Bookstore analytics involves using data to understand customer preferences, product trends, inventory health and marketing performance in a retail bookstore. Ever wondered which books sell the most or which customers bring the most profit? That’s where SQL comes in.
In this project, we will guide you step-by-step through building a complete bookstore analytics solution using SQL. By the end of this project, you will:
- Identify best-selling books and revenue drivers
- Track and alert on low inventory stock
- Segment customers by behavior (RFM)
- Measure ROI on customer acquisition
- Present insights to stakeholders
Tools and Technologies
- SQL (SQLite/PostgreSQL/MySQL)
- Subqueries, Joins, Aggregations
- Common Table Expressions (CTEs)
Dataset Overview
The bookstore database includes four key tables that represents books, customers, orders and marketing efforts. Each table connects through primary and foreign keys to form a robust relational database.
| Table | Description |
|---|---|
Books | Contains book details and stock |
Customers | Customer info with city and signup date |
Orders | Purchase data linking books and customers |
MarketingSpend | Cost to acquire each customer |
Step-by-Step Implementation for Bookstore Analytics with SQL
Below are the steps that you can follow for implementing this project:
All queries are written and tested using SQLite, a lightweight, serverless SQL engine that is perfect for quick analysis and learning. You can easily run the code using any online SQL platform like SQLite Online or local database setup.
Step 1: Create the Database Schema
We begin by creating the tables using SQL CREATE TABLE statements. These include foreign key relationships for orders and marketing spend.
-- 1. Books table
CREATE TABLE Books (
book_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
title TEXT,
genre TEXT,
price DECIMAL(6,2),
stock INTEGER
);
-- 2. Customers table
CREATE TABLE Customers (
customer_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
city TEXT,
signup_date DATE
);
-- 3. Orders table
CREATE TABLE Orders (
order_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id INTEGER,
book_id INTEGER,
quantity INTEGER,
order_date DATE,
FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES Customers(customer_id),
FOREIGN KEY (book_id) REFERENCES Books(book_id)
);
-- 4. MarketingSpend table
CREATE TABLE MarketingSpend (
spend_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id INTEGER,
spend_amount DECIMAL(7,2),
FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES Customers(customer_id)
);
Output:

Step 2: Insert Sample Data
In this step we will insert sample data into all four tables: Books, Customers, Orders and MarketingSpend
-- Books
INSERT INTO Books VALUES
(1, 'Data Science 101', 'Education', 29.99, 100),
(2, 'The Art of SQL', 'Technology', 34.50, 50),
(3, 'Mystery at the Bookstore', 'Fiction', 15.00, 20),
(4, 'Learn Python the Hard Way', 'Education', 40.00, 30),
(5, 'Fantasy World Chronicles', 'Fantasy', 22.50, 10);
-- Customers
INSERT INTO Customers VALUES
(1, 'Alice', 'New York', '2023-01-10'),
(2, 'Bob', 'San Francisco', '2023-03-15'),
(3, 'Charlie', 'Austin', '2023-06-20'),
(4, 'Diana', 'New York', '2024-01-10'),
(5, 'Evan', 'Chicago', '2024-04-05');
-- Orders
INSERT INTO Orders VALUES
(1, 1, 1, 2, '2024-06-01'),
(2, 2, 2, 1, '2024-06-02'),
(3, 1, 3, 1, '2024-06-03'),
(4, 3, 1, 3, '2024-06-04'),
(5, 4, 5, 2, '2024-06-04'),
(6, 5, 2, 2, '2024-06-05'),
(7, 2, 4, 1, '2024-06-05'),
(8, 1, 1, 1, '2024-06-06');
-- Marketing Spend
INSERT INTO MarketingSpend VALUES
(1, 1, 50.00),
(2, 2, 75.00),
(3, 3, 40.00),
(4, 4, 60.00),
(5, 5, 35.00);
Output:
Step 3: Analyze Book Performance
Here we will use SQL Joins and aggregations to calculate total units sold and total revenue per book
SELECT
b.title,
SUM(o.quantity) AS total_units_sold,
SUM(o.quantity * b.price) AS total_revenue
FROM Orders o
JOIN Books b ON o.book_id = b.book_id
GROUP BY b.title
ORDER BY total_revenue DESC;
Output:

Step 4: Inventory Alerts
In this step we will trigger alerts for books running low on stock. We need to maintain healthy stock levels to prevent lost sales
SELECT
title, stock
FROM Books
WHERE stock < 15;
Output:

