Hibernate - One-to-One Mapping
Last Updated :
24 Mar, 2025
Prerequisite: Basic knowledge of hibernate framework, Knowledge about databases, Java
Hibernate is a framework that provides some abstraction layer, meaning that the programmer does not have to worry about the implementations, Hibernate does the implementations for you internally like Establishing a connection with the database, writing queries to perform CRUD operations, etc. It is a java framework that is used to develop persistence logic. Persistence logic means storing and processing the data for long use. More precisely Hibernate is an open-source, non-invasive, lightweight java ORM(Object-relational mapping) framework to develop objects which are independent of the database software and make independent persistence logic in all JAVA, JEE.
What is one-to-one mapping?
One to one represents that a single entity is associated with a single instance of the other entity. An instance of a source entity can be at most mapped to one instance of the target entity. We have a lot of examples around us that demonstrate this one-to-one mapping.
- One person has one passport, a passport is associated with a single person.
- Leopards have unique spots, a pattern of spots is associated with a single leopard.
- We have one college ID, a college ID is uniquely associated with a person.
You can find more day-to-day life examples if you observe. In database management systems one-to-one mapping is of two types-
- One-to-one unidirectional
- One-to-one bidirectional
One-to-one unidirectional
In this type of mapping one entity has a property or a column that references to a property or a column in the target entity. Let us see this with the help of an example-
 ER Diagram
ER DiagramIn this example student table to associated with the student_gfg_detail with the help of a foreign key student_gfg_detail_id which references student_gfg_detail.id. The target entity (student_gfg_detail) does not have a way to associate with the student table but the student table can access the student_gfg_table with the help of a foreign key. The above relationship can be generated with the help of the following SQL script.
DROP SCHEMA IF EXISTS `hb-one-to-one-mapping`;
CREATE SCHEMA `hb-one-to-one-mapping`;
use `hb-one-to-one-mapping`;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student_gfg_detail`;
-- -----------------------------------------------------
-- Table `hb-one-to-one-mapping`.`student_gfg_detail`
-- -----------------------------------------------------
CREATE TABLE `student_gfg_detail` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`college` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL,
`no_of_problems_solved` INT DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `instructor`;
-- -----------------------------------------------------
-- Table `hb-one-to-one-mapping`.`student`
-- -----------------------------------------------------
CREATE TABLE `hb-one-to-one-mapping`.`student` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`first_name` VARCHAR(45) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`last_name` VARCHAR(45) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`email` VARCHAR(45) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`student_gfg_detail_id` INT UNIQUE,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
FOREIGN KEY (`student_gfg_detail_id`)
REFERENCES `hb-one-to-one-mapping`.`student_gfg_detail` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION)
ENGINE = InnoDB
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET = latin1;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
While creating the student table we reference the primary key in the student_gfg_detail table i.e. student_gfg_detail.id. We have set ON DELETE NO ACTION and ON DELETE NO ACTION deliberately as we will set these values inside Hibernate. Now let's add entries to the database with the help of Hibernate. First, let's define our hibernate configuration file.
XML
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- JDBC Database connection settings -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hb-one-to-one-mapping?useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
</property>
<property name="connection.username">your_username</property>
<property name="connection.password">your_password</property>
<!-- JDBC connection pool settings ... using built-in test pool -->
<property name="connection.pool_size">1</property>
<!-- Select our SQL dialect -->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<!-- Echo the SQL to stdout -->
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<!-- Set the current session context -->
<property name="current_session_context_class">thread</property>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
We will be using MySQL as the JDBC driver. You can use any other vendor implementation also. In the configuration file, we set up the session factory with the database connection settings, connection pool settings, SQL dialect, etc. One important property here to note is current_session_context_class. Most applications using Hibernate need some form of "contextual" session, where a given session is in effect throughout the scope of a given context. Here this property specifies that the current session is in the context of only one thread. Also do not forget to change your_username with your database username and your_password with your database password.
Now we need to add hibernate JAR file and MySQL database connector to our external libraries. I will be using maven to add those JAR files but you can also download them from the official sources and add them manually to your external libraries. Let's define our pom.xml file
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.geeksforgeeks</groupId>
<artifactId>Hibernate-One-to-One-Mapping</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-vibur</artifactId>
<version>5.6.5.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Now that we have added the related dependencies let's add start with defining our entities.
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.entity;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "first_name") private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name") private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email") private String email;
@OneToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name = "student_gfg_detail_id")
private StudentGfgDetail studentGfgDetail;
public Student() {}
public Student(String firstName, String lastName,
String email)
{
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
}
public int getId() { return id; }
public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; }
public String getFirstName() { return firstName; }
public void setFirstName(String firstName)
{
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() { return lastName; }
public void setLastName(String lastName)
{
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() { return email; }
public void setEmail(String email)
{
this.email = email;
}
public StudentGfgDetail getStudentGfgDetail()
{
return studentGfgDetail;
}
public void
setStudentGfgDetail(StudentGfgDetail studentGfgDetail)
{
this.studentGfgDetail = studentGfgDetail;
}
@Override public String toString()
{
return "Student{"
+ "id=" + id + ", firstName='" + firstName
+ '\'' + ", lastName='" + lastName + '\''
+ ", email='" + email + '\''
+ ", studentGfgDetail=" + studentGfgDetail
+ '}';
}
}
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "student_gfg_detail")
public class StudentGfgDetail {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "college") private String college;
@Column(name = "no_of_problems_solved")
private int noOfProblemsSolved;
public StudentGfgDetail() {}
public StudentGfgDetail(String college,
int noOfProblemsSolved)
{
this.college = college;
this.noOfProblemsSolved = noOfProblemsSolved;
}
public int getId() { return id; }
public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; }
public String getCollege() { return college; }
public void setCollege(String college)
{
this.college = college;
}
public int getNoOfProblemsSolved()
{
return noOfProblemsSolved;
}
public void
setNoOfProblemsSolved(int noOfProblemsSolved)
{
this.noOfProblemsSolved = noOfProblemsSolved;
}
@Override public String toString()
{
return "StudentGfgDetail{"
+ "id=" + id + ", college='" + college + '\''
+ ", noOfProblemsSolved=" + noOfProblemsSolved
+ '}';
}
}
All the latest frameworks these days heavily rely on annotations as it makes code shorter and easier to understand, let's understand what is happening step by step. As we store the Student object and StudentGfgDetail objects in our database, we annotate them with @Entity. The @Table annotation specifies the primary table associated with the entity, we pass the name of the table inside the annotation.
- @Id - Specifies that the given field is the primary key of the entity.
- @GeneratedValue - This defines the strategy to generate the primary key, here we use GenerationType.IDENTITY which is auto increments the value of Id, if we don't want to use this we would have to specify the primary key explicitly every time we create an object.
- @Column - This simply maps a given field to a column inside the database.
The key thing here to note is the following part-
@OneToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name = "student_gfg_detail_id")
private StudentGfgDetail studentGfgDetail;
We add a single object of StudentGfgDetail inside the Student class which is annotated with @OneToOne annotation which specifies the one-to-one mapping. This annotation contains an element called cascade which specifies the cascading strategy. Cascading is a feature that is used to manage the state of the target entity whenever the state of the parent entity changes. Basic Hibernate cascade types are-
- CascadeType.ALL - Propagates all operations from parent to target entity.
- CascadeType.PERSIST - Propagates persist from parent to target entity.
- CascadeType.MERGE - Propagates merge from parent to target entity.
- CascadeType.REMOVE - Propagates remove from parent to target entity.
- CascadeType.REFRESH - Propagates refresh from parent to target entity.
- CascadeType.DETACH - Propagates detach from parent to target entity.
For example if cascade = CascadeType.REMOVE then if the parent entity is deleted from the database then the target entity will also be deleted from the database i.e. if a Student entity is deleted from the database then the related StudentGfgDetail will get automatically deleted in the same operation. The @JoinColumn annotation specifies the column for joining the target entity. Here it is specified that StudentGfgDetail should be joined to the column student_gfg_detail_id which is correct as student_gfg_detail_id is acting as our foreign key.
This sets up a one-to-one unidirectional relationship as Student can access the StudentGfgDetail entity but it is not true vice-versa. Now after we are done defining our entities let's get into real action, let's modify our database with the help of hibernate. Let's add an entry to our database-
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.application;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.Student;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.StudentGfgDetail;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class AddingEntryDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create session factory
SessionFactory factory
= new Configuration()
.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml")
.addAnnotatedClass(Student.class)
.addAnnotatedClass(StudentGfgDetail.class)
.buildSessionFactory();
// Create session
try (factory; Session session
= factory.getCurrentSession()) {
// Get the current session
// Create relevant object.
