DevOps is all about automating and streamlining the software development lifecycle so that code moves from development to production quickly, reliably, and securely.
Here is how the DevOps model flow works:
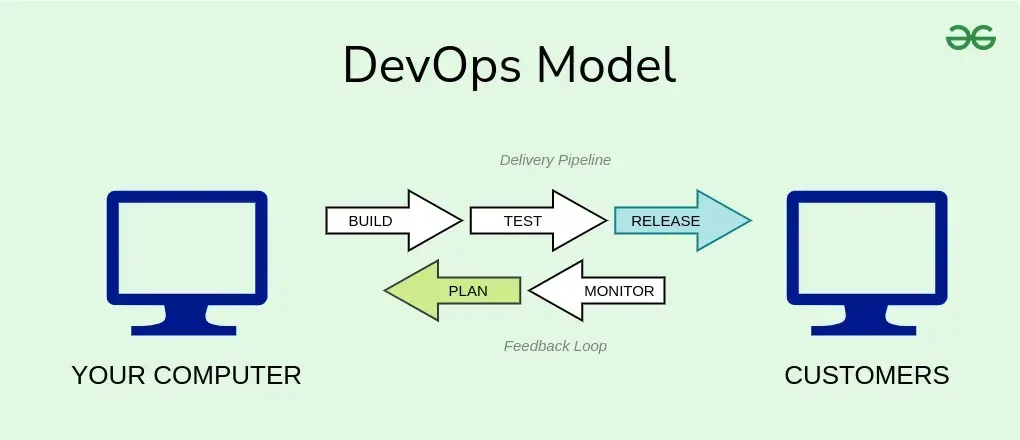
Stages of DevOps are:
Build Stage
1. Developers write and organize code, using version control tools like Git to track changes.
2. The system automatically compiles and packages the code into a deployable format.
3. Dependencies (external libraries and tools) are included to ensure smooth operation.
4. Common Tools: Git, Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, Gradle, Maven.
Test Stage
1. The software undergoes thorough testing to catch bugs and security risks before release.
2. Different testing methods include:
- Unit Testing: Checks individual pieces of code.
- Integration Testing: Ensures different parts of the system work together.
- Performance Testing: Measures speed and scalability.
- Security Testing: Identifies potential vulnerabilities.
3. Automated tests help ensure the software is stable before moving forward.
4. Common Tools: Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, SonarQube.
Release Stage
1. The software is deployed in a staging environment to simulate real-world conditions.
2. If everything checks out, the software is rolled out to production using deployment strategies like:
- Blue-Green Deployment: Two identical environments switch traffic for a seamless update.
- Canary Deployment: A small percentage of users get the new version first, ensuring safety.
- Rolling Updates: The update is gradually pushed out to all users.
3. Common Tools: Docker, Kubernetes, Ansible, Helm, ArgoCD.
Continuous Feedback Loop
A key aspect of DevOps is learning from real-world performance and using that feedback to improve future releases.
- Monitoring & Logging: Track system performance and detect errors.
- User Feedback: Gather insights from customers to enhance features.
- Incident Response: Alert systems notify teams of failures for quick fixes.
- Process Improvement: Teams analyze past releases to optimize automation and workflow.
- Common Tools: Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack, Datadog, New Relic.
How to Adopt a DevOps Model?
To adopt a DevOps model, ensure the following points:
- Assess Current Workflow: Evaluate your existing development and operations processes to identify gaps, inefficiencies, and areas for automation.
- Set Clear DevOps Goals: Define measurable objectives such as faster deployment cycles, better collaboration, or improved system stability.
- Build a Collaborative Culture: Break silos between development, operations, QA, and security teams by encouraging communication and shared responsibilities.
- Automate Infrastructure and Testing: Use tools like Jenkins, Docker, and Ansible to automate code integration, deployment, testing, and infrastructure provisioning.
- Implement CI/CD Pipelines: Establish Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment pipelines for faster, error-free code delivery.
- Monitor and Optimize Continuously: Use real-time monitoring and feedback loops (via tools like Prometheus, Grafana) to track performance and improve systems iteratively.
DevOps for AI and ML
Even though Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are still growing in DevOps, they are already making a big difference.
- Handling Big Data: DevOps tools generate a huge amount of data from testing, deployment, and monitoring. AI and ML are great at reading all this data quickly, finding useful insights, and helping teams make faster and smarter decisions.
- Saving Time with Smart Suggestions: AI can learn how developers and operations teams work, then suggest better ways to do tasks or automatically set up the needed tools and servers, reducing manual work.
- Spotting Bugs Early: AI and ML can look at code and test results to find problems (like bugs) early. They can detect unusual patterns that may cause issues later and warn the DevOps team before users are affected.
- Improving Security: These technologies can scan security logs and alerts to find threats, such as hacking attempts or breaches. Once something risky is found, they can even respond automatically. For example, by blocking access or sending alerts.
How DevOps Helped GeeksforGeeks Save AWS Costs
In this section we will try to understand how DevOps changes at GeeksforGeeks helped reduce AWS bills by up to 70%. By replacing expensive services with open-source tools and adding smart automation.
These are actual changes made in GeeksforGeeks production setup.
1. Caching: From AWS ElasticCache to Open-Source Redis
What we used Before
We relied on AWS ElastiCache (Redis) for caching data like page content, user sessions, etc. It worked well but came with a high cost, especially as the number of nodes increased.

