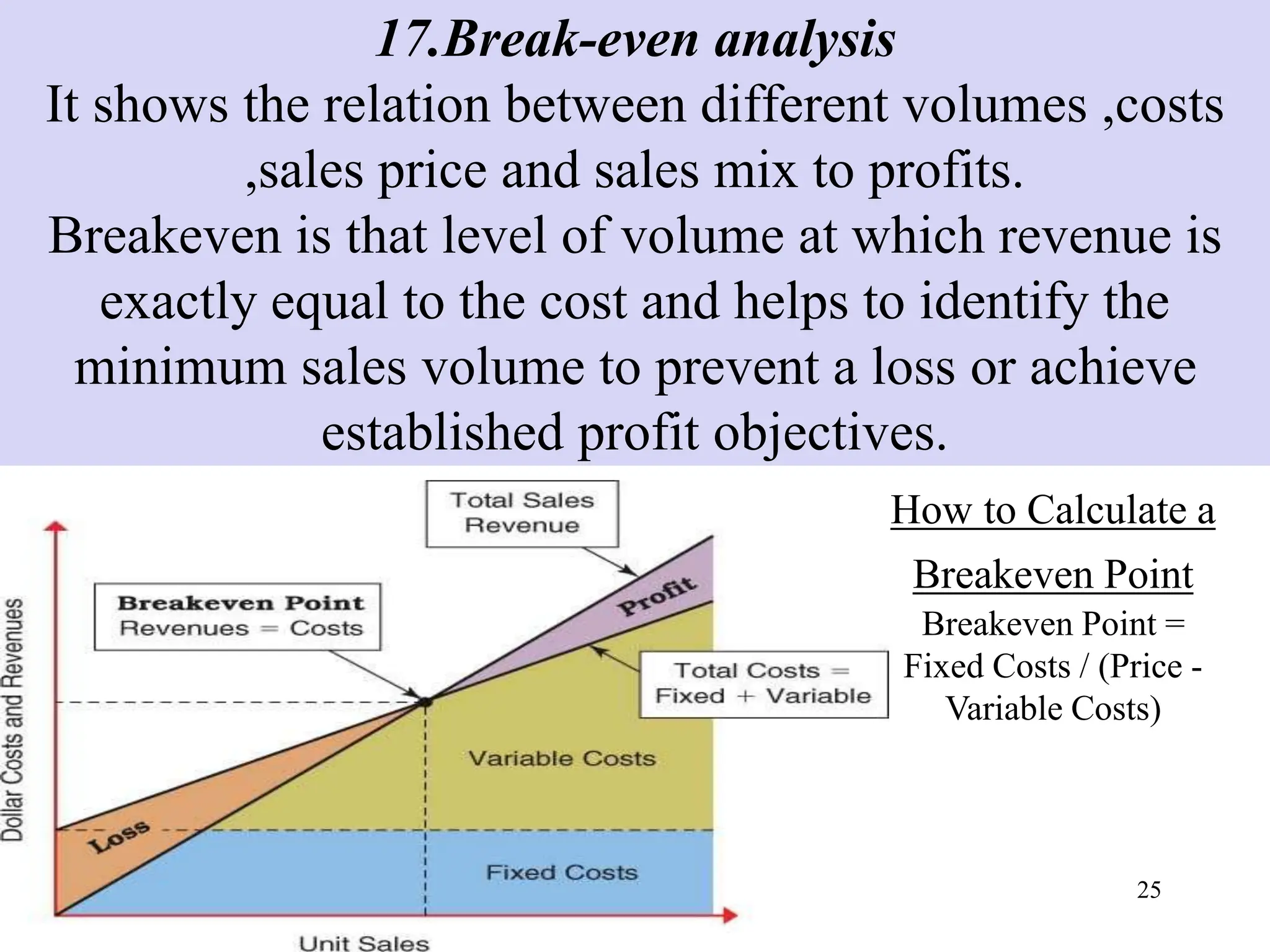
The document presents an overview of control systems and techniques used in management, highlighting the importance of measuring performance against standards and objectives. It details various control techniques, including personal observation, records, policies, disciplinary actions, and budgeting, as well as special techniques like standard costing and management information systems. Key characteristics of an effective control system are also outlined, emphasizing flexibility, accuracy, and a focus on results.