Angular2 with TypeScript
3 likes873 views
Basics of TypeScript Angular2 quick start guide Angular2 Services, Components, Modules, Navigation & Routing
1 of 60
Downloaded 31 times





































![Templates continued..
Let's write some code now
• Create a ToDoListComponent
• It will have 2 variables, todos list and a selectedTodo
• Bootstrap todo list
• Create a template todo-list-component.html
• Display a list of bootstrapped todos.
Hint: use directives option in AppComponent config
metadata to make it aware about ToDoListComponent.
directives: [TodoListComponent]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2withtypescript1-160730123733/85/Angular2-with-TypeScript-38-320.jpg)

![Templates continued..
Template Syntax
• Html
• Interpolations {{selectedTodo}}, {{2+2}}
• Template Expressions [property]="expression"
• Template Statements: responds to an even raised by
a binding target for ex (event)="statement"
• Binding Syntax: binding data value to and from the
data model.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2withtypescript1-160730123733/85/Angular2-with-TypeScript-40-320.jpg)
![Template Syntax continued..
Data Direction Syntax Binding Type
One-way
from data source
to view target
{{expression}}
[target] = "expression"
bind-target = "expression"
Interpolation
Property
Attribute
Class
Style
One-way
from view target
to data source
(target) = "statement"
on-target = "statement"
Event
Two-way [(target)] = "expression"
bindon-target = "expression"
Two-way
Binding types other than interpolation have a target name to the left of the equal
sign, either surrounded by punctuation ([], ()) or preceded by a prefix (bind-, on-,
bindon-).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2withtypescript1-160730123733/85/Angular2-with-TypeScript-41-320.jpg)




![Exercises
• Create a model class Todo with following fields
– Title of string type
– Priority of integer type
• Create a FormComponent
– It will have a list of todos
– A todo object to hold currently editing todo item
– A method to which add the todo item in the list
– Add a template which renders form. See screenshot on next
slide for reference.
Hint: use ngModel to bind form elements to component
variables. For eg [(ngModel)] = “currentTodo.title”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2withtypescript1-160730123733/85/Angular2-with-TypeScript-46-320.jpg)





![Exercises
● Create a TodoService which maintains a list of todo items.
● It will have a method to add a new Todo to the list.
● Inject TodoService in TodoListComponent and
TodoFormComponent.
● TodoListComponent will just render the list as a unordered
list. (ul > li)
● This list should be sorted by priority (high priority task first)
.
● TodoFormComponent will be responsible for rendering the
todo form and it will use service method to add todos in the
list.
Hint: use the following syntax to inject services while
bootstraping. bootstrap(AppComponent, [BackendService,
HeroService, Logger]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2withtypescript1-160730123733/85/Angular2-with-TypeScript-53-320.jpg)







Ad
Recommended
Angular2 with type script



Angular2 with type scriptRavi Mone Angular2 with Typescript,
NOTE : The content in the presentation was wrt the current version beta.14. May or may not valid when the version changes
Introduction to Angular2



Introduction to Angular2Ivan Matiishyn This document provides an introduction to Angular 2, including:
- Angular 2 is a JavaScript framework for building single-page applications that uses dependency injection, change detection, and components.
- TypeScript allows adding types to JavaScript for complex apps and is used extensively in Angular 2.
- The Angular 2 ecosystem utilizes decorators like @Component and @NgModule to define metadata for components and modules. Components also have lifecycle hooks.
- The document demonstrates how to set up an Angular 2 app using the Angular CLI, including creating modules, components, services, and bootstrapping the app. It compares the component architecture between Angular 1 and 2.
Introduction to Angular 2



Introduction to Angular 2Naveen Pete Slide deck presented during my session on "Introduction to Angular 2" at UNICOM DevCon 2016 conference on Thursday, Dec 1, 2016. The conference was at Mövenpick Hotel & Spa, Bengaluru.
Angular 2: core concepts



Angular 2: core conceptsCodemotion This document provides an overview of core Angular 2 concepts, including:
1) Angular 2 introduces components instead of controllers and uses a one-way data flow instead of $scope. It is also written in TypeScript.
2) Angular 2 has a new dependency injection system, improved performance, better mobile support, and server-side rendering capabilities compared to AngularJS 1.x.
3) Key concepts in Angular 2 include components, communication between components, dependency injection, and the component lifecycle. Change detection and zones are also discussed.
The evolution of Angular 2 @ AngularJS Munich Meetup #5



The evolution of Angular 2 @ AngularJS Munich Meetup #5Johannes Weber The evolution of Angular 2
Angular 1 was born in 2009. Since that a lot of web standards are born and supported by most of the browsers natively. So it's time to use the new possibilities. That's how Angular 2 started. It's not just a major update. It's a whole rewrite!
The key theme of this talk it to get an overview of Angular 2. I’ll walk you through what you need to know to stay up to date, explain the main concepts behind A2 and the current state.
It is rounded off with some practical suggestions on how to proceed today - to make the transition from Angular 1.x to Angular 2.x easier.
Original slides with animated gifs can be found here: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/122ptcLESkfSw8omK9ekG8FksD_zvegGrqOL2GR5PE80/edit?usp=sharing
Angular 2 - An Introduction



