Subquery optimization is the process of improving the performance of SQL queries that use subqueries by reducing redundant executions, rewriting them efficiently, and leveraging indexes. It ensures faster query execution, lower resource usage, and better scalability of database operations.
It helps break complex problems into smaller parts and is used in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE.
1) SELECT with Subquery
Used to filter or compare rows based on the result of another query.
Syntax
SELECT col_list
FROM table
WHERE col OP (SELECT expr FROM table);
Explanation of Syntax
- SELECT col_list → columns to display in the outer query.
- FROM table → main table from which rows are selected.
- WHERE col OP → condition (>, <, =, IN, etc.).
- (SELECT expr FROM table) → subquery that returns a value or set of values for comparison.
2) INSERT with Subquery
It is Used to insert rows based on data retrieved from another query.
Syntax
INSERT INTO table (col1, col2)
SELECT expr1, expr2
FROM table
WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM table WHERE condition);
Explanation of Syntax
INSERT INTO table (col1, col2) → target table and columns to insert into.SELECT expr1, expr2 → values fetched from another query.FROM table → source table.WHERE NOT EXISTS (subquery) → ensures row is inserted only if subquery finds no match.
3) UPDATE with Subquery
Used to update rows based on values calculated by another query.
Syntax
UPDATE table
SET col = expr
WHERE col OP (SELECT expr FROM table);
Explanation of Syntax
UPDATE table → the table to be updated.SET col = expr → new value to assign.WHERE col OP → condition (>, <, =, etc.).(SELECT expr FROM table) → subquery provides value for comparison.
4) DELETE with Subquery
It is Used to delete rows that match or don’t match another query’s result.
Syntax
DELETE FROM table
WHERE key NOT IN (SELECT key FROM other_table);
Explanation of Syntax
DELETE FROM table → deletes rows from the target table.WHERE key NOT IN → condition specifies which rows to delete.(SELECT key FROM other_table) → subquery returns a list of valid keys; others get deleted.
It is Used for row-by-row comparison, where the subquery depends on the outer query.
Syntax
SELECT col
FROM table e
WHERE e.col OP ( SELECT AGG(col)
FROM table
WHERE condition = e.condition);
Explanation of Syntax
SELECT col FROM table e → outer query retrieves rows.WHERE e.col OP → compares each row’s value with subquery result.SELECT AGG(col) → subquery with an aggregate (e.g., AVG, MAX).WHERE condition = e.condition → subquery refers to outer query’s row (correlated).
Diagram Of Subquery Optimization
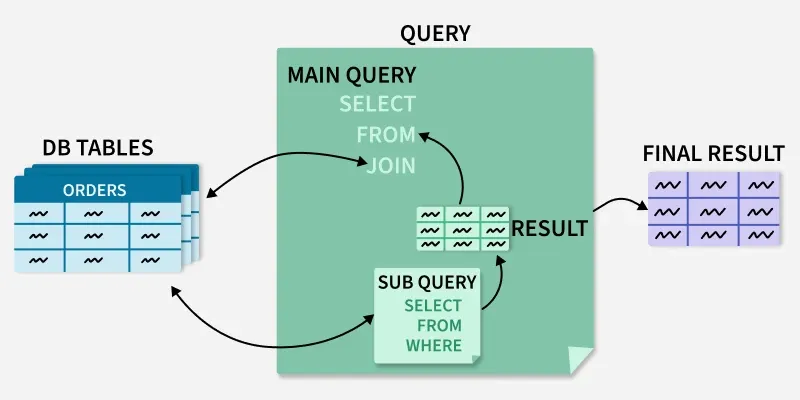
Explain the Diagram:
This diagram shows how a subquery works in SQL:
- The subquery runs first on the database tables and produces a result.
- The main query then uses this result for further filtering or selection.
- Finally, the main query output gives the final result set.
Explore
SQL Tutorial
7 min read
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security