Step 5: Segment Customers Using RFM Analysis
Use a Common Table Expression (CTE) to understand top customers and create segments.
- Recency: Time since last purchase
- Frequency: Number of orders
- Monetary: Total spent
WITH customer_metrics AS (
SELECT
c.customer_id,
c.name,
MAX(order_date) AS last_order,
COUNT(o.order_id) AS frequency,
SUM(o.quantity * b.price) AS monetary
FROM Customers c
JOIN Orders o ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
JOIN Books b ON o.book_id = b.book_id
GROUP BY c.customer_id
)
SELECT *,
julianday('2024-07-01') - julianday(last_order) AS recency_days
FROM customer_metrics;
Output:

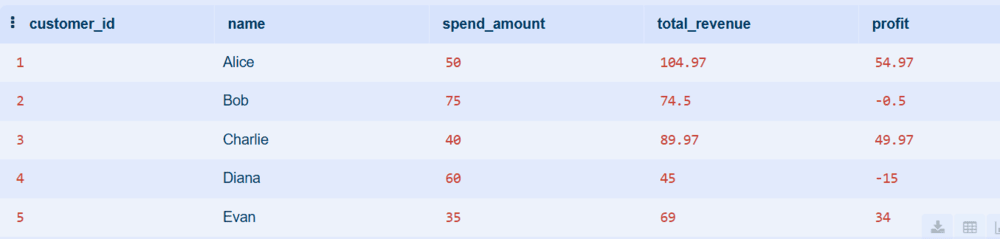
Step 6: Evaluate Marketing ROI
Compare customer lifetime revenue vs acquisition cost using joins and subqueries. We can say how much return you are getting per customer on marketing spend.
WITH customer_spend AS (
SELECT
o.customer_id,
SUM(o.quantity * b.price) AS total_revenue
FROM Orders o
JOIN Books b ON o.book_id = b.book_id
GROUP BY o.customer_id
)
SELECT
c.customer_id,
c.name,
ms.spend_amount,
cs.total_revenue,
(cs.total_revenue - ms.spend_amount) AS profit
FROM Customers c
JOIN MarketingSpend ms ON c.customer_id = ms.customer_id
JOIN customer_spend cs ON c.customer_id = cs.customer_id;
Output:
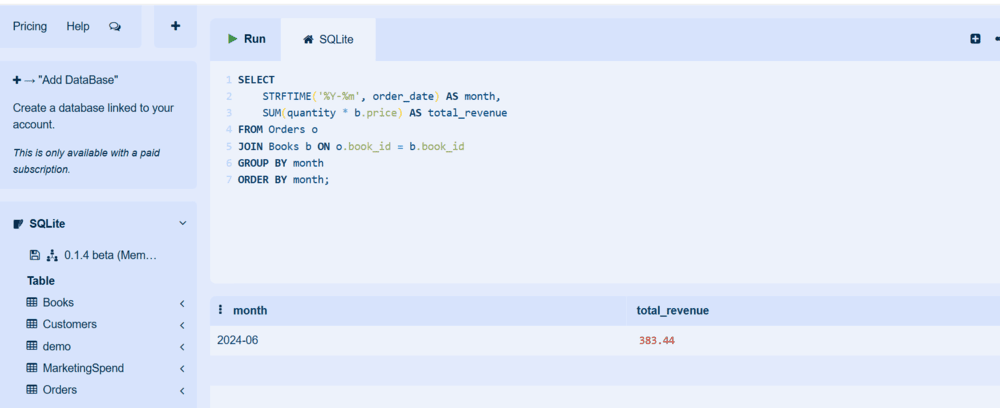
Step 7: Monthly Sales Trend
This step tracks how many books were sold and the total revenue generated each month. It helps identify sales seasonality and evaluate the performance of promotional campaigns.
SELECT
STRFTIME('%Y-%m', order_date) AS month,
SUM(quantity * b.price) AS total_revenue
FROM Orders o
JOIN Books b ON o.book_id = b.book_id
GROUP BY month
ORDER BY month;
Output:
Step 8: Returning Customers
This query identifies customers who have placed more than one order. It helps assess customer loyalty and repeat engagement with the store.
SELECT
c.customer_id,
c.name,
COUNT(DISTINCT o.order_id) AS total_orders
FROM Customers c
JOIN Orders o ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
GROUP BY c.customer_id
HAVING total_orders > 1;
Output:

