A One-to-One function, also known as an Injective function, is a type of function defined over a domain and codomain that describes a specific type of relationship between them. In a One-to-One function, each element in the domain maps to a unique element in the codomain.
A function 'f' from a set 'A' to a set 'B' is one-to-one if no two elements in 'A' are mapped to the same element in 'B.'

Let's consider these two diagrams. For diagram A, we realize that 10 maps to 1, 20 maps to 2, and 30 maps to 3.
However, for diagram B, it is clear that 10 and 30 map to 3, and then 20 maps to 1.
Since we have elements in the domain corresponding to distinct values in each domain for diagram A, it makes the function one-to-one; thus, our diagram B is not one-to-one.
This can be expressed mathematically as
f(a) = f(b) ⇒ a = b
One-to-One Functions Example
Some examples of one-to-one functions are given below:
- Identity Function: The identity function is a simple example of a one-to-one function. It takes an input and returns the same value as the output. For any real number x, the identity function is defined as:
f(x) = x
Every distinct input x corresponds to a distinct output f(x), making it a one-to-one function.
- Linear Function: A linear function is one where the highest power of the variable is 1.
For example: f(x) = 2x + 3
This is a one-to-one function because no matter what value of x you choose, you will get a unique value for f(x).
- Square Function: The square function f(x) = x² is not one-to-one on all real numbers because f(1)=f(-1). However, if we restrict the domain to x ≥ 0 (non-negative real numbers) or x ≤ 0, then it becomes one-to-one.
Let's prove one such example for a one-to-one function.
Example: Prove that the function f(x) = 1/(x + 2), x ≠ -2 is one-to-one.
Solution:
According one-to-one function we know that
f(a) = f(b)replace a with x and x with b
f(a) = 1/(a+2) , f(b) = 1/(b+2)
⇒ 1/(a+2) = 1/(b+2)cross multiply the above equation
1(b+2)=1(a+2)
b+2=a+2
⇒ b=a+2-2∴ a=b
Now, since a = b the function is said to be one-to-one function.
Properties One-to-One Functions
Let's consider that f and g are two one-to-one functions; the properties are as follows:
- If f and g are both one-to-one, then f ∘ g follows injectivity.
- If g ∘ f is one-to-one, then function f is one-to-one, but function g may not be.
- f: X → Y is one-to-one, if and only if, given any functions g, h : P → X, whenever f ∘ g = f ∘ h, then g = h. In other words, one-one functions are exactly the monomorphisms in the category of sets.
- If f: X → Y is one-to-one and P is a subset of X, then f-1(f(A)) = P. Thus, P can be retrieved from its image f(P).
- If f: X → Y is one-to-one and P and Q are both subsets of X, then f(P ∩ Q) = f(P) ∩ f(Q).
- If X and Y are finite sets with the same number of elements, then f: X → Y is one-to-one if and only if f is onto.
One-to-One Function Graph
Graph representation of the one-to-one function

The above graph of the function f(x)= √x shows the graphical representation of a one-to-one function.
Horizontal Line Test
A function is one-to-one if each horizontal line does not intersect the graph at more than one point.