Angular 2 - An IntroductionNexThoughts Technologies The document discusses Angular 2, its components, templates, styles, and how to create and use child components. Angular 2 uses components instead of controllers, has unidirectional data flow, simplified services, and an easier learning curve compared to Angular 1. Components are directives with templates that make up Angular 2 apps. Templates contain HTML and styles define visual styles. Child components exist within parent components and communication between them can be achieved through input/output binding and events. Services are used to perform CRUD operations separately from components.
The productive developer guide to Angular 2



The productive developer guide to Angular 2Maurice De Beijer [MVP] This document provides an overview of Angular 2 and its main building blocks including modules, components, templates, data binding, directives, services, and routing. It discusses how Angular 2 differs from Angular 1 and is more opinionated. It also provides code examples for setting up the main module, creating components and templates, using dependency injection for services, and making HTTP requests from services.
Introduction to Angular 2



Introduction to Angular 2Knoldus Inc. AngularJS 1.3 is by far the best version of Angular available today. It was just released a few weeks ago. It's chock full of bug fixes, feature enhancements and performance improvements.
YouTube link: - https://youtu.be/bghVyCbxj6g
Angular 2 - The Next Framework



Angular 2 - The Next FrameworkCommit University Angular 2 is the next version of the AngularJS framework. It was released in 2016 after 2 years of development. Some key features of Angular 2 include optimized performance for both desktop and mobile applications, ahead of time compilation for faster loading, and native support for reactive programming. The document then provides examples of core Angular concepts like components, directives, services, dependency injection and change detection. It explains how Angular 2 applications are bootstrapped and discusses some of the internal workings like the change detection engine.
An introduction to Angular2 



An introduction to Angular2 Apptension This document provides an overview of Angular 2, including:
- Angular 2 is a rewrite of AngularJS and introduces many breaking changes.
- It uses Typescript as its language and compiles to plain JavaScript.
- Key concepts include components, templates, directives, dependency injection, and services.
- Components define views using templates, styles, and class logic. They can communicate via inputs and outputs.
- Directives add behavior to the existing DOM using selectors like elements, attributes, or classes.
Building Universal Applications with Angular 2



Building Universal Applications with Angular 2Minko Gechev Angular is one of the most popular frameworks for the development of Single-Page Applications (SPA). Recently Google announced its second major version, which brings some brand new ideas and improvements. For instance, Angular 2 is written in TypeScript, has much faster change detection and allows development of universal (isomorphic) applications.
In this talk we're going to introduce the motivation behind the new design decisions and the improvements in Angular 2. We'll take a look at the building blocks the framework provides for the development of professional single-page applications.
AngularJS2 / TypeScript / CLI



AngularJS2 / TypeScript / CLIDomenico Rutigliano Exploring AngularJS 2, TypeScript and the new AngularJS CLI, which simplifies the creation and deployment of web applications
Understanding Angular 2 - Shmuela Jacobs - Codemotion Milan 2016



Understanding Angular 2 - Shmuela Jacobs - Codemotion Milan 2016Codemotion Angular 2 is a complete rewrite of the AngularJS framework, which introduces new approaches and leverages the latest technologies. Simplifying and generalizing core concepts, the performance is improved and the range of capabilities is broadened. In this session Shmuela will help you understand the core concepts of Angular 2 apps: the component-based architecture, dependency injection, change detection, and more.
Migrating an application from Angular 1 to Angular 2 



Migrating an application from Angular 1 to Angular 2 Ross Dederer This document discusses migrating from Angular 1 to Angular 2. It provides an overview of Angular 2 including its modular and component-based architecture. It also discusses TypeScript and how it is used with Angular 2. The document then walks through migrating a sample Silverlight application to an equivalent Angular 2 application, covering converting the viewmodel to a component and porting the view. It emphasizes keeping a similar MVVM pattern and discusses new Angular 2 concepts like templates, metadata and bindings.
Angular2



Angular2Software Infrastructure This document provides an overview of Angular2 including what it is, when it was announced, key differences from Angular1, core concepts, change detection, and mobile support. Angular2 was announced in 2014, is written entirely in Typescript, and is designed from the ground up for mobile with a focus on memory efficiency. It introduces new concepts like components and dependency injection while removing controllers and scopes. Change detection is handled through zones and by each component. A demo of a task manager application is provided and upgrading from Angular1 is discussed.
Angular 2 Crash Course



Angular 2 Crash CourseElisha Kramer This presentation is dedicated to studying the fundamentals of Angular 2.
To follow along with the presentation, watch this 3-part YouTube Series here: http://bit.ly/2mnLZNz
You can also download Traversy's Spotify App here: http://bit.ly/2m1TxI3
Angular 2