Student student = new Student("Vyom", "Yadav",
"[email protected]");
StudentGfgDetail studentGfgDetail
= new StudentGfgDetail("GFG College", 20);
student.setStudentGfgDetail(studentGfgDetail);
// Begin the transaction
session.beginTransaction();
// Save the student object.
// This will also save the StudentGfgDetail
// object as we have used CascadeType.ALL
session.save(student);
// Commit the transaction
session.getTransaction().commit();
System.out.println(
"Transaction Successfully Completed!");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Now let's discuss this step by step-
- We create the Session factory with the help of the configuration file as we had set up the details in the configuration file. Then we add annotated classes, basically classes we annotated in the previous steps, and then just build the session factory.
- Get the current session from the session factory.
- Create relevant objects and call setter methods.
- Begin the transaction.
- Save the Student object, this also saves the associated StudentGfgDetail as we used CascadeType.ALL in the previous steps.
- Get the transaction and commit the changes.
- Close the current session.
- Close the session factory as we don't want to create more sessions.
If we run the code above with proper configuration we should see similar output-
 Output
Output
The output may not be 100% the same as it depends on the version of hibernate you are using but it should be very close to the output above. Let's double-check whether those values were inserted into the database or not.
 student Table
student Table student_gfg_detail Table
student_gfg_detail Table
Now that we have verified that we were able to add an entry to the database and our operations were working let's try to update these entries.
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.application;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.Student;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.StudentGfgDetail;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class UpdateEntryDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create session factory
SessionFactory factory
= new Configuration()
.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml")
.addAnnotatedClass(Student.class)
.addAnnotatedClass(StudentGfgDetail.class)
.buildSessionFactory();
// Create session
try (factory; Session session
= factory.getCurrentSession()) {
// Begin the transaction
session.beginTransaction();
// Get object with id = 1
int id = 1;
Student student
= session.get(Student.class, id);
StudentGfgDetail studentGfgDetail
= student.getStudentGfgDetail();
// modify the student and its details
student.setEmail("[email protected]");
studentGfgDetail.setNoOfProblemsSolved(40);
// Update the student object.
// This will also update the StudentGfgDetail
// object as we have used CascadeType.ALL
session.update(student);
// Commit the transaction
session.getTransaction().commit();
System.out.println(
"Transaction Successfully Completed!");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
The only piece of code we need to understand is-
// Get object with id = 1
int id = 1;
Student student = session.get(Student.class, id);
StudentGfgDetail studentGfgDetail = student.getStudentGfgDetail();
// modify the student and its details
student.setEmail("[email protected]");
studentGfgDetail.setNoOfProblemsSolved(40);
// Update the student object.
// This will also update the StudentGfgDetail object as we have used CascadeType.ALL
session.update(student);
- We get the student with id = 1.
- Modify the details.
- Update the value.
One thing here to note here is that we should be inside to use the get(Student.class, id) method, that's why this piece of code comes after we begin the transaction. The output if we run the code with proper configuration-
 Output
Output
Again the output depends on hibernate version but it should be similar. We can also verify these changes inside the database-
 Note that email changed
Note that email changed Note that the no_of_problems_solved changed
Note that the no_of_problems_solved changed
Reading a value from a database can also be done very easily, just modify the section under begin transaction as-
// Get object with id = 1
int id = 1;
Student student = session.get(Student.class, id);
StudentGfgDetail studentGfgDetail = student.getStudentGfgDetail();
System.out.println(student);
System.out.println(studentGfgDetail);
// Commit the transaction
session.getTransaction().commit();
// close the session
session.close();
We could print the data to the standard output stream or a file, according to our needs. Note that there is no need to save as we aren't modifying the data, we are simply reading it. Deletion can also be done similarly-
// Get object with id = 1
int id = 1;
Student student = session.get(Student.class, id);
// Delete the student, this will also delete the associated entity
// as we use CascadeType.ALL
session.delete(student);
// Commit the transaction
session.getTransaction().commit();
// close the session
session.close();
Note that the associated StudentGfgDetail entity will also be deleted as we are using CascadeType.ALL
One-to-one bidirectional
Until now the relationship was unidirectional i.e. we could access StudentGfgDetail from the Student entity but not vice-versa, but why would we want to have a bidirectional relationship, and what is the problem with a unidirectional relationship?
Problem:
If we somehow just delete the StudentGfgDetail entity and leave the Student entity as it is then the Student entity will have a foreign key that refers to a non-existing object which introduces the problem of dangling foreign key which is, of course, a bad practice. The option to delete the Student entity when the StudentGfgDetail entity is deleted depends on the design of the database, we might want to keep the Student entity as a record of users who left the community or just delete it. Luckily we can achieve both of the things mentioned above without modifying our database and just with the help of Hibernate, just modify StudentGfgDetail.java-
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.entity;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "student_gfg_detail")
public class StudentGfgDetail {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "college") private String college;
@Column(name = "no_of_problems_solved")
private int noOfProblemsSolved;
@OneToOne(mappedBy = "studentGfgDetail",
cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private Student student;
public StudentGfgDetail() {}
public StudentGfgDetail(String college,
int noOfProblemsSolved)
{
this.college = college;
this.noOfProblemsSolved = noOfProblemsSolved;
}
public int getId() { return id; }
public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; }
public String getCollege() { return college; }
public void setCollege(String college)
{
this.college = college;
}
public int getNoOfProblemsSolved()
{
return noOfProblemsSolved;
}
public void
setNoOfProblemsSolved(int noOfProblemsSolved)
{
this.noOfProblemsSolved = noOfProblemsSolved;
}
public Student getStudent() { return student; }
public void setStudent(Student student)
{
this.student = student;
}
@Override public String toString()
{
return "StudentGfgDetail{"
+ "id=" + id + ", college='" + college + '\''
+ ", noOfProblemsSolved=" + noOfProblemsSolved
+ ", student=" + student + '}';
}
}
The only thing we need to cover here is-
@OneToOne(mappedBy = "studentGfgDetail",
cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private Student student;
Now we don't have a column referencing to student table in our student_gfg_detail table so what is this piece of code?
This is where Hibernate comes into helping us, mappedBy = "studentGfgDetail" tells Hibernate to look for a field named studentGfgDetail in the Student class and link that particular instance to the current student object. Now that we have understood the linkage let's try to add an entry into the database, but this time we will save the StudentGfgDetail object explicitly which will implicitly also save the related Student object because of CascadeType.ALL.
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.application;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.Student;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.StudentGfgDetail;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class AddEntryBidirectionalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create session factory
SessionFactory factory
= new Configuration()
.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml")
.addAnnotatedClass(Student.class)
.addAnnotatedClass(StudentGfgDetail.class)
.buildSessionFactory();
// Create session
try (factory; Session session
= factory.getCurrentSession()) {
// Create relevant object.
Student student = new Student("JJ", "Olatunji",
"[email protected]");
StudentGfgDetail studentGfgDetail
= new StudentGfgDetail("GFG College", 0);
student.setStudentGfgDetail(studentGfgDetail);
studentGfgDetail.setStudent(student);
// Begin the transaction
session.beginTransaction();
// Save the studentGfgDetail object.
// This will also save the student object as we
// have used CascadeType.ALL
session.save(studentGfgDetail);
// Commit the transaction
session.getTransaction().commit();
System.out.println(
"Transaction Successfully Completed!");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Note that we don't have any key referencing to the student in the student_gfg_detail table still, we can save it through the StudentGfgDetail object.
Output:
 Output
Output
We can see that hibernate did two insertions so we know that both the values have been successfully inserted, now let's try to read these values by just retrieving the StudentGfgDetail object.
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.application;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.Student;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.StudentGfgDetail;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class ReadEntryBidirectionalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create session factory
SessionFactory factory
= new Configuration()
.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml")
.addAnnotatedClass(Student.class)
.addAnnotatedClass(StudentGfgDetail.class)
.buildSessionFactory();
// Create session
try (factory; Session session
= factory.getCurrentSession()) {
// Begin the transaction
session.beginTransaction();
int theId = 5;
StudentGfgDetail studentGfgDetail = session.get(
StudentGfgDetail.class, theId);
System.out.println(
studentGfgDetail.getStudent());
System.out.println(studentGfgDetail);
// Commit the transaction
session.getTransaction().commit();
System.out.println(
"Transaction Successfully Completed!");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
As we can see, we just retrieved the StudentGfgDetail object, and that object in turn implicitly retrieved the Student object.
