In Java, a compiler and an interpreter are two tools that translate programs from high-level code to machine code. Both are essential for executing Java programs, but they work differently.
Java Compiler
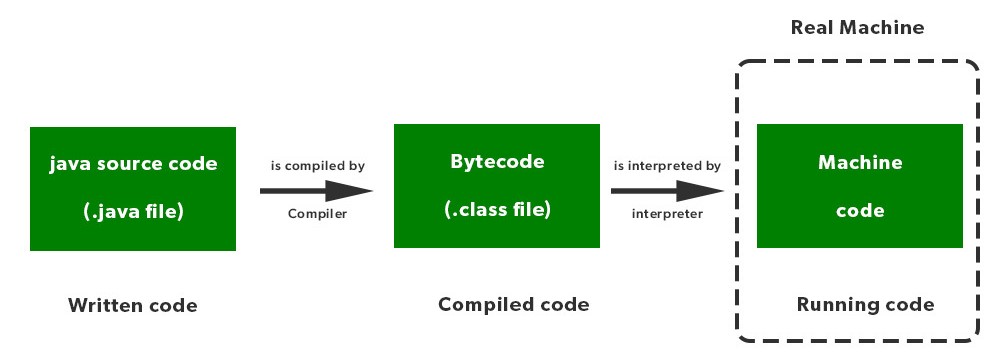
A Java compiler translates the entire source code into bytecode (intermediate code) before execution. The bytecode is platform-independent and can be executed by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
- Operated using javac.exe from the command prompt.
- Generates bytecode (.class files).
- Performs syntax and type checking.
- Can add additional code if required.
- Requires more memory but produces faster execution.
Compiler Options:
- -help: it prints a summary of standard options.
- -version: returns the compiler information.
- -verbose: provides detailed compilation information.
- -nowarn: it is used to turn off warnings.

Java Compiler: Step-by-Step Process

Roles of Java Compiler
- Scans the complete source code at once and highlights errors.
- Ensures correctness by checking syntax and type errors.
- Produces bytecode ready for execution.
- Adds additional necessary code automatically.
Java Interpreter
A Java interpreter (JVM) executes the bytecode line by line, translating it into native machine code at runtime.
- Converts bytecode into machine-specific code.
- Operates line by line.
- Stops execution if an error occurs on any line.
- Slower execution compared to compiler, but uses less memory.
Interpreter Options
- -version: displays interpreter version.
- -verbose: displays interpreter information.
- -help: displays interpreter options.

Java Interpreter: Step-by-Step Execution
Roles of Java Interpreter
- To convert the bytecode into the native code of the machine.
- This process is done line by line.
- If the error comes on any line, the process is stopped over there.
Compiler vs Interpreter in Java
Feature | Compiler | Interpreter |
|---|---|---|
Translation | Entire program at once | Line by line |
Error Detection | All errors at once | One error at a time |
Debugging | Slower | Faster |
Execution Speed | Faster | Slower |
Memory Usage | High | Low |
Example Languages | C, C++ | Java, Python |