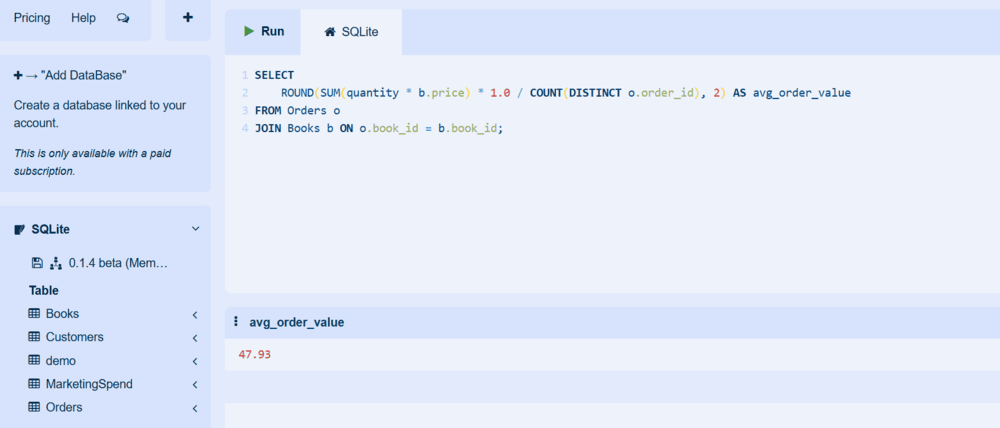
Step 9: Average Order Value (AOV)
This step calculates how much revenue is generated per order on average. It is a key business metric for understanding customer purchasing behavior.
SELECT
ROUND(SUM(quantity * b.price) * 1.0 / COUNT(DISTINCT o.order_id), 2) AS avg_order_value
FROM Orders o
JOIN Books b ON o.book_id = b.book_id;
Output:
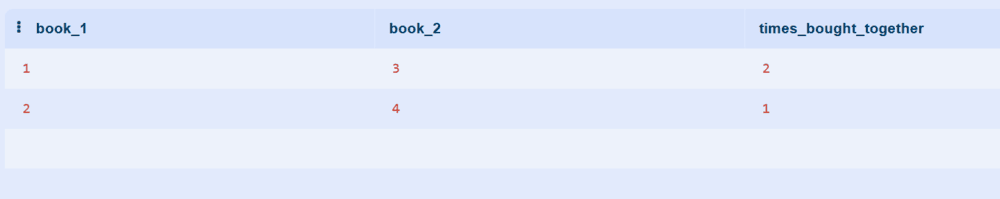
Step 10: Books Frequently Bought Together
Identify books that are often purchased by the same customer, enabling better recommendations and bundle promotions. Use this to suggest complementary books during checkout.
SELECT
o1.book_id AS book_1,
o2.book_id AS book_2,
COUNT(*) AS times_bought_together
FROM Orders o1
JOIN Orders o2
ON o1.customer_id = o2.customer_id AND o1.order_id != o2.order_id
WHERE o1.book_id < o2.book_id
GROUP BY book_1, book_2
ORDER BY times_bought_together DESC
LIMIT 10;
Output:
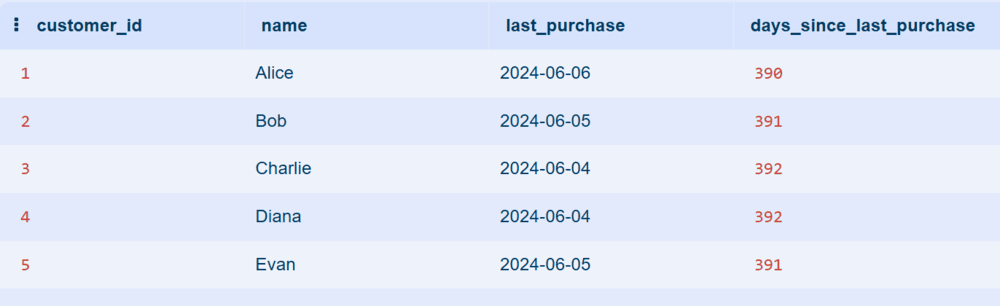
Step 11: Churned Customers
This step detects customers who haven’t made a purchase in the last 365 days, identifying users who may need re-engagement campaigns.
SELECT
c.customer_id,
c.name,
MAX(o.order_date) AS last_purchase,
ROUND(julianday('2025-07-01') - julianday(MAX(o.order_date))) AS days_since_last_purchase
FROM Customers c
JOIN Orders o ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
GROUP BY c.customer_id
HAVING days_since_last_purchase > 365;
Output:
Target Audience for This Project
- Students looking to build a strong SQL foundation
- Aspiring data analysts wanting hands-on project work
- Professionals who want to demonstrate applied SQL knowledge
- Small business owners curious about their own data
The analysis reveals that top customers drive revenue through frequent purchases of mid-priced books, while understocked bestsellers highlight the need for better inventory management. Smart marketing works well, showing how using data can help bookstores make better decisions and grow their business.
You can download the complete project files and SQL scripts from the link below: Bookstore Analytics with SQL
