What is Nested Select Statement in PostgreSQL?
Last Updated :
11 Nov, 2024
Nested select statements, also known as subqueries which is a fundamental concept in PostgreSQL and play an important role in data retrieval and manipulation. In PostgreSQL, a powerful relational database management system, the nested select statements allow for complex queries by nesting one query within another.
In this article, We will explain the concept of nested select statements in PostgreSQL by understanding the various examples and so on.
What is a Nested Select Statement?
In PostgreSQL, a Nested query is a query within another PostgreSQL query and embedded within the WHERE clause. It is also known as a subquery, which is a query nested within another query.
It allows us to use the result of one query as a condition or value in another query. Nested select statements can be used in various parts of a SQL query, such as the SELECT, FROM, WHERE, and HAVING clauses.
Syntax:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name OPERATOR (SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE condition);
Key Terms
- SELECT column1, column2, ... specifies the columns to retrieve in the outer query.
- FROM table_name specifies the table from which to retrieve data in the outer query.
- WHERE column_name OPERATOR (SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE condition) is the nested select statement.
- column_name is the column to compare in the outer query.
- OPERATOR is a comparison operator (e.g., =, >, <, IN, EXISTS).
- (SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE condition) is the inner query that returns a result set.
Examples of Nested Select statement in PostgreSQL
To understand What is Nested select statement in PostgreSQL we need a table on which we will perform various operations and queries. Here we will consider a table called employees which contains id, name, salary, and department as Columns.
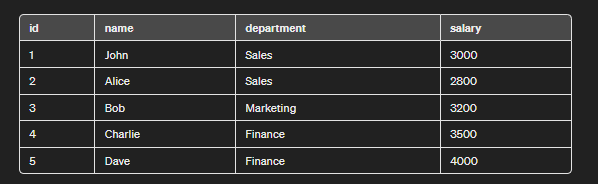
Example 1: Using Nested Select to Filter Results
Suppose we want to retrieve the names of employees who work in the 'Sales' department. We can achieve this using a nested select statement as follows:
Query:
SELECT name
FROM employees
WHERE department = (
SELECT id
FROM departments
WHERE name = 'Sales'
);
Output

Explanation:
In the above query, We retrieves the names of employees who belong to the 'Sales' department. It uses a subquery to first find the department ID for 'Sales' and then uses that ID to filter the employees table.
Example 2: Using Nested Select to Calculate Aggregate Functions
Suppose we want to find the average salary of employees in the 'Marketing' department. We can use a nested select statement with an aggregate function to achieve this
Query:
SELECT AVG(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE department = (
SELECT id
FROM departments
WHERE name = 'Marketing'
);
Output

Explanation:
In the above query, We calculates the average salary of employees in the 'Marketing' department. It uses a subquery to find the department ID for 'Marketing' and then calculates the average salary for employees in that department.
Example 3: Using Nested Select to Perform Comparison
Suppose we want to find employees whose salary is higher than the average salary in the 'Finance' department. We can use a nested select statement to achieve this:
Query:
SELECT name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary > (
SELECT AVG(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE department = (
SELECT id
FROM departments
WHERE name = 'Finance'
)
);
Output

Explanation
In the above query, We retrieves the names and salaries of employees whose salaries are higher than the average salary of the 'Finance' department. It uses a subquery to calculate the average salary of the 'Finance' department and then compares each employee's salary to that average.
Example 4: Using Nested Select to Retrieve Top N Records
Suppose we want to retrieve the top 3 highest-paid employees. We can use a nested select statement with the ORDER BY and LIMIT clauses to achieve this:
Query:
SELECT name, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 3;
Output

Explanation:
In the above query, We retrieves the names and salaries of the top 3 highest-paid employees. It sorts the 'employees' salaries in descending order and limits the result to the first 3 rows.
Conclusion
Overall, the nested select statements in PostgreSQL offer a flexible approach to retrieving data by embedding one query within another. These subqueries can be used in various parts of a SQL query, such as the SELECT, FROM, WHERE and HAVING clauses, providing flexibility in data retrieval. Through examples, we've learnt how nested select statements can be used to filter results, calculate aggregate functions, perform comparisons, and retrieve top records.
Similar Reads
SQL Interview Questions Are you preparing for a SQL interview? SQL is a standard database language used for accessing and manipulating data in databases. It stands for Structured Query Language and was developed by IBM in the 1970's, SQL allows us to create, read, update, and delete data with simple yet effective commands.
15+ min read
SQL Tutorial SQL is a Structured query language used to access and manipulate data in databases. SQL stands for Structured Query Language. We can create, update, delete, and retrieve data in databases like MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, etc. Overall, SQL is a query language that communicates with databases.In this S
11 min read
Non-linear Components In electrical circuits, Non-linear Components are electronic devices that need an external power source to operate actively. Non-Linear Components are those that are changed with respect to the voltage and current. Elements that do not follow ohm's law are called Non-linear Components. Non-linear Co
11 min read
SQL Commands | DDL, DQL, DML, DCL and TCL Commands SQL commands are crucial for managing databases effectively. These commands are divided into categories such as Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), Data Control Language (DCL), Data Query Language (DQL), and Transaction Control Language (TCL). In this article, we will e
7 min read
SQL Joins (Inner, Left, Right and Full Join) SQL joins are fundamental tools for combining data from multiple tables in relational databases. Joins allow efficient data retrieval, which is essential for generating meaningful observations and solving complex business queries. Understanding SQL join types, such as INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JO
6 min read
Normal Forms in DBMS In the world of database management, Normal Forms are important for ensuring that data is structured logically, reducing redundancy, and maintaining data integrity. When working with databases, especially relational databases, it is critical to follow normalization techniques that help to eliminate
7 min read
Spring Boot Tutorial Spring Boot is a Java framework that makes it easier to create and run Java applications. It simplifies the configuration and setup process, allowing developers to focus more on writing code for their applications. This Spring Boot Tutorial is a comprehensive guide that covers both basic and advance
10 min read
ACID Properties in DBMS In the world of DBMS, transactions are fundamental operations that allow us to modify and retrieve data. However, to ensure the integrity of a database, it is important that these transactions are executed in a way that maintains consistency, correctness, and reliability. This is where the ACID prop
8 min read
Class Diagram | Unified Modeling Language (UML) A UML class diagram is a visual tool that represents the structure of a system by showing its classes, attributes, methods, and the relationships between them. It helps everyone involved in a project—like developers and designers—understand how the system is organized and how its components interact
12 min read
Steady State Response In this article, we are going to discuss the steady-state response. We will see what is steady state response in Time domain analysis. We will then discuss some of the standard test signals used in finding the response of a response. We also discuss the first-order response for different signals. We
9 min read