Output:
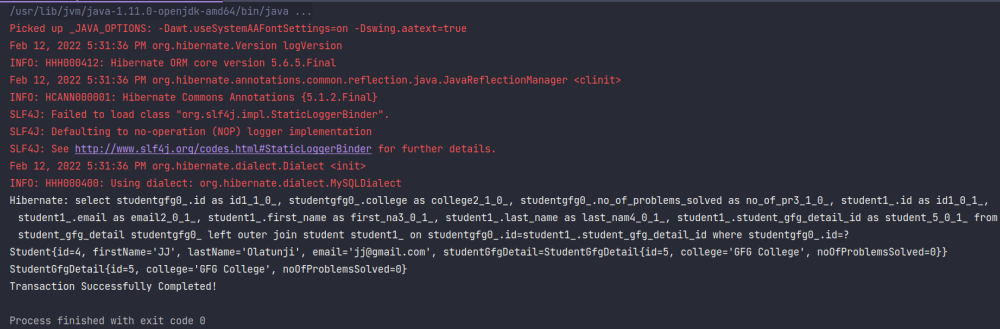 Output
OutputNote: Before retrieving any item from the database, double-check the ID of the Student or StudentGfgDetail as it can vary in different systems due to the number of runs.
We can update and delete the items, in the same manner, we did in unidirectional but beware now updating or deleting any entity will also delete the associated entity!
Similar Reads
Spring Tutorial Spring Framework is a comprehensive and versatile platform for enterprise Java development. It is known for its Inversion of Control (IoC) and Dependency Injection (DI) capabilities that simplify creating modular and testable applications. Key features include Spring MVC for web development, Spring
13 min read
Basics of Spring Framework
Introduction to Spring FrameworkThe Spring Framework is a powerful, lightweight, and widely used Java framework for building enterprise applications. It provides a comprehensive programming and configuration model for Java-based applications, making development faster, scalable, and maintainable.Before Enterprise Java Beans (EJB),
9 min read
Spring Framework ArchitectureThe Spring framework is a widely used open-source Java framework that provides a comprehensive programming and configuration model for building enterprise applications. Its architecture is designed around two core principles: Dependency Injection (DI) Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP)The Spring fram
7 min read
10 Reasons to Use Spring Framework in ProjectsSpring is the season that is known for fresh leaves, new flowers, and joy which makes our minds more creative. Do you know there is a bonus for us? We have another Spring as well. Our very own Spring framework! It is an open-source application framework that is used for building Java applications an
6 min read
Spring InitializrSpring Initializr is a popular tool for quickly generating Spring Boot projects with essential dependencies. It helps developers set up a new application with minimal effort, supporting Maven and Gradle builds. With its user-friendly interface, it simplifies project configuration, making it an essen
4 min read
Difference Between Spring DAO vs Spring ORM vs Spring JDBCThe Spring Framework is an application framework and inversion of control container for the Java platform. The framework's core features can be used by any Java application, but there are extensions for building web applications on top of the Java EE platform. Spring-DAOÂ Spring-DAO is not a spring
5 min read
Top 10 Most Common Spring Framework Mistakes"A person who never made a mistake never tried anything new" - Well said the thought of Albert Einstein. Human beings are prone to make mistakes. Be it technological aspect, mistakes are obvious. And when we talk about technology, frameworks play a very important role in building web applications. F
6 min read
Spring vs Struts in JavaUnderstanding the difference between Spring and Struts framework is important for Java developers, as both frameworks serve distinct purposes in building web applications. The main difference lies in their design and functionalitySpring: Spring is a comprehensive, modular framework offering dependen
3 min read
Software Setup and Configuration
How to Download and Install Spring Tool Suite (Spring Tools 4 for Eclipse) IDE?Spring Tool Suite (STS) is a Java IDE tailored for developing Spring-based enterprise applications. It is easier, faster, and more convenient. And most importantly it is based on Eclipse IDE. STS is free, open-source, and powered by VMware. Spring Tools 4 is the next generation of Spring tooling for
2 min read
How to Create and Setup Spring Boot Project in Spring Tool Suite?Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment which enables the developers to directly focus on the logic instead of struggling with the configuration and se
3 min read
How to Create a Spring Boot Project with IntelliJ IDEA?Spring Boot is one of the most popular frameworks for building Java applications, and IntelliJ IDEA is a top-tier IDE for Java development. In this article, we will guide you through the process of creating a Spring Boot project using IntelliJ IDEA. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced devel
3 min read
How to Create and Setup Spring Boot Project in Eclipse IDE?Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment which enables the developers to directly focus on the logic instead of struggling with the configuration and se
3 min read
How to Create a Dynamic Web Project in Eclipse/Spring Tool Suite?Eclipse is an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) used in computer programming. It includes a base workspace and an extensible plug-in system for customizing the environment. It is the second-most-popular IDE for Java development. Eclipse is written mostly in Java and its primary use is for dev
2 min read
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in IntelliJ IDEA?IntelliJ IDEA is an integrated development environment(IDE) written in Java. It is used for developing computer software. This IDE is developed by Jetbrains and is available as an Apache 2 Licensed community edition and a commercial edition. It is an intelligent, context-aware IDE for working with J
3 min read
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?Spring Tool Suite (STS) is a Java IDE tailored for developing Spring-based enterprise applications. It is easier, faster, and more convenient. Most importantly, it is based on Eclipse IDE. STS is free, open-source, and powered by VMware.Spring Tools 4 is the next generation of Spring tooling for you
3 min read
How to Turn on Code Suggestion in Eclipse or Spring Tool Suite?Eclipse is an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) used in computer programming. It includes a base workspace and an extensible plug-in system for customizing the environment. It is the second-most-popular IDE for Java development. Eclipse is written mostly in Java and its primary use is for dev
2 min read
Core Spring
Spring - Understanding Inversion of Control with ExampleSpring IoC (Inversion of Control) Container is the core of the Spring Framework. It creates objects (beans), configures them, injects dependencies, and manages their life cycles. The container uses Dependency Injection (DI) to manage application components. It retrieves object configuration from XML
7 min read
Spring - BeanFactoryThe first and foremost thing when we talk about Spring is dependency injection which is possible because Spring is a container and behaves as a factory of Beans. Just like the BeanFactory interface is the simplest container providing an advanced configuration mechanism to instantiate, configure, and
4 min read
Spring - ApplicationContextApplicationContext belongs to the Spring framework. Spring IoC container is responsible for instantiating, wiring, configuring, and managing the entire life cycle of beans or objects. BeanFactory and ApplicationContext represent the Spring IoC Containers. ApplicationContext is the sub-interface of B
5 min read
Spring - Difference Between BeanFactory and ApplicationContextSpring is one of the most popular Java EE frameworks. It is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java EE developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. It provides Aspect-oriented programming. It provides support for all generic and middleware services and ma
9 min read
Spring Dependency Injection with ExampleDependency Injection is the main functionality provided by Spring IOC(Inversion of Control). The Spring-Core module is responsible for injecting dependencies through either Constructor or Setter methods. The design principle of Inversion of Control emphasizes keeping the Java classes independent of
7 min read
Spring - Difference Between Inversion of Control and Dependency InjectionUnderstanding the difference between Inversion of Control (IoC) and Dependency Injection (DI) is very important for mastering the Spring framework. Both concepts are closely related, they serve different purposes in the context of Spring. The main difference between IoC and DI is listed below:Invers
3 min read
Spring - Injecting Objects By Constructor InjectionSpring IoC (Inversion of Control) Container is the core of Spring Framework. It creates the objects, configures and assembles their dependencies, and manages their entire life cycle. The Container uses Dependency Injection (DI) to manage the components that make up the application. It gets the infor
5 min read
Spring - Setter Injection with MapSpring Framework is a powerful tool for Java developers because it offers features like Dependency Injection (DI) to simplify application development. One of the key features of Spring is Setter Injection, which allows us to inject dependencies into our beans using setter methods. In this article, w
5 min read
Spring - Dependency Injection with Factory MethodSpring framework provides Dependency Injection to remove the conventional dependency relationship between objects. To inject dependencies using the factory method, we will use two attributes factory-method and factory-bean of bean elements.Note: Factory methods are those methods that return the inst
8 min read
Spring - Dependency Injection by Setter MethodDependency Injection is one of the core features of the Spring Framework Inversion of Control (IOC) container. It reduces the need for classes to create their own objects by allowing the Spring IOC container to do it for them. This approach makes the code more flexible, easier to test, and simpler t
5 min read
Spring - Setter Injection with Non-String MapIn Spring Framework, Dependency Injection (DI) is a core concept that allows objects to be injected into one another, reducing tight coupling. Setter-based Dependency Injection (SDI) is a technique where dependencies are injected through setter methods. In this article, we will explore how to perfor
4 min read
Spring - Constructor Injection with Non-String MapConstructor Injection is a widely used technique in the Spring Framework for injecting dependencies through a class constructor. This method ensures that all required dependencies are provided at the time of object creation, making the class immutable and easy to test. In this article, we will explo
4 min read
Spring - Constructor Injection with MapIn the Constructor Injection, the dependency injection will be injected with the help of constructors. Now to set the dependency injection as constructor dependency injection(CDI) in bean, it is done through the bean-configuration file For this, the property to be set with the constructor dependency
