The event loop in Node.js is a mechanism that allows asynchronous tasks to be handled efficiently without blocking the execution of other operations. It:
- Executes JavaScript synchronously first and then processes asynchronous operations.
- Delegates heavy tasks like I/O operations, timers, and network requests to the libuv library.
- Ensures smooth execution of multiple operations by queuing and scheduling callbacks efficiently.
Why is the Event Loop important?
The Event Loop is essential in Node.js because it allows non-blocking, asynchronous operations to be handled efficiently, even though Node.js operates on a single thread.
- It allows non-blocking execution despite Node.js being single-threaded.
- It helps handle I/O-bound tasks efficiently.
- It makes Node.js suitable for scalable applications like web servers.
Let's see a simple Asynchronous example
JavaScript
console.log("This is the first statement");
setTimeout(function() {
console.log("This is the second statement");
}, 1000);
console.log("This is the third statement");
- The first statement is logged immediately.
- setTimeout schedules the second statement to log after 1000 milliseconds.
- The third statement is logged immediately after.
- After 1000 milliseconds, the callback from setTimeout is executed, logging Second statement.
Output
 output
output
How does work Event Loop Work?
When a Node.js application runs, the event loop starts, processes the synchronous code first, and then moves to handle asynchronous tasks. The execution follows these steps:
1. Initialization
When Node.js starts, it loads the script, executes synchronous code, and registers any asynchronous tasks (e.g., timers, I/O requests, network operations).
- The call stack executes synchronous code first.
- Any asynchronous operations (setTimeout, fs.readFile, network requests) are delegated to libuv.
3. Handles Asynchronous Operations with libuv
Node.js uses a special C library called libuv to handle asynchronous operations. This library manages a thread pool that offloads heavy tasks (like file I/O, database operations, or network requests) that would otherwise block the event loop. The thread pool contains several threads that perform tasks like:
- File system I/O (fs.readFile)
- Network requests (HTTP, TCP, DNS)
- Timers (setTimeout, setInterval)
- Compression and cryptographic tasks
4. Callback Execution
Once the thread pool completes its tasks, it sends callbacks to the event queue. The event loop processes these callbacks, but only when the call stack is empty (i.e., when no synchronous code is currently executing).
5. Event Loop Phases
The event loop goes through multiple phases, each designed to handle a different set of operations. It checks for events, handles asynchronous callbacks, and executes tasks in the correct order.
6. Callback Execution from Event Queue
After the call stack is empty, the event loop picks tasks from the event queue and sends them to the call stack for execution. These tasks could include:
- Completing network requests
- Processing I/O events
- Handling timers like setTimeout or setInterval
The following diagram is a proper representation of the event loop in a Node.js server:

Phases of the Event loop
The event loop in Node.js consists of several phases, each of which performs a specific task. These phases include:

1. Timers Phase
This phase processes timers that have been set using setTimeout() and setInterval().
JavaScript
console.log('Start');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Timeout callback');
}, 2000);
console.log('End');
- setTimeout() schedules a callback to run after 2000 milliseconds.
- The event loop processes this callback in the timers phase after the synchronous code has executed.
Output:
 output
output
2. Pending Callbacks
This phase executes I/O-related callbacks that were deferred from the previous loop cycle.
JavaScript
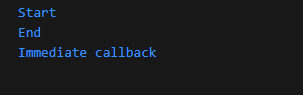
console.log('Start');
setImmediate(() => {
console.log('Immediate callback');
});
console.log('End');
- setImmediate() schedules a callback to run immediately after the current event loop cycle.
- The event loop processes this callback in the pending callbacks phase.
Output:
 output
output
3. Idle, Prepare (Internal use only)
This phase is used internally by Node.js for background tasks.
4. Poll Phase (Main Phase)
The Poll phase executes most of the tasks like- I/O, file reading, HTTP requests and much more.
JavaScript
const fs = require('fs');
const readStream = fs.createReadStream('./file.txt');
console.log('Start');
readStream.on('data', (chunk) => {
console.log(chunk.toString());
});
console.log('End');
- fs.readFile() initiates an asynchronous file read operation.
- The callback is added to the poll phase and executed once the file read is complete.
Output:
Start
End
File read complete
5. Check Phase
This phase processes any setImmediate() callbacks that have been added to the message queue.
JavaScript
console.log('Start');
setImmediate(() => {
console.log('Immediate callback');
});
console.log('End');
- setImmediate() schedules a callback to run immediately after the poll phase.
- The event loop processes this callback in the check phase.
Output
 output
output
6. Close Callbacks Phase
This phase executes callbacks for closed connections like sockets, streams, and event emitters.
JavaScript
const net = require('net');
const server = net.createServer((socket) => {
socket.on('close', () => {
console.log('Socket closed');
});
});
server.listen(8000);
- The server listens for incoming connections.
- When a socket is closed, the 'close' event is emitted, and the corresponding callback is executed in the close callbacks phase.
Output
Server listening on port 8000
process.nextTick() and Promises in the Event Loop
Apart from these phases there is also process.nextTick() and promise callback which has the highest priority in the event loop. It executes after every phase before moving to the next phase.
- process.nextTick() callbacks are always executed before the event loop moves to the next phase.
- Resolved Promise callbacks are processed immediately after process.nextTick().
Now you have seen all the phases so let's understand the order by using this code example
JavaScript
setImmediate(() => {
console.log("setImmediate is called");
});
Promise.resolve("Promise is resolved").then(console.log);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("Time function is called");
}, 0);
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log("Process.nextTick");
});
Output
 output
output
In this example
- process.nextTick() executes before moving to the next phase.
- Resolved Promises execute right after process.nextTick().
- setTimeout() executes in the timers phase.
- setImmediate() executes in the check phase.
Node.js Event Loop : A Visual Explanation
Explore
Introduction & Installation
Node.js Modules , Buffer & Streams
Node.js Asynchronous Programming
Node.js NPM
Node.js Deployments & Communication
Resources & Tools