Angular 2alinabiliashevych Angular 2 is a complete rewrite of AngularJS. It is component-based and focuses on better performance. An Angular 2 app is a tree of components. Components are declared using the @Component decorator and the app's routing is configured with the @RouteConfig decorator. The project structure separates the app into modules, components, services and tests. Data binding in Angular 2 allows for unidirectional and two-way binding between the template and component class.
Angular2



Angular2Gabi Costel Lapusneanu The document discusses Angular modules, directives, and components. Angular modules help organize an application into blocks of functionality using the @NgModule annotation. There are three types of directives - components, attribute directives, and structural directives. Components are a subset of directives that use the @Component annotation and define templates to specify elements and logic on a page. The metadata definitions for @NgModule, @Directive, and @Component are also described.
Introduction to angular 2



Introduction to angular 2Dor Moshe My lecturer to Front end developers guild meeting.
The presentation separated to two parts (~40 min + 50 min).
Angular2 - getting-ready 



Angular2 - getting-ready Nir Kaufman Presentation made for the NG-CONF Israel 2015
(http://ng-conf.co.il/)
Angular2 is just around the corner.. so, how can we prepare our angular 1.x code base to the migration?
An example project that come along with those slides available on Github (links inside)
Angular2 workshop



Angular2 workshopNir Kaufman This document outlines an agenda for an Angular2 workshop. The workshop will introduce Angular2 concepts and components, teach how to build an application using components, and cover routing and business logic. Attendees will build a restaurant ordering application to learn how to compose components, implement routing, create data models and services, and connect to backend servers. The workshop is broken into three parts - components, routing, and business logic. Attendees will work through building pieces of the application, with checkpoints provided to see working examples.
Angular 2: What's New?



Angular 2: What's New?jbandi Angular 2 is a rewrite of AngularJS for modern web development. It improves on AngularJS by being faster, easier to use and learn, and built on proven best practices. Some key differences include components replacing controllers, unidirectional data flow instead of two-way binding, and type-based dependency injection rather than naming. While the core concepts remain similar, the implementation in Angular 2 is cleaner. However, setting up a full Angular project can still be complicated due to dependencies on build tools and module bundling.
Angular 2... so can I use it now??



Angular 2... so can I use it now??Laurent Duveau Angular 2 is now in release candidate and can be used for new projects, though Angular 1 will still be supported for the next 1.5-2 years. There are two main approaches to upgrading an existing Angular 1 app to Angular 2: big bang, where the entire app is rewritten at once in Angular 2, or incremental, where individual components are upgraded one by one. Components and directives are now unified under the component model in Angular 2. TypeScript is recommended for Angular 2 development but not required, as JavaScript can also be used.
Commit University - Exploring Angular 2



Commit University - Exploring Angular 2Commit University Probabilmente il framework javascript più atteso di sempre, evoluzione di uno dei framework più longevi ed usati nello sviluppo front end. Si vedranno alcune delle novità introdotte e delle scelte radicali fatte da Google per la nuova versione di Angular
Async patterns in javascript



Async patterns in javascriptRan Wahle The document discusses various asynchronous patterns in JavaScript, including using events, callbacks with Socket.IO, promises, observables, iterators, generators, and async/await. It provides code examples for promise creation, using the Fetch API, ES2015 iterators, and TypeScript's async/await syntax. The presentation aims to demonstrate asynchronous patterns for event handling, promises, iterators/generators, and async/await in TypeScript and Angular 2.
Tech Webinar: Angular 2, Introduction to a new framework



Tech Webinar: Angular 2, Introduction to a new frameworkCodemotion Fabio Biondi e Matteo Ronchi ci presentano AngularJS 2, analizzando la nuova sintassi per la creazione di componenti che ora assumono un ruolo fondamentale all’interno del framework.
Iscriviti qui per partecipare ad altri Tech Webinar: http://goo.gl/iW81VD
Scrivici a [email protected]
Tw: @codemotionTR
Angular js 2



Angular js 2Ran Wahle AngularJs 2.0 introduces components as the fundamental building blocks, replacing directives. The presentation covers getting started with AngularJs 2.0, including dependencies, configuration, components, data binding, services, routing and migration from Angular 1. It emphasizes that Angular 2 is a rewrite built on newer standards to improve performance and reduce opinionation. Migration involves componentizing the application and using an upgrade adapter to support a hybrid Angular 1 and 2 app.
Adventures with Angular 2



Adventures with Angular 2Dragos Ionita My adventures with Angular2 from first install (BETA.3) to the official release. What made us decide to pick Angular 2 since its beta phase, why we didn't stop when we saw that it wasn't quite ok to work with beta versions, how we managed to keep our up up to date with version updates (sometimes even twice a week), how we rewrote our application several times and how we found solutions to most problems.
Angular 2.0



Angular 2.0THanekamp Slides from a Luminis Arnhem informative session, or "Brain upgrade" as we call them, about Angular 2.0.
Introduction to mongo db