3 min read
Spring - Setter Injection with Dependent ObjectDependency Injection is the main functionality provided by Spring IOC(Inversion of Control). The Spring-Core module is responsible for injecting dependencies through either Constructor or Setter methods. In Setter Dependency Injection(SDI) the dependency will be injected with the help of setters and
3 min read
Spring - Constructor Injection with Dependent ObjectIn the constructor injection, the dependency injection will be injected with the help of constructors. Now to set the dependency injection as constructor dependency injection(CDI) in bean, it is done through the bean-configuration file For this, the property to be set with the constructor dependency
3 min read
Spring - Setter Injection with CollectionDependency Injection is the main functionality provided by Spring IOC(Inversion of Control). The Spring-Core module is responsible for injecting dependencies through either Constructor or Setter methods. In Setter Dependency Injection(SDI) the dependency will be injected with the help of setters and
2 min read
Spring - Setter Injection with Non-String CollectionDependency Injection is the main functionality provided by Spring IOC(Inversion of Control). The Spring-Core module is responsible for injecting dependencies through either Constructor or Setter methods. In Setter Dependency Injection(SDI) the dependency will be injected with the help of setters and
3 min read
Spring - Constructor Injection with CollectionIn the constructor injection, the dependency injection will be injected with the help of constructors. Now to set the dependency injection as constructor dependency injection(CDI) in bean, it is done through the bean-configuration file For this, the property to be set with the constructor dependency
2 min read
Spring - Injecting Objects by Setter InjectionSpring IoC (Inversion of Control) Container is the core of Spring Framework. It creates the objects, configures and assembles their dependencies, manages their entire life cycle. The Container uses Dependency Injection(DI) to manage the components that make up the application. It gets the informatio
5 min read
Spring - Injecting Literal Values By Setter InjectionSpring IoC (Inversion of Control) Container is the core of Spring Framework. It creates the objects, configures and assembles their dependencies, manages their entire life cycle. The Container uses Dependency Injection(DI) to manage the components that make up the application. It gets the informatio
4 min read
Spring - Injecting Literal Values By Constructor InjectionSpring IoC (Inversion of Control) Container is the core of Spring Framework. It creates the objects, configures and assembles their dependencies, manages their entire life cycle. The Container uses Dependency Injection(DI) to manage the components that make up the application. It gets the informatio
5 min read
Bean Life Cycle in Java SpringThe lifecycle of a bean in Spring refers to the sequence of events that occur from the moment a bean is instantiated until it is destroyed. Understanding this lifecycle is important for managing resources effectively and ensuring that beans are properly initialized and cleaned up.Bean life cycle is
7 min read
Custom Bean Scope in SpringIn Spring, Objects are managed by the Spring IOC(Inversion of Control) container, and their lifecycle is determined by the scope. Spring provides two standard scopes, which are listed below:Singleton Scope: One instance of the bean is created per Spring IOC Container. This is the default scope.Proto
4 min read
How to Create a Spring Bean in 3 Different Ways?Spring is one of the most popular Java EE frameworks. It is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java EE 7 developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. This framework mainly focuses on providing various ways to help you manage your business objects. It made
5 min read
Spring - IoC ContainerThe Spring framework is a powerful framework for building Java applications. It can be considered a collection of sub-frameworks, also referred to as layers, such as Spring AOP, Spring ORM, Spring Web Flow, and Spring Web MVC. We can use any of these modules separately while constructing a Web appli
2 min read
Spring - AutowiringAutowiring in the Spring framework can inject dependencies automatically. The Spring container detects those dependencies specified in the configuration file and the relationship between the beans. This is referred to as Autowiring in Spring. To enable Autowiring in the Spring application we should
4 min read
Singleton and Prototype Bean Scopes in Java SpringBean Scopes refer to the lifecycle of a Bean, which means when the object of a Bean is instantiated, how long it lives, and how many objects are created for that Bean throughout its lifetime. Basically, it controls the instance creation of the bean, and it is managed by the Spring container.Bean Sco
8 min read
How to Configure Dispatcher Servlet in web.xml File?In a Spring-based web application, the DispatcherServlet acts as the Front Controller. The Front Controller is responsible for handling all incoming requests and also figuring out which part of the application should handle it.What is a Front Controller?A Front Controller is a design pattern, which
3 min read
Spring - Configure Dispatcher Servlet in Three Different WaysDispatcherServlet acts as the Front Controller for Spring-based web applications. So now what is Front Controller? So it is pretty simple. Any request is going to come into our website the front controller is going to stand in front and is going to accept all the requests and once the front controll
8 min read
How to Configure Dispatcher Servlet in Just Two Lines of Code in Spring?DispatcherServlet acts as the Front Controller for Spring-based web applications. So now what is Front Controller? So it is pretty simple. Any request is going to come into our website the front controller is going to stand in front and is going to accept all the requests and once the front controll
6 min read
Spring - When to Use Factory Design Pattern Instead of Dependency InjectionPrerequisite: Factory Pattern vs Dependency Injection Factory Design Pattern and Dependency Injection Design both are used to define the interface-driven programs in order to create objects. Dependency Injection is used to obtain a loosely coupled design, whereas the Factory Pattern adds coupling, b
2 min read
How to Create a Simple Spring Boot Application?Spring Boot is one of the most popular frameworks for building Java-based web applications. It is used because it simplifies the development process by providing default configurations and also reduces boilerplate code. In this article, we will cover the steps to create a simple Spring Boot applicat
2 min read
Spring - init() and destroy() Methods with ExampleDuring the Spring Application Development, sometimes when the spring beans are created developers are required to execute the initialization operations and the cleanup operations before the bean is destroyed. In the spring framework, we can use the init-method and the destroy-method labels in the be
13 min read
Spring WebApplicationInitializer with ExampleIn Spring, WebApplicationInitializer is an Interface and it is Servlet 3.0+ implementation to configure ServletContext programmatically in comparison to the traditional way to do this using the web.xml file. This interface is used for booting Spring web applications. WebApplicationInitializer regist
5 min read
Spring - Project ModulesEvery Spring Boot project has several modules and each module match some application layer (service layer, repository layer, web layer, model, etc..). In this article, let us see a maven-driven project as an example for showing Project Modules. Example pom.xml (overall project level) XML <?xml ve
6 min read
Spring - Remoting by HTTP InvokerHTTP Invoker is a remote communication mechanism in the Spring framework that enables remote communication between Java objects over HTTP. It allows Java objects to invoke methods on remote Java objects, just as if they were local objects. In this article, we will learn how to implement Spring remot
3 min read
Spring - Expression Language (SpEL)Spring Expression Language (SpEL) is a feature of the Spring framework that enables querying and manipulating object graphs at runtime. It can be used in both XML and annotation-based configurations, offering flexibility for developers. Dynamic Expression Evaluation: SpEL allows evaluation of expres
6 min read
Spring - Variable in SpELEvaluationContext interface is implemented by the StandardEvaluationContext class. To resolve properties or methods, it employs a reflection technique. The method setVariable on the StandardEvaluationContext can be used to set a variable. Using the notation #variableName, we may utilize this variabl
3 min read
What is Ambiguous Mapping in Spring?Spring is a loosely coupled framework of java meaning all the objects are not dependent on each other and can be easily managed & modified. Basic architecture in every spring project involves the use of controllers or REST Controllers, any build tool like maven, gradle, or groove, an RDBMS, Serv
5 min read
Spring - Add New Query Parameters in GET Call Through ConfigurationsWhen a client wants to adopt the API sometimes the existing query parameters may not be sufficient to get the resources from the data store. New clients can't onboard until the API providers add support for new query parameter changes to the production environment. To address this problem below is a
4 min read
Spring - Integrate HornetQSpring Integration is a framework for building enterprise integration solutions. It provides a set of components that can be used to build a wide range of integration solutions. HornetQ is an open-source message-oriented middleware that can be used as a messaging provider for Spring Integration. Spr
6 min read
Remoting in Spring FrameworkSpring has integration classes for remoting support that use a variety of technologies. The Spring framework simplifies the development of remote-enabled services. It saves a significant amount of code by having its own API. The remote support simplifies the building of remote-enabled services, whic
3 min read
Spring - Application EventsSpring is a popular Java-based framework that helps developers create enterprise applications quickly and efficiently. One of the most powerful features of the Spring framework is its Application Events feature, which allows developers to create custom event-driven applications. What are Spring Appl
