1. Introduction to Computer System (1).pptx
- 1. INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SYSTEM Prof. Anuja Nair Assistant Professor Computer Science & Engineering Department Institute of Technology Nirma University
- 3. Hardware • Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that constitutes a computer system. • Example: monitor, mouse, keyboard, computer data storage, hard drive disk (HDD), system unit (graphic cards, sound cards, memory, motherboard and chips), etc. all of which are physical objects that can be touched.
- 4. Software • Computer software, or simply software, also known as computer programs, is the non-tangible component of computers. • It represents the set of programs that govern the operation of a computer system and make the hardware run. • Computer software contrasts with computer hardware, which is the physical component of computers. • One major example is operating system. All computers require an operating system. E.g. OS ( Disk operating System, Windows, Linux, Mac etc.)
- 5. Types of Software • System Software • To control operation and extend the processing capabilities of computer system. • e.g. Operating System, Compiler, Assembler, etc. • Application Software • Designed for user specific need. • General purpose • e.g. MS Office, Excel etc. • Specific purpose • Custom built according to requirement of user.
- 6. System Software • Operating System • Compiler : translates high level language to machine level language • Assembler : translates assembly or low level language to machine language • Loader : which loads OS part and object program into main memory for execution purpose. E.g. bootstrap loader. • Linker : which binds code of source and library file to make executable programs. • Editor : used to write a program. • Translator : which converts one language into other. (Compiler, Assembler, Interpreter) • Macro processor : Replace symbolic meaning into equivalent code. Also, called pre-processor. • Interpreter : translates line by line high level language into machine language.
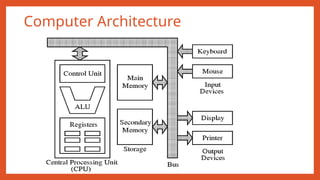
- 7. Register • A component inside a central processing unit for storing information
- 8. Central Processing Unit (CPU) • A central processing unit (CPU) is the hardware within a computer that carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. • CPU is a combination of ALU (arithmetic logic unit) and CU (Control Unit). • ALU • It performs all arithmetic calculations and takes logical decision. • CU • It manages and coordinates operations of all other components of computer system.
- 9. Bus and System Bus • In computer architecture, a bus is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. • This expression covers all related hardware components (wire, optical fiber, etc.) and software, including communication protocols.
- 10. Memory Unit • Storage unit for processing data and information. • Holds instructions and data needed for programs that are currently running • Two types of storage: • Primary/Main storage • Secondary storage
- 11. Classification of Main Memory 1. Random Access Memory (RAM) 1. Stores current program or data. 2. Stores temporary data of current program. 3. Less space in comparison to secondary storage. 4. Volatile (data losses on power off) 5. Comparatively more expensive. 6. Fast in operation. 2. Read Only Memory (ROM)
- 12. Read only Memory(ROM) • ROM is used for storing programs that are PERMENTLY resident in the computer. The ROM portion of main memory is needed for storing an initial program called bootstrap loader, witch is to start the computer software operating when power is turned on
- 13. Secondary Memory • A nonvolatile storage medium • Contents retained while power is off • Hard disk drives are most common • Records data magnetically on a circular disk • Provides fast access to large amounts of data • USB flash memory devices • High capacity device plugs into USB port • Portable, reliable, and fits easily in a pocket • e.g. Hard disk (HDD), CD, DVD, Pen Drive, Removable hard disk
- 14. Input Devices • Accept data and instructions from the user or from another computer system. • Example: Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner, Mike 14
- 15. Output Devices Return Processed data back to the user or other computer system Example: Printer, Monitor, Speaker 15
- 16. Classification of programming languages • Machine or Low level language • Assembly language • High level language • Note: Refer the document “Classification of Programming Languages”.
- 17. Summary of characteristics of languages Sr. No Language Characteristics 1. Machine Language 1. Machine dependent 2. Represented as 0s and 1s. 2. Assembly Language 1. Machine dependent 2. Uses mnemonics 3. 1 to 1 language i.e. for assembly language instruction generated 3. High-level Language 1. Machine independent 2. Uses instructions which seem English – like. 3. 1 to many language i.e. for high level instruction, many machine language generated (OS specific).
- 18. Compiler • Compiler is a computer program (or set of programs) that transforms source code written in a programming language (the source language) into another computer language (the target language, often having a binary form known as object code). The most common reason for wanting to transform source code is to create an executable program. • The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high- level programming language to a lower level language (e.g., assembly language or machine code). • If the compiled program can run on a computer whose CPU or operating system is different from the one on which the compiler runs, the compiler is known as a cross-compiler. • A program that translates from a low level language to a higher level one is a decompiler. • A program that translates between high-level languages is usually called a source-to-source compiler.
- 19. Interpreter A translating program that translates and executes the statements in sequence • Assembler or compiler produce machine code as output, which is then executed in a separate step i.e. translates line by line conversion of high level language into low level programs. • An interpreter translates a statement and then immediately executes the statement • Interpreters can be viewed as simulators 19
- 20. Compilers 20
- 21. Assembler • An assembler is a program that takes basic computer instructions (assembly language) and converts them into a pattern of bits (machine language) that the computer's processor can use to perform its basic operations. • e.g. Microprocessor 8085, 8088. • Instruction: ADD R1, R2 • Note: Refer the document “compiler_assembler_linker_loader”.
- 22. Compiler vs. Interpreter Sr. No. Particular Compiler Interpreter 1. Scheme Compiler scans the whole program at a time and lists out error if any. Interpreter scans the program line by line and stop scanning whenever error occurs. 2. Manner Compiler converts the whole source code into object code at a time. Interpreter converts the source programs. 3. Source Code After compilation, source code is not required. For every execution run, source is required. 4. Speed Execution is faster Execution is slower. 5. Object Code The object code is generated when the program is error free. Generates object code for each line immediately if it is error free. 6. Memory Requires more memory. Requires less memory.
- 23. THANK YOU