Introduction to mongo dbRohit Bishnoi The document discusses MongoDB operations like inserting, finding, updating, and deleting documents. It provides examples of inserting documents with different data structures like arrays embedded documents. It also demonstrates various find operations with filters, projections, sorting, skipping, limiting results. Operations to count and get distinct values are also covered. The document concludes by discussing how Thoughtbuzz uses MongoDB to store heterogeneous social media data from different sources in a single collection to provide unified analytics without requiring joins.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Angular 2 - The Next Framework



Angular 2 - The Next FrameworkCommit University Angular 2 is the next version of the AngularJS framework. It was released in 2016 after 2 years of development. Some key features of Angular 2 include optimized performance for both desktop and mobile applications, ahead of time compilation for faster loading, and native support for reactive programming. The document then provides examples of core Angular concepts like components, directives, services, dependency injection and change detection. It explains how Angular 2 applications are bootstrapped and discusses some of the internal workings like the change detection engine.
An introduction to Angular2 



An introduction to Angular2 Apptension This document provides an overview of Angular 2, including:
- Angular 2 is a rewrite of AngularJS and introduces many breaking changes.
- It uses Typescript as its language and compiles to plain JavaScript.
- Key concepts include components, templates, directives, dependency injection, and services.
- Components define views using templates, styles, and class logic. They can communicate via inputs and outputs.
- Directives add behavior to the existing DOM using selectors like elements, attributes, or classes.
Building Universal Applications with Angular 2



Building Universal Applications with Angular 2Minko Gechev Angular is one of the most popular frameworks for the development of Single-Page Applications (SPA). Recently Google announced its second major version, which brings some brand new ideas and improvements. For instance, Angular 2 is written in TypeScript, has much faster change detection and allows development of universal (isomorphic) applications.
In this talk we're going to introduce the motivation behind the new design decisions and the improvements in Angular 2. We'll take a look at the building blocks the framework provides for the development of professional single-page applications.
AngularJS2 / TypeScript / CLI



AngularJS2 / TypeScript / CLIDomenico Rutigliano Exploring AngularJS 2, TypeScript and the new AngularJS CLI, which simplifies the creation and deployment of web applications
Understanding Angular 2 - Shmuela Jacobs - Codemotion Milan 2016



Understanding Angular 2 - Shmuela Jacobs - Codemotion Milan 2016Codemotion Angular 2 is a complete rewrite of the AngularJS framework, which introduces new approaches and leverages the latest technologies. Simplifying and generalizing core concepts, the performance is improved and the range of capabilities is broadened. In this session Shmuela will help you understand the core concepts of Angular 2 apps: the component-based architecture, dependency injection, change detection, and more.
Migrating an application from Angular 1 to Angular 2 



Migrating an application from Angular 1 to Angular 2 Ross Dederer This document discusses migrating from Angular 1 to Angular 2. It provides an overview of Angular 2 including its modular and component-based architecture. It also discusses TypeScript and how it is used with Angular 2. The document then walks through migrating a sample Silverlight application to an equivalent Angular 2 application, covering converting the viewmodel to a component and porting the view. It emphasizes keeping a similar MVVM pattern and discusses new Angular 2 concepts like templates, metadata and bindings.
Angular2



Angular2Software Infrastructure This document provides an overview of Angular2 including what it is, when it was announced, key differences from Angular1, core concepts, change detection, and mobile support. Angular2 was announced in 2014, is written entirely in Typescript, and is designed from the ground up for mobile with a focus on memory efficiency. It introduces new concepts like components and dependency injection while removing controllers and scopes. Change detection is handled through zones and by each component. A demo of a task manager application is provided and upgrading from Angular1 is discussed.
Angular 2 Crash Course



Angular 2 Crash CourseElisha Kramer This presentation is dedicated to studying the fundamentals of Angular 2.
To follow along with the presentation, watch this 3-part YouTube Series here: http://bit.ly/2mnLZNz
You can also download Traversy's Spotify App here: http://bit.ly/2m1TxI3
Angular 2



Angular 2alinabiliashevych Angular 2 is a complete rewrite of AngularJS. It is component-based and focuses on better performance. An Angular 2 app is a tree of components. Components are declared using the @Component decorator and the app's routing is configured with the @RouteConfig decorator. The project structure separates the app into modules, components, services and tests. Data binding in Angular 2 allows for unidirectional and two-way binding between the template and component class.
Angular2



Angular2Gabi Costel Lapusneanu The document discusses Angular modules, directives, and components. Angular modules help organize an application into blocks of functionality using the @NgModule annotation. There are three types of directives - components, attribute directives, and structural directives. Components are a subset of directives that use the @Component annotation and define templates to specify elements and logic on a page. The metadata definitions for @NgModule, @Directive, and @Component are also described.
Introduction to angular 2



Introduction to angular 2Dor Moshe My lecturer to Front end developers guild meeting.
The presentation separated to two parts (~40 min + 50 min).
Angular2 - getting-ready 