5 min read
Spring c-namespace with ExamplePrerequisite: How to Create a Spring Bean in 3 Different Ways? The Spring c-namespace will be discussed in this article. We are going to assume you're familiar with how to create a Bean within an XML configuration file. The first question that comes to mind is what Spring c-namespace is and how it w
3 min read
Parse Nested User-Defined Functions using Spring Expression Language (SpEL)In dynamic programming, evaluating complex expressions that uses nested user-defined functions can be very challenging. In Java, we can use Spring Expression Language (SpEL) to parse and execute such expressions at runtime. In this article, we will learn how to parse and execute nested user-defined
4 min read
Spring - AbstractRoutingDataSourceIn this article, we'll look at Spring's AbstractRoutingDatasource as an abstract DataSource implementation that dynamically determines the actual DataSource based on the current context. Now this question will come to our mind when we may need it i.e. when we should go for AbstractRoutingDatasource
6 min read
Circular Dependencies in SpringIn this article, we will discuss one of the most important concepts of Spring i.e. Circular dependency. Here we will understand what is circular dependency in Spring and how we can resolve circular dependency issues in Spring. What is Circular Dependency? In software engineering, a circular dependen
5 min read
Spring - ResourceLoaderAware with ExamplePrerequisite: Introduction to Spring Framework In this article, we will discuss the various ways through which we can load resources or files (e.g. text files, XML files, properties files, etc.) into the Spring application context. These resources or files may be present at different locations like
4 min read
Spring Framework Standalone CollectionsSpring Framework allows to inject of collection objects into a bean through constructor dependency injection or setter dependency injection using <list>,<map>,<set>, etc. Given below is an example of the same. Example Projectpom.xml:Â XML <project xmlns="http://maven.apache
2 min read
How to Create a Project using Spring and Struts 2?Prerequisites: Introduction to Spring FrameworkIntroduction and Working of Struts Web Framework In this article, we will discuss how the Spring framework can be integrated with the Struts2 framework to build a robust Java web application. Here I am going to assume that you know about Spring and Stru
6 min read
Spring - Perform Update Operation in CRUDCRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations are the building block for developers stepping into the software industry. CRUD is mostly simple and straight forward except that real-time scenarios tend to get complex. Among CRUD operations, the update operation requires more effort to get right comp
13 min read
How to Transfer Data in Spring using DTO?In Spring Framework, Data Transfer Object (DTO) is an object that carries data between processes. When you're working with a remote interface, each call is expensive. As a result, you need to reduce the number of calls. The solution is to create a Data Transfer Object that can hold all the data for
7 min read
Spring - Resource Bundle Message Source (i18n)A software is a multi purpose usage one. Â By using Message Source, it can be applicable to all languages. That concept is called i18n, that is according to the user locality, dynamic web pages are rendered in the user screen. We need to keep all the constants in a separate properties file which matc
5 min read
Spring Application Without Any .xml ConfigurationSpring MVC Application Without the web.xml File, we have eliminated the web.xml file, but we have left with the spring config XML file that is this file "application-config.xml". So here, we are going to see how to eliminate the spring config XML file and build a spring application without any .xml
4 min read
Spring - BeanPostProcessorSpring Framework provides BeanPostProcessor Interface. It allows custom modification of new bean instances that are created by the Spring Bean Factory. If we want to implement some custom logic such as checking for marker interfaces or wrapping beans with proxies after the Spring container finishes
5 min read
Spring and JAXB IntegrationThe term JAXB stands for Java Architecture for XML Binding. Java programmers may use it to translate Java classes to XML representations. Java objects may be marshaled into XML and vice versa using JAXB. Sun provides an OXM (Object XML Mapping) or O/M framework. Note: The biggest and only advantage
5 min read
Spring - Difference Between Dependency Injection and Factory PatternDependency Injection and Factory Pattern are almost similar in the sense that they both follow the interface-driven programming approach and create the instance of classes. A. Factory Pattern In Factory Pattern, the client class is still responsible for getting the instance of products by class getI
4 min read
Spring - REST PaginationSpring Framework is built on top of servlets. This particular web framework comes with very essential features with which we can develop efficient and effective web applications. On top of Spring Framework, Spring Boot was released in April 2014. The main aim behind the Spring Boot was the feature o
6 min read
Spring - Remoting By BurlapCoucho can provide both Hessian and Burlap. Burlap is an xml-based Hessian substitute. We may use the BurlapServiceExporter and BurlapProxyFactoryBean classes to implement burlap's remoting service. Implementation: You need to create the following files for creating a simple burlap application: Calc
2 min read
Spring - Remoting By HessianWe may use the HessianServiceExporter and HessianProxyFactoryBean classes to implement the hessian remoting service. The major advantage of Hessian's is that Hessian works well on both sides of a firewall. Hessian is a portable language that may be used with other languages like PHP and.Net. Impleme
2 min read
Spring with Castor ExampleWith the use of CastorMarshaller class, we can achieve marshal a java object into XML code and vice-versa of it with the help of using castor. The castor is the implemented class for Marshaller and Unmarshaller interfaces within it, thus it does not require other further configurations by its defaul
3 min read
Spring - REST XML ResponseREST APIs have become increasingly popular due to their simplicity and flexibility in architecting applications. A REST API, which stands for Representational State Transfer, is often referred to as RESTful web services. Unlike traditional MVC controllers that return views, REST controllers return d
8 min read
Spring - Inheriting BeanIn Spring, bean inheritance allows for reusing configuration from a parent bean and customizing it in child beans. This feature helps in reducing redundancy and managing configurations more efficiently. Unlike Java class inheritance, Spring bean inheritance is more about configuration inheritance ra
4 min read
Spring - Change DispatcherServlet Context Configuration File NameDispatcherServlet acts as the Front Controller for Spring-based web applications. So now what is Front Controller? So it is pretty simple. Any request is going to come into our website the front controller is going to stand in front and is going to accept all the requests and once the front controll
6 min read
Spring - JMS IntegrationJMS is a standard Java API that allows a Java application to send messages to another application. It is highly scalable and allows us to loosely couple applications using asynchronous messaging. Using JMS we can read, send, and read messages. Benefits of using JMS with Spring IntegrationLoad balanc
8 min read
Spring - Difference Between RowMapper and ResultSetExtractorUnderstanding the difference between RowMapper and ResultSetExtractor is very important for anyone working with JDBC in Java. Both play important roles in fetching and processing data from the database. The main difference between RowMapper and ResultSetExtractor lies in their responsibilities. RowM
3 min read
Spring with XstreamXstream is a simple Java-based serialization/deserialization library to convert Java Objects into their XML representation. It can also be used to convert an XML string to an equivalent Java Object. It is a fast, and efficient extension to the Java standard library. It's also highly customizable. Fo
3 min read
Spring - RowMapper Interface with ExampleSpring is one of the most popular Java EE frameworks. It is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java EE 7 developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. This framework mainly focuses on providing various ways to help you manage your business objects. It made
6 min read
Spring - util:constantSpring 2.0 version introduced XML Schema-based configuration. It makes Spring XML configuration files substantially clearer to read and in addition to that, it allows the developer to express the intent of a bean definition. These new custom tags work best for infrastructure or integration beans: fo
4 min read
Spring - Static Factory MethodStatic factory methods are those that can return the same object type that implements them. Static factory methods are more flexible with the return types as they can also return subtypes and primitives too. Static factory methods are used to encapsulate the object creation process. In the Spring fr
4 min read
Spring - FactoryBeanSpring is one of the most popular Java EE frameworks. It is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java EE 7 developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. This framework mainly focuses on providing various ways to help you manage your business objects. It made
5 min read
Difference between EJB and SpringEJB and Spring both are used to develop enterprise applications. But there are few differences exists between them. So, in this article we have tried to cover all these differences. 1. Enterprise Java Beans (EJB) : EJB stand for Enterprise Java Beans. It is a server side software component that summ
3 min read
Spring Framework AnnotationsSpring framework is one of the most popular Java EE frameworks. It is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java EE 7 developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. Spring framework mainly focuses on providing various ways to help you manage your business obje
6 min read
