In database design, understanding and implementing relationships between entities is crucial. These relationships, such as one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many, establish connections between tables using key constraints.
Let's explore each type of relationship with examples and SQL implementation.
One-to-One Relationship
In this relationship, each row/record of the Let's table is exactly related to one row in the second table and vice versa.
Example: Let's consider 2 tables "Student" and "Class_Details". Now "Student" has 2 columns - "Enrolment_No", "Name" and "Class_Details" has 4 columns "Roll_No", "Class", "Division", and "Enrolment_No".
In the example, you can see that a student will have only one enrolment number allotted, only one roll number, and only one class and division. Then it may change year-wise or semester-wise but a student cannot have multiple classes or enrollment numbers or roll numbers simultaneously. Here, a one-to-one relationship occurs. Let's understand One-to-One relationships with the help of a table diagram and their output.
Create tables "Student" and "Class_Details" with required columns or attributes as mentioned in the above example.
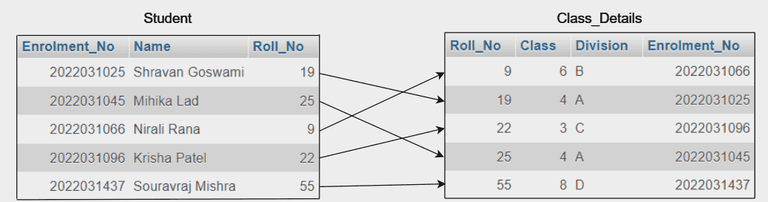 One-to-one relationship between student and class_details
One-to-one relationship between student and class_detailsHere, you can see that each student's table record is exactly related to one record in the class_details table. Each student has a unique Enrolment number and Roll number. It is not possible for a student to be enrolled in 2 classes or divisions at same time. Each student is related from its name details and its class uniquely.
SQL Query
Now, to retrieve data from the tables we write the following query to view the details of both the tables.
SELECT students.Enrolment_No, students.Name, students.Roll_No, class_details.Class, class_details.Division
FROM students
JOIN class_details ON students.Enrolment_No = class_details.Enrolment_No;
 Query for retrieving records from both the table
Query for retrieving records from both the tableThe above query retrieves records using the primary key and foreign key of another table which is in turn a primary key of the first table. The above query uses 'Enrolment_No' for referencing the records from both tables. In this query, we retrieved data using the primary key of the Student table and as a foreign key of the class_details table.
Output:
 Output of above query of students to class_details table
Output of above query of students to class_details tableExplanation: Through the above output or result we can see that each record of the first table is related exactly to one another record in the next table. You can also notice that in one-to-one relationship output, no multiple records are possible.
one-to-one relationship(vice-versa)
In the definition, we saw that the one-to-one relationship is also vice-versa, this means the class_details table is also related to exactly one record in students table.
 One-to-one relation from class_details to students entity representing vice-versa condition
One-to-one relation from class_details to students entity representing vice-versa conditionLet's see the query for a one-to-one relationship from the class_details table to the student's table.
SELECT class_details.Roll_No, class_details.Class, class_details.Division, students.Enrolment_No, students.Name
FROM class_details
JOIN students ON class_details.Roll_No = students.Roll_No;
 The query for vice-versa condition i.e. one-to-one relationship from class_details to students
The query for vice-versa condition i.e. one-to-one relationship from class_details to studentsAs you can see, in the above query, we used the class_details table primarily to retrieve the data using presenting one-to-one relation.
Output:
 Output for the above query
Output for the above queryExplanation: You can see that we have the same number of records that we got in the output from the students table to the class_details table i.e. 5 and it is the same number of records while retrieving from class_details to the students table. You can also see that each record is associated with only one record in another table. We got 5 records from both way of retrieving the data using one-to-one relation from table students and class_details and vice-versa.
One-to-Many Relationship
In this relationship, each row/record of the Let'sfirst table can be related to multiple rows in the second table.
Example:
Let's consider 2 tables "Parent" and "Child". Now the "Parent" table has columns "ParentID", "Name"... and so on, and "Child" has columns or attributes "ChildID", "Name", "Age", "ParentID" and so on.
In the above example we used the logic of parent and child and you can see that a parent can have many children, but a child cannot have many/multiple parents.
Create tables 'parent' and 'child' as mentioned in the above table and let's see one-to-many relation between these 2 tables.
 one-to-many relationship between parent and child table
one-to-many relationship between parent and child tableWe can see that each record from the table parent is associated with one or more than one record(s) in the child table representing one-to-many relationships. Here, a one-to-many relationship occurs when the vice-versa of the above condition should not be true. If the vice-versa or reverse condition for a one-to-many relationship becomes true then it is a many-to-many relationship.
SQL Query:
Let's see the query to retrieve data representing one-to-many relationshipsparent-to-child:
SELECT parent.parentID, parent.Name, parent.age, parent.Address, child.ChildID, child.Name, child.age
FROM parent
JOIN child ON parent.parentID = child.ParentID
 Query for retrieving data from parent and child table
Query for retrieving data from parent and child tableThe above query retrieves all possible records from parent-to-child relationship entities.
 Output for the above query representing one-to-many relationships
Output for the above query representing one-to-many relationshipsExplanation: In the output of the above query, you can see that the parent's name is occurring more than one time with different child names representing a parent associated with one or more than one child. For example, we can see that HarishKumar Verma has two children, Jiya Verma, and Vihaan Verma, Vishvaas Modi has 3 children i.e. Vrisha Modi, Mihir Modi, and Farah Modi, and last Vidhit Chopra has only a single child i.e. Nickie Chopra representing one record/row associated with one or more than one child.