Angular2 - getting-ready Nir Kaufman Presentation made for the NG-CONF Israel 2015
(http://ng-conf.co.il/)
Angular2 is just around the corner.. so, how can we prepare our angular 1.x code base to the migration?
An example project that come along with those slides available on Github (links inside)
Angular2 workshop



Angular2 workshopNir Kaufman This document outlines an agenda for an Angular2 workshop. The workshop will introduce Angular2 concepts and components, teach how to build an application using components, and cover routing and business logic. Attendees will build a restaurant ordering application to learn how to compose components, implement routing, create data models and services, and connect to backend servers. The workshop is broken into three parts - components, routing, and business logic. Attendees will work through building pieces of the application, with checkpoints provided to see working examples.
Angular 2: What's New?



Angular 2: What's New?jbandi Angular 2 is a rewrite of AngularJS for modern web development. It improves on AngularJS by being faster, easier to use and learn, and built on proven best practices. Some key differences include components replacing controllers, unidirectional data flow instead of two-way binding, and type-based dependency injection rather than naming. While the core concepts remain similar, the implementation in Angular 2 is cleaner. However, setting up a full Angular project can still be complicated due to dependencies on build tools and module bundling.
Angular 2... so can I use it now??



Angular 2... so can I use it now??Laurent Duveau Angular 2 is now in release candidate and can be used for new projects, though Angular 1 will still be supported for the next 1.5-2 years. There are two main approaches to upgrading an existing Angular 1 app to Angular 2: big bang, where the entire app is rewritten at once in Angular 2, or incremental, where individual components are upgraded one by one. Components and directives are now unified under the component model in Angular 2. TypeScript is recommended for Angular 2 development but not required, as JavaScript can also be used.
Commit University - Exploring Angular 2



Commit University - Exploring Angular 2Commit University Probabilmente il framework javascript più atteso di sempre, evoluzione di uno dei framework più longevi ed usati nello sviluppo front end. Si vedranno alcune delle novità introdotte e delle scelte radicali fatte da Google per la nuova versione di Angular
Async patterns in javascript



Async patterns in javascriptRan Wahle The document discusses various asynchronous patterns in JavaScript, including using events, callbacks with Socket.IO, promises, observables, iterators, generators, and async/await. It provides code examples for promise creation, using the Fetch API, ES2015 iterators, and TypeScript's async/await syntax. The presentation aims to demonstrate asynchronous patterns for event handling, promises, iterators/generators, and async/await in TypeScript and Angular 2.
Tech Webinar: Angular 2, Introduction to a new framework



Tech Webinar: Angular 2, Introduction to a new frameworkCodemotion Fabio Biondi e Matteo Ronchi ci presentano AngularJS 2, analizzando la nuova sintassi per la creazione di componenti che ora assumono un ruolo fondamentale all’interno del framework.
Iscriviti qui per partecipare ad altri Tech Webinar: http://goo.gl/iW81VD
Scrivici a [email protected]
Tw: @codemotionTR
Angular js 2



Angular js 2Ran Wahle AngularJs 2.0 introduces components as the fundamental building blocks, replacing directives. The presentation covers getting started with AngularJs 2.0, including dependencies, configuration, components, data binding, services, routing and migration from Angular 1. It emphasizes that Angular 2 is a rewrite built on newer standards to improve performance and reduce opinionation. Migration involves componentizing the application and using an upgrade adapter to support a hybrid Angular 1 and 2 app.
Adventures with Angular 2



Adventures with Angular 2Dragos Ionita My adventures with Angular2 from first install (BETA.3) to the official release. What made us decide to pick Angular 2 since its beta phase, why we didn't stop when we saw that it wasn't quite ok to work with beta versions, how we managed to keep our up up to date with version updates (sometimes even twice a week), how we rewrote our application several times and how we found solutions to most problems.
Viewers also liked (9)
Angular 2.0



Angular 2.0THanekamp Slides from a Luminis Arnhem informative session, or "Brain upgrade" as we call them, about Angular 2.0.
Introduction to mongo db



Introduction to mongo dbRohit Bishnoi The document discusses MongoDB operations like inserting, finding, updating, and deleting documents. It provides examples of inserting documents with different data structures like arrays embedded documents. It also demonstrates various find operations with filters, projections, sorting, skipping, limiting results. Operations to count and get distinct values are also covered. The document concludes by discussing how Thoughtbuzz uses MongoDB to store heterogeneous social media data from different sources in a single collection to provide unified analytics without requiring joins.
Angular2 rxjs



Angular2 rxjsChristoffer Noring 1. Rxjs provides a better way of handling asynchronous code through observables which are streams of values over time. Observables allow for cancellable, retryable operations and easy composition of different asynchronous sources.
2. Common Rxjs operators like map, filter, and flatMap allow transforming and combining observable streams. Operators make observables quite powerful for tasks like async logic, event handling, and API requests.
3. In Angular, observables are used extensively for tasks like HTTP requests, routing, and component communication. Key aspects are using async pipes for subscriptions and unsubscribing during lifecycle hooks. Rxjs greatly simplifies many common asynchronous patterns in Angular applications.
Angular js best practice