Spring Core AnnotationsSpring Annotations are a form of metadata that provides data about a program. Annotations are used to provide supplemental information about a program. It does not have a direct effect on the operation of the code they annotate. It does not change the action of the compiled program.Spring Framework
5 min read
Spring - Stereotype AnnotationsSpring is one of the most popular Java EE frameworks. It is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java EE 7 developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. This framework mainly focuses on providing various ways to help you manage your business objects. Spring
10 min read
Spring @Bean Annotation with ExampleThe @Bean annotation in Spring is a powerful way to define and manage beans in a Spring application. Unlike @Component, which relies on class-level scanning, @Bean explicitly declares beans inside @Configuration classes, offering greater flexibility in object creation. In this article, we will explo
9 min read
Spring Boot @Controller Annotation with ExampleSpring is one of the most popular frameworks for building enterprise-level Java applications. It is an open-source, lightweight framework that simplifies the development of robust, scalable, and maintainable applications. Spring provides various features such as Dependency Injection (DI), Aspect-Ori
3 min read
Spring @Value Annotation with ExampleThe @Value annotation in Spring is one of the most important annotations. It is used to assign default values to variables and method arguments. It allows us to inject values from spring environment variables, system variables, and properties files. It also supports Spring Expression Language (SpEL)
6 min read
Spring @Configuration Annotation with ExampleThe @Configuration annotation in Spring is one of the most important annotations. It indicates that a class contains @Bean definition methods, which the Spring container can process to generate Spring Beans for use in the application. This annotation is part of the Spring Core framework. Let's under
4 min read
Spring @ComponentScan Annotation with ExampleSpring is one of the most popular frameworks for building enterprise-level Java applications. It is an open-source, lightweight framework that simplifies the development of robust, scalable, and maintainable applications. Spring provides various features such as Dependency Injection (DI), Aspect-Ori
3 min read
Spring @Qualifier Annotation with ExampleSpring is one of the most popular Java EE frameworks. It is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java EE 7 developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. Spring focuses on providing various ways to manage business objects, making web application development e
6 min read
Spring Boot @Service Annotation with ExampleSpring is one of the most popular frameworks for building enterprise-level Java applications. It is an open-source, lightweight framework that simplifies the development of robust, scalable, and maintainable applications. Spring provides various features such as Dependency Injection (DI), Aspect-Ori
3 min read
Spring Boot @Repository Annotation with ExampleSpring is one of the most popular frameworks for building enterprise-level Java applications. It is an open-source, lightweight framework that simplifies the development of robust, scalable, and maintainable applications. Spring provides various features such as Dependency Injection (DI), Aspect-Ori
5 min read
Spring - Required AnnotationConsider a scenario where a developer wants to make some of the fields as mandatory fields. using the Spring framework, a developer can use the @Required annotation to those fields by pushing the responsibility for such checking onto the container. So container must check whether those fields are be
7 min read
Spring @Component Annotation with ExampleSpring is one of the most popular frameworks for building enterprise applications in Java. It is an open-source, lightweight framework that allows developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable applications. Spring focuses on providing various ways to manage business objects efficiently. It simp
3 min read
Spring @Autowired AnnotationThe @Autowired annotation in Spring marks a constructor, setter method, property, or configuration method to be autowired. This means that Spring will automatically inject the required dependencies (beans) at runtime using its Dependency Injection mechanism. The image below illustrates this concept:
3 min read
Spring - @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy Annotation with ExampleSpring is one of the most popular Java EE frameworks. It is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java EE 7 developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. This framework mainly focuses on providing various ways to help you manage your business objects. It made
13 min read
Java Spring - Using @PropertySource Annotation and Resource InterfaceIn Java applications, Sometimes we might need to use data from external resources such as text files, XML files, properties files, image files, etc., from different locations (e.g., a file system, classpath, or URL). @PropertySource Annotation To achieve this, the Spring framework provides the @Pro
6 min read
Java Spring - Using @Scope Annotation to Set a POJO's ScopeIn the Spring Framework, when we declare a POJO (Plain Old Java Object) instance, what we are essentially creating is a template for a bean definition. This means that, just like a class, we can have multiple object instances created from a single template. These beans are managed by the Spring IoC
7 min read
Spring @Required Annotation with ExampleSpring Annotations provide a powerful way to configure dependencies and implement dependency injection in Java applications. These annotations act as metadata, offering additional information about the program. The @Required annotation in Spring is a method-level annotation used in the setter method
5 min read
Spring Boot Tutorial Spring Boot is a Java framework that makes it easier to create and run Java applications. It simplifies the configuration and setup process, allowing developers to focus more on writing code for their applications. This Spring Boot Tutorial is a comprehensive guide that covers both basic and advance
10 min read
Spring MVC Tutorial In this tutorial, we'll cover the fundamentals of Spring MVC, including setting up your development environment, understanding the MVC architecture, handling requests and responses, managing forms, and integrating with databases. You'll learn how to create dynamic web pages, handle user input, and i
7 min read
Spring with REST API
Spring Data
What is Spring Data JPA?Spring Data JPA is a powerful framework that simplifies database access in Spring Boot applications by providing an abstraction layer over the Java Persistence API (JPA). It enables seamless integration with relational databases using Object-Relational Mapping (ORM), eliminating the need for boilerp
6 min read
Spring Data JPA - Find Records From MySQLSpring Data JPA simplifies database interactions in Spring Boot applications by providing a seamless way to work with relational databases like MySQL. It eliminates boilerplate code and allows developers to perform CRUD operations efficiently using JPA repositories. With Spring Boot and Spring Data
3 min read
Spring Data JPA - Delete Records From MySQLSpring Boot simplifies database operations using Spring Data JPA, which provides built-in methods for CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations. In modern application development, data manipulation is a critical task, and Java Persistence API (JPA) simplifies this process. Java persistence API
4 min read
Spring Data JPA - @Table AnnotationSpring Data JPA is a powerful framework that simplifies database interactions in Spring Boot applications. The @Table annotation in JPA (Java Persistence API) is used to specify the table name in the database and ensure proper mapping between Java entities and database tables. This is especially use
3 min read
Spring Data JPA - Insert Data in MySQL TableSpring Data JPA makes it easy to work with databases in Spring Boot by reducing the need for boilerplate code. It provides built-in methods to perform operations like inserting, updating, and deleting records in a MySQL table. In this article, we will see how to insert data into a MySQL database usi
2 min read
Spring Data JPA - Attributes of @Column Annotation with ExampleSpring Data JPA is a powerful framework that simplifies database interactions in Spring Boot applications. The @Column annotation in Spring Data JPA is widely used to customize column properties such as length, default values, and constraints in a database table. Understanding how to use @Column eff
2 min read
Spring Data JPA - @Column AnnotationIn Spring Data JPA, the @Column annotation is used to define column-specific attributes for an entity field in the database. It allows developers to customize column names, set length, define nullability, and more. This is essential when working with relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and
2 min read
Spring Data JPA - @Id AnnotationSpring Data JPA is a important part of Spring Boot applications, providing an abstraction over JPA (Java Persistence API) and simplifying database interactions. JPA is a specification that defines a standard way to interact with relational databases in Java, while Hibernate is one of the most widely
3 min read
Introduction to the Spring Data FrameworkSpring Data is a powerful data access framework in the Spring ecosystem that simplifies database interactions for relational (SQL) and non-relational (NoSQL) databases. It eliminates boilerplate code and provides an easy-to-use abstraction layer for developers working with JPA, MongoDB, Redis, Cassa
3 min read
Spring Boot - How to Access Database using Spring Data JPASpring Data JPA is a robust framework that simplifies the implementation of JPA (Java Persistence API) repositories, making it easy to add a data access layer to the applications. CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete) operations are the fundamental actions we can perform on a database. In this art
5 min read
How to Make a Project Using Spring Boot, MySQL, Spring Data JPA, and Maven?For the sample project, below mentioned tools got used Java 8Eclipse IDE for developmentHibernate ORM, Spring framework with Spring Data JPAMySQL database, MySQL Connector Java as JDBC driver.Example Project Using Spring Boot, MySQL, Spring Data JPA, and Maven Project Structure: Â As this is getting
4 min read
Spring JDBC
