AWS Outposts - Planning and Deploying
Last Updated :
09 Dec, 2024
Amazon Web Services offers various services to its customers as a pay-as-you-go model. Various businesses use AWS services inside their software products and they deploy their applications in various regions that AWS offers. Some businesses want to use services offered by AWS but because of latency and data loss concerns they hesitate to use those services and avoid AWS.
Here AWS Outpost comes into the picture AWS Outposts is a service provided by AWS. Outposts offers the AWS cloud to users in an on-premises location so that users can access their applications with low latency. Outposts give the same AWS infrastructure, services, APIs, and tools present in the AWS cloud to any on-premises facility. Outposts use the same hardware and software that is used in AWS public data centers.

How AWS Outposts Work?
Amazon Web Services Outposts are specifically engineered to function with a continuous and uniform connection between your on-premise Outpost and an AWS Region. In order to establish a link between the nearest AWS Region and the local workloads in your on-premises environment, it is necessary to connect your Outpost to your on-premises network. Your local network must have the capability to connect to the wide area network (WAN) in order to access both the Region and the internet. Additionally, it should offer LAN or WAN connectivity to the local network where your on-premises workloads or applications are located.

Why We Use AWS Outposts?
AWS Outposts give a smooth connection between local infrastructure and the AWS cloud, providing enterprises the flexibility to expand AWS services to their own co-location sites. Customers can use Outposts to address low-latency applications and the local data-processing requirements of their applications.
Some Industry Use Cases For Outposts
- Manufacturing Automation: In process control systems, some applications require low latency in communication. So, we can integrate this application with on-premise Outposts.
- Healthcare: Data locality requirements of some AWS services for analysis and machine learning.
- Telecommunications: Use cloud services and tools to orchestrate, update, scale, and manage the lifecycle of cloud and on-premises networks.
- Media And Entertainment: Support live and real-time event streaming applications that require low latency.
- Financial Services: Deliver banking, payment, and processing in real-time with low latency to customers.
- Retail: Establish a connected store with real-time data sharing with low latency.
Planning Your AWS Outposts Deployment
If you are planning to set up AWS Outposts on-premise, you have to consider this:
- Evaluation of Workloads: You need to take a look at your current workloads and decide which ones would gain the most from being hosted on AWS Outposts.
- Network Connectivity: You have to ensure fair network connectivity between your on-premises system and the AWS Outposts instance. This may involve setting up VPN connections or leveraging AWS Direct Connect for dedicated network lines.
- Power and Cooling: You have to meet the power and cooling requirements at the deployment site to accommodate the AWS Outposts rack. Ensure that the infrastructure can handle the extra load without compromising performance or reliability.
- Security and Compliance: Since this is on-premise, you will need to follow best practices for security to keep your data and equipment safe.
- Allocating Resources: You need to figure out what computing, storage, and networking resources your AWS Outposts setup needs based on how much work you expect it to do and how fast you want it to do it.
AWS Outposts Family Members
If you are looking at a hybrid cloud solution then AWS Outposts is a powerful tool to look for as it offer benefits of Amazon Web Services right to your doorstep. The AWS Outposts family consists of two main components: Outposts Rack and Outposts Servers. Let’s take a closer look at what these products are and how they can work for you.
1. AWS Outpost Rack
Imagine the AWS infrastructure you are used to but instead of a remote data center, its in your own space. Thats AWS Outposts Rack. This is a managed service that deploys AWS infrastructure and appliances directly to your on-premises or edge environments effectively extending your AWS cloud environment into your data centers
Specifications
- Dimensions: 80 inches (203 cm) high, 24 inches (61 cm) wide and 48 inches (122 cm) deep.
- Weight: Varies by configuration; ensure the installation site can support the specified weight, including any freight and standard elevators along the path.
- Power Requirements: Supports 5–15 kVA power supply with redundant feeds. A central power bus bar distributes power to each server with whips supporting various common power types.
- Networking: Supports uplink speeds of 1, 10, 40 and 100 Gbps. Each Outposts Rack has two physical network devices that connect to your local network, requiring a minimum of two physical links between these devices and your local network devices.
- Environmental Conditions: Ambient temperature must be between 41°F (5°C) and 95°F (35°C) with relative humidity between 8% and 80% (non-condensing).
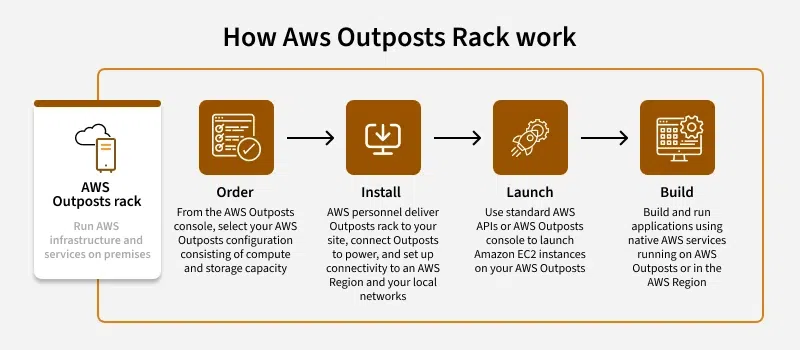
How it Works?
- Easy integration: Outposts Rack fits into your existing AWS infrastructure. You use the same AWS Management Console, APIs, and tools, making it easy to keep everything consistent across your on-premises and cloud resources.
- Complete hardware and software management: AWS manages all maintenance, repair and updates. You get pre-configured computing and storage resources, which means you can focus on applications that require low latency or local data processing without worrying about managing the infrastructure
- Secure Connection: This provides a fast, secure connection to your chosen AWS domain, enabling your local applications to easily access AWS services, and benefit from scalability and a wide range of AWS features
- Flexible and Scalable: As your needs change, Outposts Rack can be sized to accommodate more computing or storage capacity, allowing flexibility to meet workloads.
2. AWS Outposts Servers
Outposts Servers are a part of the AWS Outposts own family tailor-made specifically for serve primarily based programs that require high overall performance and reliability. They supply the same integration and control as the Outposts Rack but are optimized for environments desiring fast processing near customers or facts assets.
How do they work?
- Dedicated resources: Each server comes with dedicated computing resources for a specific task, ensuring that your critical applications have what they need to run optimally.
- Optimized for edge computing: These servers are ideal for environments like manufacturing, healthcare, or streaming, where data usage at its source requires low latency and high bandwidth
- Managed by AWS: Like Rack, AWS also handles hardware management—maintenance, updates, and security patches—freeing up your IT team to focus on applications rather than infrastructure.
- Seamless integration with AWS services: Outposts servers integrate seamlessly with AWS services, making it easy to set up hybrid environments that use both cloud and on-premise resources This supports synchronization, backup, and disaster recovery, and helps to your work continues to work .