Angular js best practiceMatteo Scandolo Slide from the talk: "Angular js best practice - for Enterprise development and distributed Teams" at Angular Conf 2015 in Turin.
Angular redux



Angular reduxNir Kaufman Slides from the "Data flow architecture in angular2 with redux". Introduction to Redux, it's inspirations and implementation. Join the "AngularJS-IL" meetup group for more community events and workshops! (http://www.meetup.com/AngularJS-IL/events/229660127/)
Angular 2 Architecture (Bucharest 26/10/2016)



Angular 2 Architecture (Bucharest 26/10/2016)Eyal Vardi In this meetup Eyal Vardi will talk about Angular 2.0 architecture. The session will focus on the main parts of Angular 2.0:
Application Bootstrap
Angular Compiler
Hierarchical Injector
Component Lifecycle Hooks
Change Detector
Renderer
Dynamic component creation
Each part will be explained and analyzed. In some cases we will dive into Angular 2.0 source code. Our purpose is to list the Do's & Don’ts of Angular.
The session is mostly targeted for developers which already have some experience with Angular 2.0.
How Angular2 Can Improve Your AngularJS Apps Today!



How Angular2 Can Improve Your AngularJS Apps Today!Nir Kaufman Are you ready to migrate your Angular1 project to Angular2? through this slides you will discover some tips that can make your current application better and ready for future migration. A link for reference project can be found inside.
Angular 2 Architecture



Angular 2 ArchitectureEyal Vardi In this meetup Eyal Vardi will talk about Angular 2.0 architecture. The session will focus on the main parts of Angular 2.0:
Application Bootstrap
Angular Compiler
Hierarchical Injector
Component Lifecycle Hooks
Change Detector
Renderer
Angular 2.0 & jQuery
Dynamic component creation
Tips & Tricks
Each part will be explained and analyzed. In some cases we will dive into Angular 2.0 source code. Our purpose is to list the Do's & Don’ts of Angular.
The session is mostly targeted for developers which already have some experience with Angular 2.0.
El barco



El barcodaniel2997 El documento describe diferentes tipos de embarcaciones a vela utilizadas entre los siglos XII y XV, como las carracas, carabelas y galeones. Luego discute el paso a la era del vapor en el siglo XIX, con la introducción de máquinas de vapor y cascos de hierro. Finalmente, brinda detalles sobre el desarrollo del submarino, incluido el primer diseño submarino de David Bushnell en 1776.
Ad
Similar to Angular2 with TypeScript (20)
Angular 2 overview in 60 minutes



Angular 2 overview in 60 minutesLoiane Groner This document provides an overview of Angular 2 including:
- Main blocks like components, directives, services, routing etc.
- How to set up a development environment with Node.js and TypeScript
- Examples of core features like data binding, communication between components, dependency injection, and HTTP requests
- Tips for organizing projects, lazy loading modules, ahead of time compilation, and using the Angular CLI
An afternoon with angular 2



An afternoon with angular 2Mike Melusky This document summarizes a presentation about Angular 2 given by Michael Melusky. The presentation covered introductions to Angular 2, TypeScript, components, data binding, communication between components, routing, directives, pipes, services, and integrating Firebase. It provided overviews and examples of key Angular 2 concepts like components, data binding, dependency injection, and services. It also explained how to set up an Angular 2 project using the Angular CLI and TypeScript basics.
17612235.ppt



17612235.pptyovixi5669 Angular is a platform for building web applications using Typescript. It helps structure code and remove trivial code. Angular applications are built with modules that organize functionality. The root module is AppModule. Components control views and interact with templates. Data binding in templates allows communication between components. Directives alter DOM. Services contain business logic rather than components. Dependency injection provides services to components. Routing uses routes to map URLs to components.
Foster - Getting started with Angular



Foster - Getting started with AngularMukundSonaiya1 The presentation helps to get started with Angular by explaining: - What is Typescript?
- What is Angular?
- Create Application
- Project Structure
- Building Blocks
- Modules
- Components
- Templates
- Directives
- Routing
The project code is available here: https://github.com/MukundSonaiya/angular-sessions
Fly High With Angular - How to build an app using Angular



Fly High With Angular - How to build an app using AngularVacation Labs This document provides an overview of Angular including getting started, prerequisites, architecture, components, data binding, directives, pipes, forms and validation. It discusses that Angular is an open-source front-end web application platform that provides structured front end code through components. It also summarizes how to generate an Angular project using the Angular CLI, basic component creation, common data binding techniques, directives like ngIf and ngFor, template-driven and reactive forms, and validation.
An evening with Angular 2