Spring - JDBC TemplateIn this article, we will discuss the Spring JDBC Template and how to configure the JDBC Template to execute queries. Spring JDBC Template provides a fluent API that improves code simplicity and readability, and the JDBC Template is used to connect to the database and execute SQL Queries. What is JDB
7 min read
Spring JDBC ExampleSpring JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) is a powerful module in the Spring Framework that simplifies database interaction by eliminating boilerplate code required for raw JDBC. It provides an abstraction over JDBC, making database operations more efficient, less error-prone, and easier to manage. T
4 min read
Spring - SimpleJDBCTemplate with ExampleThe SimpleJDBCTemplate includes all the features and functionalities of the JdbcTemplate class, and it also supports the Java 5 features such as var-args(variable arguments) and autoboxing. Along with the JdbcTemplate class, it also provides the update() method, which takes two arguments the SQL que
5 min read
Spring - Prepared Statement JDBC TemplateIn Enterprise applications, accessing and storing data in a relational database is a common requirement. Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an essential part of Java SE, and it provides a set of standard APIs to interact with relational databases in a way that is not tied to any database vendor. W
6 min read
Spring - NamedParameterJdbcTemplateThe Java Database Connectivity API allows us to connect to various data sources such as relational databases, spreadsheets, and flat files. The JdbcTemplate is the most basic approach for data access. Spring Boot simplifies the configuration and management of data sources, which makes it easier for
5 min read
Spring - Using SQL Scripts with Spring JDBC + JPA + HSQLDBIn this article, we will be running the SQL scripts with Spring JDBC +JPA + HSQLDB. These scripts are used to perform SQL commands at the time of application start. Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an application programming interface (API) for the programming language Java, which defines how a
4 min read
Spring - ResultSetExtractorSpring Framework is a powerful and widely used tool for building Java applications. With the evolution of Spring Boot, JDBC, and modern Java features, working with databases has become easier. In this article, we will discuss how to use the ResultSetExtractor interface with Spring JDBC to fetch reco
4 min read
Spring Hibernate
Spring Hibernate Configuration and Create a Table in DatabaseSpring Boot and Hibernate are a powerful combination for building scalable and efficient database-driven applications. Spring Boot simplifies application development by reducing boilerplate code, while Hibernate, a popular ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) framework, enables easy database interactions
4 min read
Hibernate LifecycleIn this article, we will learn about Hibernate Lifecycle, or in other words, we can say that we will learn about the lifecycle of the mapped instances of the entity/object classes in hibernate. In Hibernate, we can either create a new object of an entity and store it into the database, or we can fet
4 min read
Java - JPA vs HibernateJPA stands for Java Persistence API (Application Programming Interface). It was initially released on 11 May 2006. It is a Java specification that provides functionality and standards for ORM tools. It is used to examine, control, and persist data between Java objects and relational databases. It is
4 min read
Spring ORM Example using HibernateSpring ORM is a module of the Java Spring framework used to implement the ORM(Object Relational Mapping) technique. It can be integrated with various mapping and persistence frameworks like Hibernate, Oracle Toplink, iBatis, etc. for database access and manipulation. This article covers an example o
5 min read
Hibernate - One-to-One MappingPrerequisite: Basic knowledge of hibernate framework, Knowledge about databases, JavaHibernate is a framework that provides some abstraction layer, meaning that the programmer does not have to worry about the implementations, Hibernate does the implementations for you internally like Establishing a
15 min read
Hibernate - Cache Eviction with ExampleCaching in Hibernate means storing and reusing frequently used data to speed up your application. There are two kinds of caching: Session-level and SessionFactory-level. Level 1 cache is a cache that stores objects that have been queried and persist to the current session. This cache helps to reduce
9 min read
Hibernate - Cache ExpirationCaching in Hibernate means storing and reusing frequently used data to speed up your application. There are two kinds of caching: Session-level and SessionFactory-level. Level 1 cache is a cache that stores objects that have been queried and persist to the current session. This cache helps to reduce
9 min read
Hibernate - Enable and Implement First and Second Level CacheIf you're a Java developer, you've probably heard of Hibernate. It's a free, open-source ORM framework that lets you map your Java objects to tables in a relational database. Basically, it makes database programming a breeze since you don't have to worry about writing SQL queries - you can just work
10 min read
Hibernate - Save Image and Other Types of Values to DatabaseIn Hibernate, you can save images and other types of values as attributes of your entity classes using appropriate data types and mappings. To save images and other types of values using Hibernate, you first need to create an entity class that represents the data you want to save. In this entity cla
5 min read
Hibernate - PaginationPagination is the process of dividing a large set of data into smaller, more manageable chunks or pages for easier navigation and faster loading times. It is a common technique used in web applications to display a large amount of data to users, while also providing them with a way to navigate throu
5 min read
Hibernate - Different Cascade TypesIn Hibernate, when we deal with entities connected through relationships like a Customer who has multiple Orders, sometimes we want to perform some operations like save, update, delete, and refresh on the parent to automatically apply to its child entities. This behavior is called cascading.Cascadin
4 min read
Hibernate Native SQL Query with ExampleHibernate is a popular object-relational mapping (ORM) tool used in Java applications. It allows developers to map Java objects to database tables and perform CRUD (create, read, update, delete) operations on the database without writing SQL queries manually. Native SQL queries are useful when you n
7 min read
Hibernate - CachingCaching in Hibernate refers to the technique of storing frequently accessed data in memory to improve the performance of an application that uses Hibernate as an Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework. Hibernate provides two levels of caching: First-Level Cache: Hibernate uses a session-level cac
6 min read
Hibernate - @Embeddable and @Embedded AnnotationThe @Embeddable and @Embedded annotations in Hibernate are used to map an object’s properties to columns in a database table. These annotations are used in combination to allow the properties of one class to be included as a value type in another class and then be persisted in the database as part o
4 min read
Hibernate - Eager/Lazy LoadingFetchType is an enumerated type in the Java Persistence API (JPA) that specifies whether the field or property should be lazily loaded or eagerly loaded. It is used in the javax.persistence.FetchType enum. In Hibernate, the FetchType is used to specify the fetching strategy to be used for an associa
4 min read
Hibernate - get() and load() MethodHibernate is a Java framework that provides a powerful set of tools for persisting and accessing data in a Java environment. It is often used in conjunction with Spring. Spring and Hibernate are both widely used in the Java community, and they can be used together to build powerful and efficient Jav
3 min read
Hibernate ValidatorHibernate Validators offer field-level validation for every attribute of a bean class, which means you can easily validate a field content against null/not null, empty/not empty, with min/max value to a specific value, valid email, and valid credit card, etc., For each and everything, we have specif
10 min read
CRUD Operations using HibernateHibernate is a powerful Java ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) framework that simplifies database interactions by mapping Java objects to relational tables. It allows developers to perform CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) without writing complex SQL queries.In this article, we will cover
5 min read
Hibernate Example without IDEHibernate is a powerful tool used to build applications that need to interact with a database. It is a Java framework that implements the ORM(Object Relational Mapping) technique. What is ORM? ORM stands for Object Relational Mapping. It is a technique that is used to make Java objects persistent b
3 min read
Hibernate - Inheritance MappingThe inheritance hierarchy can be seen easily in the table of the database. In Hibernate we have three different strategies available for Inheritance Mapping Table Per HierarchyTable Per Concrete classTable Per Subclass Hierarchy can be diagrammatically seen easily. Â In this article let us see about
5 min read
Automatic Table Creation Using HibernateHibernate is a Java framework that implements ORM(Object Relational Mapping) design pattern. It is used to map java objects into a relational database. It internally uses JDBC(Java Database Connectivity), JTA(Java Transaction API), and JNDI(Java Naming and Directory Interface). It helps to make java
3 min read
Hibernate - Batch ProcessingHibernate is storing the freshly inserted objects in the second-level cache. Because of this, there is always the possibility of OutOfMemoryException when  Inserting more than one million objects. But there will be situations to inserting huge data into the database. This can be accomplished by batc
5 min read
Hibernate - Component MappingIn general, a student can have an address/employee can have an address. For these kind of requirements, we can follow Component mapping. It is nothing but a class having a reference to another class as a member variable. i.e. inside the 'student' class, we can have the 'address' class as a member va
8 min read