In the above example, it intersects the horizontal line only at one point. So f(x) is a one-to-one function, which means that it has an inverse function.
Inverse of a one-to-one function
Let f be a one-to-one function with a domain A and Range B. Then the inverse of f is a function with domain B and Range A defined by f-1 (y) =x if and only if f(x) = y for any y in B.
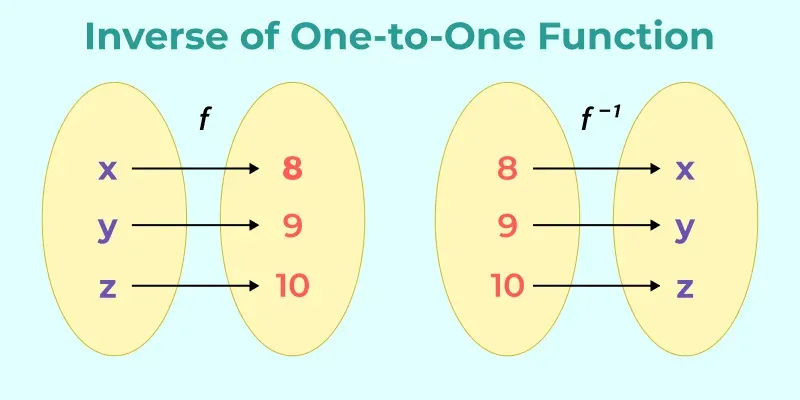
Always remember that a function has an inverse if and only if it is one-to-one. Many odd-degree polynomial functions (like f(x) = x3) are one-to-one because they are strictly increasing or decreasing on all real numbers. However, not every function with an odd exponent is one-to-one.
Example: f(x) = 3x + 2. Find the inverse of the function.
Solution:
write the function in y = f(x) form
⇒ y = 3x + 2lets interchange y and x variables
⇒ x = 3y + 2solve y in terms of x
⇒ x - 2 = 3ydivide the equation with 3
⇒ (x-2)/3 = 3y/3
⇒ y = (x-2)/3∴ f-1(x) = (x-2)/3
One-to-One Function vs Onto Function
The following illustration provides the clear difference between one-to-one and onto functions:
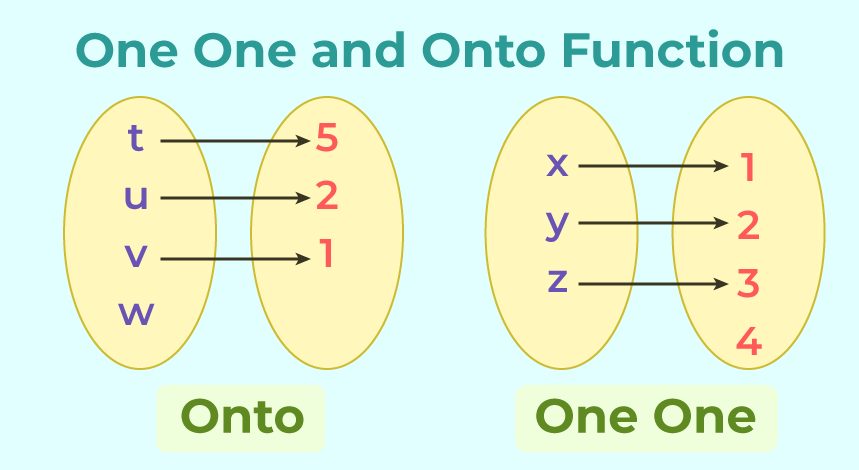
The key differences between One-to-One and Onto Functions are listed in the following table:
| One-to-One (Injective) Function | Onto (Surjective) Function |
|---|---|
| A function in which no two different elements in the domain map to the same element in the codomain. In other words, each element in the domain maps to a unique element in the codomain. | A function in which every element in the codomain is mapped to by at least one element in the domain. In other words, the range of the function equals the entire codomain. |
| f(x1) ≠ f(x2) if x1 ≠ x2 for all x1, x2 in the domain. | For every y in the codomain, there exists an x in the domain such that f(x) = y. |
| The graph of a one-to-one function never has a horizontal line that intersects it at more than one point. | |
| f(x) = 2x is one-to-one because no two distinct values of x produce the same output. | f(x) = √x is onto if the codomain is restricted to non-negative real numbers, since every non-negative number has a preimage. |
| A one-to-one function generally has an inverse function. | A function has an inverse if and only if it is both one-to-one and onto. |
| The cardinality of the domain and codomain can be equal or different for one-to-one functions. | The cardinality of the codomain is usually greater than or equal to the cardinality of the domain for onto functions. |
Related Articles:
Solved Problems on One-to-One Function
Question 1: Determine if the following function is one-to-one: f(x) = 3x - 1.
Solution:
To check if it's one-to-one, we need to show that no two distinct x-values map to the same y-value.
Suppose f(a) = f(b), where a ≠ b.
3a - 1 = 3b - 1
3a = 3b
a = bSince the only way for f(a) = f(b) is when a = b, this function is indeed one-to-one.
Question 2: Determine if the following function is one-to-one: g(x) = x2
Solution:
We'll use the horizontal line test by graphing the function. If any horizontal line intersects the graph more than once, it's not one-to-one.
The graph of g(x) = x^2 is a parabola opening upwards. Some horizontal lines (for example, y = 4) intersect the graph at two points (x = 2 and x = –2). Therefore, the function is not one-to-one.
Practice Problems on One-to-One Functions
Question 1: Determine whether the following function is one-to-one:
- f(x) = 2x + 3
- g(x) = 3x2 - 1
- h(x) = 3√x
Question 2: Find a function that is one-to-one from the set of real numbers to the set of real numbers.
Question 3: Given the function g(x) = x2 + 1, determine if it is one-to-one on its entire domain.
Question 4: Consider the function h(x) = ex. Is it a one-to-one function?
Question 5: Find the inverse function of f(x) = 4x - 7 and determine its domain.
Question 6: Determine if the function p(x) = √x is one-to-one.
Question 7: Given q(x) = x/2, find the domain and range of the function.
Question 8: Check whether the function r(x) = sin (x) is one-to-one over the interval [0, π].
Question 9: Consider the function s(x) = |x|. Is it a one-to-one function?
Question 10: Determine if the function t(x) = 1/x is one-to-one and find its domain.