Creating an AWS Outpost: A Step-By-Step Guide

- Now you have to choose configuration. There will be a two options: servers and racks.

- The following details in screenshots are the open configurations of AWS Outposts


- For this article, we will choose One Server Configuration and click on Next.

- Now we have to select Outpost. Here we will create new Outpost and fill in the required details. At last, we have to select Site. If you created a site, then select that or choose the option "Create new Site."

- Now Create a new site by giving name to the site and an operating address, then click on Next.

- Define the operating addresses that are asked in the following screenshot.

- Now select "Contract term," "Payment Option," and fill in the proper shipping address, and click on Next.

- Now review the details and place an order.
After placing an order, the AWS Outpost team will contact you for confirmation and ask for a visit date for installation. According to your conversation and follow-up, the AWS Outpost team will visit your location for installation. At the installation time, there must be an electrician available, as well as your network engineer.By following these steps, customers can plan AWS Outposts deployment and know how AWS Outpost is deployed on-premises.
Similar Reads
Deploying Web Applications On AWS Lightsail Amazon Web Service offers a service called Lightsail which is used for deploying and managing web applications. It is well suited for small-scale businesses and developers it will scale and manage the application in the cloud. What is Amazon Lightsail?For anyone who needs to develop websites or web
8 min read
How to Deploy Angular App in AWS Angular projects and applications are becoming more and more important as they are gaining popularity in the software industry, thus it becomes important to understand how we can deploy the angular apps that we create from the local system to the AWS cloud server, let us understand step by step how
8 min read
Automation And Tooling - Introduction To DevOps On AWS AWS Stands for Amazon Web Services is a cloud platform provided by Amazon. It offers computing, storage, networking, etc. services to organizations or individual users over the Internet. organizations can host their servers, databases, and other networking needs on AWS without worrying about managin
7 min read
How to Deploy Kubernetes on AWS? Kubernetes, the open-supply box orchestration platform, has emerged as the solution for dealing with containerized applications. When deploying Kubernetes in the cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS) gives a robust and scalable environment. In this manual, we can walk you through the manner of deploying
7 min read
Deploy a Website Using AWS Amplify Pre-requisite: AWS Amplify Amplify is a suite of tools and frameworks developed by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that are used for managing hosting services for web apps as well as for launching software applications on AWS. On AWS, two well-known services include Amplify Studio and Hosting. Amplify Stu
2 min read