Hibernate - Mapping ListIn Hibernate, in order to go for an ordered collection of items, mostly List is the preferred one, Along with List, we have different collection mapping like Bag, Set, Map, SortedSet, SortedMap, etc., But still in many places mapping list is the most preferred way as it has the index element and hen
3 min read
Hibernate - Collection MappingCollection elements are much needed to have one-to-many, many-to-many, relationships, etc., Any one type from below can be used to declare the type of collection in the Persistent class. Persistent class from one of the following types: java.util.Listjava.util.Setjava.util.SortedSetjava.util.Mapjava
5 min read
Hibernate - Bag MappingFor a multi-national company, usually, selections are happened based on technical questions/aptitude questions. If we refer to a question, each will have a set of a minimum of 4 options i.e each question will have N solutions. So we can represent that by means of "HAS A" relationship i.e. 1 question
4 min read
Hibernate - Difference Between List and Bag MappingHibernate supports both List and Bag Mapping and Set Mapping too. Hence there will be a tradeoff, regarding which is the best data type to use. The choice will be purely based on requirements but still, let us see the differences between them. Whenever there is a one-to-many relationship or many-to-
3 min read
Hibernate - SortedSet MappingSortedSet can be viewed in a group of elements and they do not have a duplicate element and ascending order is maintained in its elements. By using <set> elements we can use them and the entity should have a Sortedset of values. As an example, we can have a freelancer who works for multiple co
6 min read
Hibernate - SortedMap MappingSortedMap is a map that always maintains its corresponding entries in ascending key order. In Hibernate, using the <map> element and 'sort' as 'natural' we can maintain the SortedMap. Let us see that by using the one-to-many relationship concept. For example, for a programming language like Ja
6 min read
Hibernate - Native SQLHibernate by means of a Native SQL facility, can directly interact with the database like MySQL, Oracle, etc., and all the database-specific queries can be executed via this facility. This feature is much useful if the application is an old application and running for a long time. All of a sudden we
8 min read
Hibernate - Logging by Log4j using xml FileThe process of Hibernate Logging by Log4j using an XML file deals with the ability of the computer programmer to write the log details of the file he has created by executing it permanently. The most important tools in Java language like the Log4j and Log back frameworks. These frameworks in Java la
5 min read
Hibernate - Many-to-One MappingHibernate is an open-source, ORM(Object Relational Mapping) framework that provides CRUD operations in the form of objects. It is a non-invasive framework. It can be used to develop DataAcessLayer for all java projects. It is not server-dependent. It means hibernate code runs without a server and wi
5 min read
Hibernate - Logging By Log4j Using Properties FileApache log4j is a java-based logging utility. Apache log4j role is to log information to help applications run smoothly, determine what’s happening, and debug processes when errors occur. log4j may logs login attempts (username, password), submission form, and HTTP headers (user-agent, x-forwarded-h
2 min read
Hibernate - Table Per Concrete Class Using AnnotationHibernate is a framework that provides some abstraction layer, meaning that the programmer does not have to worry about the implementations, it does the implementations for you internally like writing queries to perform CRUD operations, establishing a connection with the database, etc. It is an open
7 min read
Hibernate - Table Per Subclass using AnnotationHibernate is an open-source, non-invasive, lightweight java ORM(Object-relational mapping) framework that is used to develop persistence logic that is independent of Database software. An ORM(Object-relational mapping) framework simplifies data creation, data manipulation, and data access. Â It is a
5 min read
Hibernate - InterceptorsInterceptors are used in conjunction with Java EE managed classes to allow developers to invoke interceptor methods on an associated target class, in conjunction with method invocations or lifecycle events. Common uses of interceptors are logging, auditing, and profiling. The Interceptors 1.1 specif
6 min read
Hibernate - Many-to-Many MappingIn RDBMS, we can see a very common usage of parent-child relationships. It can be achieved in Hibernate via One-to-many relationshipMany-to-one relationshipOne-to-one relationshipMany-to-many relationship Here we will be discussing how to perform Hibernate - Many-to-Many mappings. Below are the exa
12 min read
Hibernate - Types of MappingHibernate is a Java framework that simplifies the development of Java applications to interact with the database. It is an open-source, lightweight, ORM (Object Relational Mapping) tool. Hibernate implements the specifications of JPA (Java Persistence API) for data persistence. There are different r
2 min read
Hibernate - Criteria QueriesHibernate is a framework that provides some abstraction layer, meaning that the programmer does not have to worry about the implementations, Hibernate does the implementations for you internally like Establishing a connection with the database, writing queries to perform CRUD operations, etc. To get
12 min read
Hibernate - Table Per Hierarchy using AnnotationHibernate is a framework that provides some abstraction layer, meaning that the programmer does not have to worry about the implementations, it does the implementations for you internally like writing queries to perform CRUD operations, establishing a connection with the database, etc. It is an open
8 min read
Hibernate - Table Per Subclass Example using XML FileIn Table Per Subclass, subclass tables are mapped to the Parent class table by primary key and foreign key relationship. In a Table per Subclass strategy : For each class of hierarchy there exist a separate table in the database.While creating the database tables foreign key relationship is required
5 min read
Hibernate - Table Per Hierarchy using XML FileHibernate is capable of storing the inherited properties of an object along with its new properties in its database when an object is saved in the database. In Hibernate, inheritance between POJO classes is applied when multiple POJO classes of a module contain some common properties. In a real-time
6 min read
Hibernate - Create POJO ClassesPOJO stands for Plain Old Java Object. In simple terms, we use POJO to make a programming model for declaring object entities. The classes are simple to use and do not have any restrictions as compared to Java Beans. To read about POJO classes and Java Bean refer to the following article - POJO cla
3 min read
Hibernate - Web ApplicationA web application with hibernate is easier. A JSP page is the best way to get user inputs. Those inputs are passed to the servlet and finally, it is inserted into the database by using hibernate. Here JSP page is used for the presentation logic. Servlet class is meant for the controller layer. DAO c
10 min read
Hibernate - Table Per Concrete Class using XML FileHibernate is capable of storing the inherited properties of an object along with its new properties in its database when an object is saved in the database. In Hibernate, inheritance between POJO classes is applied when multiple POJO classes of a module contain some common properties. In a real-time
5 min read
Hibernate - Generator ClassesHibernate is an open-source, non-invasive, lightweight java ORM(Object-relational mapping) framework that is used to develop persistence logic that is independent of Database software. In JDBC to develop persistence logic, we deal with primitive types. Whereas in Hibernate framework we use Objects t
5 min read
Hibernate - SQL DialectsHibernate is an open-source, non-invasive, lightweight java ORM(Object-relational mapping) framework that is used to develop persistence logic that is independent of Database software. An ORM(Object-relational mapping) framework simplifies data creation, data manipulation, and data access. It is a p
3 min read
Hibernate - Query LanguagepolymorphicHibernate is a Java framework that makes it easier to create database-interactive Java applications. In HQL, instead of a table name, it uses a class name. As a result, it is a query language that is database-independent. Hibernate converts HQL queries into SQL queries, which are used to
4 min read
Hibernate - Difference Between ORM and JDBCHibernate is a framework that is used to develop persistence logic that is independent of Database software. In JDBC to develop persistence logic, we deal with primitive types. Whereas Hibernate framework we use Objects to develop persistence logic that is independent of database software. ORM (Obje
4 min read
Hibernate - AnnotationsAnnotation in JAVA is used to represent supplemental information. As you have seen @override, @inherited, etc are an example of annotations in general Java language. For deep dive please refer to Annotations in Java. In this article, we will discuss annotations referred to hibernate. So, the motive
7 min read
Hibernate Example using XML in EclipseHibernate is a framework that provides some abstraction layer, meaning that the programmer does not have to worry about the implementations, Hibernate does the implementations for you internally like Establishing a connection with the database, writing queries to perform CRUD operations, etc. In thi
6 min read
Hibernate - Create Hibernate Configuration File with the Help of PluginHibernate is a framework that provides some abstraction layer, meaning that the programmer does not have to worry about the implementations, Hibernate does the implementations for you internally like writing queries to perform CRUD operations, establishing a connection with the database, etc. It is
3 min read
Hibernate Example using JPA and MySQLHibernate is a framework that provides some abstraction layer, meaning that the programmer does not have to worry about the implementations, Hibernate does the implementations for you internally like writing queries to perform CRUD operations, establishing a connection with the database, etc. It is
4 min read
Hibernate - One-to-Many MappingHibernate is used to increase the data manipulation efficiency between the spring application and the database, insertion will be done is already defined with the help of hibernating. JPA (Java persistence API) is like an interface and hibernate is the implementation of the methods of the interface.
5 min read