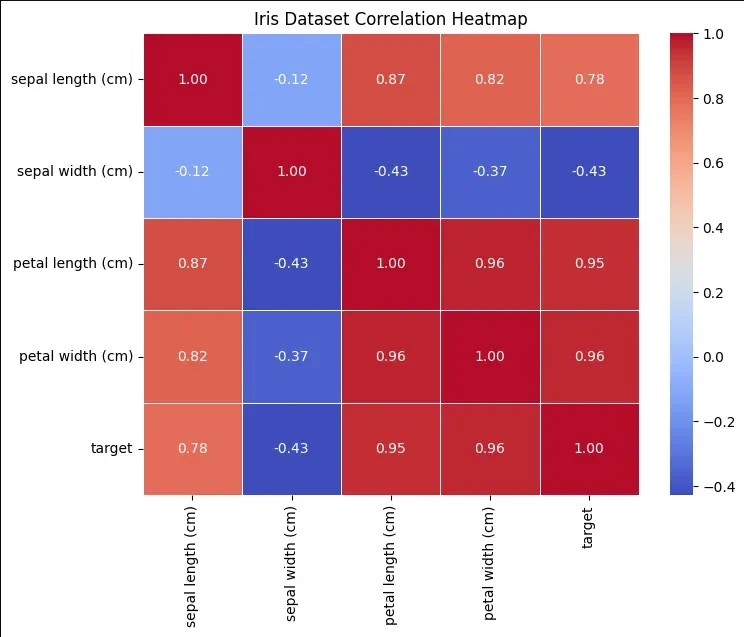
Example with Real Dataset (Iris Dataset)
In this example we will consider Iris dataset and find correlation between the features of the dataset.
- dataset = datasets.load_iris(): Loads the Iris dataset, which includes flower feature data and species labels.
- dataframe["target"] = dataset.target: Adds a target column to the DataFrame containing the species labels.
- dataframe.corr(): Computes the correlation matrix for the numerical features in the DataFrame.
- plt.figure(figsize=(8,6)): Sets the figure size to 8 inches by 6 inches.
- sns.heatmap(matrix, annot=True, cmap="coolwarm", fmt=".2f", linewidths=0.5): Plots the correlation matrix as a heatmap, displaying values with two decimal places, using a color scale from blue (negative correlation) to red (positive correlation) and adds lines between cells for clarity.
from sklearn import datasets
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dataset = datasets.load_iris()
dataframe = pd.DataFrame(data=dataset.data, columns=dataset.feature_names)
dataframe["target"] = dataset.target
matrix = dataframe.corr()
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
sns.heatmap(matrix, annot=True, cmap="coolwarm", fmt=".2f", linewidths=0.5)
plt.title("Iris Dataset Correlation Heatmap")
plt.show()
from sklearn import datasetsimport pandas as pdimport seaborn as snsimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltdataset = datasets.load_iris()dataframe = pd.DataFrame(data=dataset.data, columns=dataset.feature_names)dataframe["target"] = dataset.targetmatrix = dataframe.corr()plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))sns.heatmap(matrix, annot=True, cmap="coolwarm", fmt=".2f", linewidths=0.5)plt.title("Iris Dataset Correlation Heatmap")plt.show()Output:

By using libraries like NumPy and Pandas creating a correlation matrix in Python becomes easy and helps in understanding the hidden relationships between different variables in a dataset.
Related Articles:
- Correlation: Meaning, Significance, Types and Degree of Correlation
- Correlation Matrix in R Programming
- How to Create a Correlation Matrix using Pandas?
- Exploring Correlation in Python
- Plotting Correlation Matrix using Python