An evening with Angular 2Mike Melusky This document summarizes a presentation about Angular 2 given by Michael Melusky. The presentation covered introductions to Angular 2, TypeScript, components, data binding, communication between components, routing, directives, pipes and filters, services, and Firebase integration. It provided examples of TypeScript code, Angular components, data binding syntax, using directives like ngIf and ngFor, and creating services to avoid duplicating code between components. The speaker's goal was to give an overview of the core aspects of building applications with Angular 2.
Angular 9 



Angular 9 Raja Vishnu Presentation about new Angular 9.
It gives introduction about angular framework.
Provides information about why we use angular,
additional features and fixes from old versions. It will clearly explain how to create a new angular project and how to use angular commands and their usages.
It will also explain about the key components like angular architecture, routing, dependency injection etc.,
Angular



AngularVinod Kumar Kayartaya Angular is a JavaScript framework for building client-side web applications. It was created and is maintained by Google. Some key points:
- Angular uses components to build modular applications
- It utilizes TypeScript for type safety and features like classes and interfaces
- The framework emphasizes dependency injection, data binding, and directives
Angular



Angularkhoado2002 Angular is an open-source TypeScript-based front-end web application platform maintained by Google. It uses MVC and dependency injection patterns. Key features include components, services, routing and calling remote services. Version 1 was released in 2009 as AngularJS and the latest version is Angular 5. It is used to build large web applications and sites like Google and Uber.
Angular 18 course for begineers and experienced



Angular 18 course for begineers and experiencedtejaswinimysoola short but yet complete ppt on angular
Angularjs2 presentation



Angularjs2 presentationdharisk The document provides an overview of Angular including:
- Angular is an open source JavaScript framework for building web applications in HTML and JavaScript. It provides services and objects to create applications faster.
- Typescript is a programming language that adds optional static typing to JavaScript. It compiles to JavaScript.
- Modules, components, templates, metadata, services, and routes are architectural concepts in Angular that define application structure and functionality.
- Components control views and consist of templates, classes, and metadata. Services provide shared functionality across modules. Routes enable navigation between views.
Angular js



Angular jsFelixits Get into the rewarding AngularJS domain
With AngularJS, developers need not worry about a host of programming languages, a basic proficiency in HTML and JavaScript is enough to get you started. No need to code extensively to enforce the MVC architecture of web app development. With AngularJS, little or no coding is required to implement MVC and keep your code clean and organized. With our engrossing and interactive learning session you will be able to build scalable and robust web applications. Get hands-on experience working with features like two-way data binding and dynamic templating in AngularJS.
Angular js



Angular jsFelixits Felix-IT System is a leading training and solutions company offering courses in Mobile Technologies like Apple iOS, Google Android Windows 8 and HTML5 & CSS3 Applications Development.We are a one-stop destination for fresh graduates and experienced IT enthusiasts, where robust and interactive training is provided with an assurance of job on successful completion of the course. Our experience in the Mobile domain is outstanding with a team of industry veterans. We have customized courses for individual students, experienced students and corporations to ensemble all requirements. We are a team of technology evangelists, trainers and veteran engineers who are working together to create great value applications to reach new benchmarks in the mobile application world through their strategic designs and innovative approach.
Angular2 + rxjs



Angular2 + rxjsChristoffer Noring This document provides an overview of Angular 2 and Rxjs. Some key points covered include:
- Angular 2 is backed by Google and designed to be faster and more memory efficient than Angular 1. It uses TypeScript and focuses on components.
- Bootstrapping, modules, directives, bindings and pipes work differently in Angular 2 compared to Angular 1 with fewer overall concepts.
- Observables and operators from Rxjs allow for asynchronous programming and composing asynchronous operations. Common operators like map, filter and flatMap are discussed.
- Services can be used to share data between components. Components follow a lifecycle with hooks like ngOnInit and ngOnDestroy.
-
Angularj2.0



Angularj2.0Mallikarjuna G D Introduction, history, component, modules, services, typescript, import, export, folder structure, advantages, routes
Building a TV show with Angular, Bootstrap, and Web Services



Building a TV show with Angular, Bootstrap, and Web ServicesDavid Giard Presentation on using Angular 2, TypeScript, BootStrap, and Web API to display metadata of online TV show.
Exploring Angular 2 - Episode 1



Exploring Angular 2 - Episode 1Ahmed Moawad The aim of these series is exploring Angular 2 and it's amazing features. with the simplest way and the meaningful examples and labs to be practiced. Good Luck in Exploring :D
Angular 2 introduction



Angular 2 introductionChristoffer Noring Template forms allow creating forms directly in the template using directives like ngModel. Reactive forms use FormBuilder to build forms programmatically and attach validators and value changes. Both approaches allow collecting and validating user input, and associating forms with models. Forms are a key part of many applications for user input and data collection.
Angular Project Report



Angular Project ReportKodexhub Deepanshu thanks Lovely Professional University for providing him the opportunity to complete a project on Angular 6. He learned a lot and is grateful for the experience. He also thanks his parents and friend for their help in finalizing the project within the limited timeframe. The document then provides summaries of key aspects of Angular 6, including its architecture which follows an MVC pattern, forms, data binding, pipes, services, routing, and modules.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Azure vs AWS Which Cloud Platform Is Best for Your Business in 2025