Each record from the child table is associated with only one record in the parent table and it also fits the logic that a parent may have one or more than one child but a child cannot have multiple parents. Similarly, you can also design the relation as per the business logic which fits into which relationship better.
Many-to-Many Relationship
In this relationship, multiple rowsthe /record of first table can be related to multiple rows in the second table and vice versa.
Example: Consider tables "Facultythe " and "Department". Now the "Faculty" table has columns "FacultyID", "Faculty_Name", "Course" and so on, and "Department" has columns "DepartmentID", "Department_Name" and so on.
Now, each faculty member can be associated with multiple departments, and each department can be associated with multiple faculty members establishing many-to-many relationships.
Create Table:
Example of many-to-many relationships from faculty to department entities:
 Example of many-to-many relationships from faculty to department entities
Example of many-to-many relationships from faculty to department entitiesExample of many-to-many relationship from department to faculty entities:
 Example of many-to-many relationship from department to faculty entities
Example of many-to-many relationship from department to faculty entitiesNow, in above example as per the business logic, you can see that faculty works in more than one department and vice-versa is also true that departments have multiple faculties working with them.
Now if we see technically then, records in the faculty table are associated with more than one record in the department table, and records from department table are associated with more than one faculties or records in the faculty entity.
SQL Query:
Now let's see the query for retrieving data using record association from faculty to department entity referencing using FacultyID as the primary key.
SELECT faculty.FacultyID, faculty.Faculty_Name, faculty.Course, department.DepartmentID, department.Department_Name, department.Department_Grading
FROM faculty
JOIN department ON faculty.FacultyID = department.FacultyID
 faculty to department table
faculty to department table This query works like, the FacultyID matched or present in records of the department table will get associated with it. Let's understand by looking at the output
Output:
 Output of above query from faculty to department table
Output of above query from faculty to department tableExplanation: FacultyID present in the department table will be associated with those records in department which have the FacultyID as the same in the faculty table. For example, FacultyID 61801, 61802, 61803 are associated with Departments so the FacultyID is repeating for representing multiple departments
Now let's see the query from record association from the department table to the faculty table to represent the many-to-many relationship.
SQL Query:
SELECT department.departmentID, department.Department_Name, department.Department_Grading, faculty.FacultyID, faculty.Faculty_Name AS facultyName, faculty.Course
FROM department
JOIN faculty ON department.DepartmentID = faculty.DepartmentID;
 Retrieving records/data using departmentID as a reference from department to faculty table
Retrieving records/data using departmentID as a reference from department to faculty tableOutput:
 This is the output of the above query
This is the output of the above queryExplanation: Now, in the above example you can see that the department name, and grading is repeating multiple times to represent multiple faculties.
Conclusion
We learned types of relationships i.e. one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many relationships between entities, or while designing tables using SQL. We learnt the implementation of these relationships and how to apply them as per the business logic. Also learnt and saw how to write query to retrieve records/rows or data using these relationships concepts.
Similar Reads
SQL Interview Questions Are you preparing for a SQL interview? SQL is a standard database language used for accessing and manipulating data in databases. It stands for Structured Query Language and was developed by IBM in the 1970's, SQL allows us to create, read, update, and delete data with simple yet effective commands.
15+ min read
SQL Tutorial SQL is a Structured query language used to access and manipulate data in databases. SQL stands for Structured Query Language. We can create, update, delete, and retrieve data in databases like MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, etc. Overall, SQL is a query language that communicates with databases.In this S
11 min read
Non-linear Components In electrical circuits, Non-linear Components are electronic devices that need an external power source to operate actively. Non-Linear Components are those that are changed with respect to the voltage and current. Elements that do not follow ohm's law are called Non-linear Components. Non-linear Co
11 min read
SQL Commands | DDL, DQL, DML, DCL and TCL Commands SQL commands are crucial for managing databases effectively. These commands are divided into categories such as Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), Data Control Language (DCL), Data Query Language (DQL), and Transaction Control Language (TCL). In this article, we will e
7 min read
SQL Joins (Inner, Left, Right and Full Join) SQL joins are fundamental tools for combining data from multiple tables in relational databases. Joins allow efficient data retrieval, which is essential for generating meaningful observations and solving complex business queries. Understanding SQL join types, such as INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JO
6 min read
Normal Forms in DBMS In the world of database management, Normal Forms are important for ensuring that data is structured logically, reducing redundancy, and maintaining data integrity. When working with databases, especially relational databases, it is critical to follow normalization techniques that help to eliminate
7 min read
Spring Boot Tutorial Spring Boot is a Java framework that makes it easier to create and run Java applications. It simplifies the configuration and setup process, allowing developers to focus more on writing code for their applications. This Spring Boot Tutorial is a comprehensive guide that covers both basic and advance
10 min read
ACID Properties in DBMS In the world of DBMS, transactions are fundamental operations that allow us to modify and retrieve data. However, to ensure the integrity of a database, it is important that these transactions are executed in a way that maintains consistency, correctness, and reliability. This is where the ACID prop
8 min read
Class Diagram | Unified Modeling Language (UML) A UML class diagram is a visual tool that represents the structure of a system by showing its classes, attributes, methods, and the relationships between them. It helps everyone involved in a project—like developers and designers—understand how the system is organized and how its components interact
12 min read
Steady State Response In this article, we are going to discuss the steady-state response. We will see what is steady state response in Time domain analysis. We will then discuss some of the standard test signals used in finding the response of a response. We also discuss the first-order response for different signals. We
9 min read