What we use Now
We moved to:
- Redis (open-source) hosted on our own EC2 instances
- Grafana for monitoring cache hit/miss ratio and performance
We now only pay for EC2 compute cost (not for managed Redis service).
Savings
- Cost dropped by 60–70%
- More control over performance tuning
- Visual insights using Grafana
2. Optimizing Video Delivery
The National Skill Up Portal by GeeksforGeeks is an e-learning platform offering free video-based skill development across India. With lakhs of learners daily, delivering smooth, fast, and cost-effective video access became essential.
Initial Challenges:
1. Videos were served directly from the origin (Amazon S3/EC2).
2. Every request, even from nearby users, fetched data from the origin.
3. Issues faced:
- High AWS bandwidth costs
- Slow performance in remote regions due to latency.

Solution: Integrating Amazon CloudFront for Edge Caching
To resolve this, the development team integrated Amazon CloudFront, a Content Delivery Network (CDN) that delivers content from edge locations closer to users.
Key Benefits:
- Edge Caching for 1 Year:
Videos are cached at edge locations after first access. Future requests are served locally, reducing load on the origin. - 50–70% Bandwidth Cost Reduction:
Most traffic now goes through CloudFront, cutting AWS transfer costs significantly. - Faster Access Nationwide:
Students across all regions now experience smoother playback with minimal buffering.

3. Smart Automation: Stop EC2 Instances After Work Hours
What was Happening
Our development/testing EC2 instances were running 24x7 — even when no one was using them at night.

What we Did
We wrote a Bash script + Cronjob combo:
- Automatically stops EC2 instances at 10 PM
- Starts them again at 9 AM
- Fully automated with no human effort
Savings
- No charges for idle machines at night
- Saved 50% compute cost on dev/test infra
- Easy to maintain
DevOps Vs Waterfall
The following table explains the comparison between DevOps and Waterfall Model
Factor | DevOps | Waterfall |
|---|
Process | Continuous development & deployment | Step-by-step, rigid process |
|---|
Collaboration | Dev, Ops, and QA work together | Teams work separately |
|---|
Speed | Rapid, frequent releases | Slow, long release cycles |
|---|
Automation | High (CI/CD, testing, monitoring) | Mostly manual processes |
|---|
Flexibility | Easily adapts to changes | Hard to modify once planned |
|---|
Risk Handling | Continuous monitoring, early issue detection | Errors found late in the cycle |
|---|
Why DevOps Wins: Waterfall follows a fixed, sequential approach, making it slow and inflexible. DevOps ensures continuous integration, testing, and delivery, reducing delays and risks.
Similar Reads
DevOps Tutorial DevOps is a combination of two words: "Development" and "Operations." It’s a modern approach where software developers and software operations teams work together throughout the entire software life cycle.The goals of DevOps are:Faster and continuous software releases.Reduces manual errors through a
7 min read
Introduction
What is DevOps ?DevOps is all about automating and streamlining the software development lifecycle so that code moves from development to production quickly, reliably, and securely.Here is how the DevOps model flow works:Stages of DevOps are:Build Stage1. Developers write and organize code, using version control to
6 min read
DevOps LifecycleThe DevOps lifecycle is a structured approach that integrates development (Dev) and operations (Ops) teams to streamline software delivery. It focuses on collaboration, automation, and continuous feedback across key phases planning, coding, building, testing, releasing, deploying, operating, and mon
10 min read
The Evolution of DevOps - 3 Major Trends for FutureDevOps is a software engineering culture and practice that aims to unify software development and operations. It is an approach to software development that emphasizes collaboration, communication, and integration between software developers and IT operations. DevOps has come a long way since its in
7 min read
Version Control
Continuous Integration (CI) & Continuous Deployment (CD)
Containerization
Orchestration
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Monitoring and Logging
Microsoft Teams vs Slack Both Microsoft Teams and Slack are the communication channels used by organizations to communicate with their employees. Microsoft Teams was developed in 2017 whereas Slack was created in 2013. Microsoft Teams is mainly used in large organizations and is integrated with Office 365 enhancing the feat
4 min read
Security in DevOps