Azure vs AWS Which Cloud Platform Is Best for Your Business in 2025Infrassist Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Azure vs. AWS is a common comparison when businesses evaluate cloud platforms for performance, flexibility, and cost-efficiency.
Oracle Cloud and AI Specialization Program



Oracle Cloud and AI Specialization ProgramVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Oracle Cloud and AI Specialization Program
Domino IQ – What to Expect, First Steps and Use Cases



Domino IQ – What to Expect, First Steps and Use Casespanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/domino-iq-what-to-expect-first-steps-and-use-cases/
HCL Domino iQ Server – From Ideas Portal to implemented Feature. Discover what it is, what it isn’t, and explore the opportunities and challenges it presents.
Key Takeaways
- What are Large Language Models (LLMs) and how do they relate to Domino iQ
- Essential prerequisites for deploying Domino iQ Server
- Step-by-step instructions on setting up your Domino iQ Server
- Share and discuss thoughts and ideas to maximize the potential of Domino iQ
Creating an Accessible Future-How AI-powered Accessibility Testing is Shaping...



Creating an Accessible Future-How AI-powered Accessibility Testing is Shaping...Impelsys Inc. Web accessibility is a fundamental principle that strives to make the internet inclusive for all. According to the World Health Organization, over a billion people worldwide live with some form of disability. These individuals face significant challenges when navigating the digital landscape, making the quest for accessible web content more critical than ever.
Enter Artificial Intelligence (AI), a technological marvel with the potential to reshape the way we approach web accessibility. AI offers innovative solutions that can automate processes, enhance user experiences, and ultimately revolutionize web accessibility. In this blog post, we’ll explore how AI is making waves in the world of web accessibility.
Providing an OGC API Processes REST Interface for FME Flow



Providing an OGC API Processes REST Interface for FME FlowSafe Software This presentation will showcase an adapter for FME Flow that provides REST endpoints for FME Workspaces following the OGC API Processes specification. The implementation delivers robust, user-friendly API endpoints, including standardized methods for parameter provision. Additionally, it enhances security and user management by supporting OAuth2 authentication. Join us to discover how these advancements can elevate your enterprise integration workflows and ensure seamless, secure interactions with FME Flow.
Establish Visibility and Manage Risk in the Supply Chain with Anchore SBOM



Establish Visibility and Manage Risk in the Supply Chain with Anchore SBOMAnchore Over 70% of any given software application consumes open source software (most likely not even from the original source) and only 15% of organizations feel confident in their risk management practices.
With the newly announced Anchore SBOM feature, teams can start safely consuming OSS while mitigating security and compliance risks. Learn how to import SBOMs in industry-standard formats (SPDX, CycloneDX, Syft), validate their integrity, and proactively address vulnerabilities within your software ecosystem.
The State of Web3 Industry- Industry Report



The State of Web3 Industry- Industry ReportLiveplex Web3 is poised for mainstream integration by 2030, with decentralized applications potentially reaching billions of users through improved scalability, user-friendly wallets, and regulatory clarity. Many forecasts project trillions of dollars in tokenized assets by 2030 , integration of AI, IoT, and Web3 (e.g. autonomous agents and decentralized physical infrastructure), and the possible emergence of global interoperability standards. Key challenges going forward include ensuring security at scale, preserving decentralization principles under regulatory oversight, and demonstrating tangible consumer value to sustain adoption beyond speculative cycles.
Kubernetes Security Act Now Before It’s Too Late



Kubernetes Security Act Now Before It’s Too LateMichael Furman In today's cloud-native landscape, Kubernetes has become the de facto standard for orchestrating containerized applications, but its inherent complexity introduces unique security challenges. Are you one YAML away from disaster?
This presentation, "Kubernetes Security: Act Now Before It’s Too Late," is your essential guide to understanding and mitigating the critical security risks within your Kubernetes environments. This presentation dives deep into the OWASP Kubernetes Top Ten, providing actionable insights to harden your clusters.
We will cover:
The fundamental architecture of Kubernetes and why its security is paramount.
In-depth strategies for protecting your Kubernetes Control Plane, including kube-apiserver and etcd.
Crucial best practices for securing your workloads and nodes, covering topics like privileged containers, root filesystem security, and the essential role of Pod Security Admission.
Don't wait for a breach. Learn how to identify, prevent, and respond to Kubernetes security threats effectively.
It's time to act now before it's too late!
Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean account



Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean accountangelo60207 Prevent infrastructure costs from becoming a significant line item on your startup’s budget! Serial entrepreneur and software architect Angelo Mandato will share his experience with AWS Activate (startup credits from AWS) and knowledge on how to architect a lean and mean AWS account ideal for budget minded and bootstrapped startups. In this session you will learn how to manage a production ready AWS account capable of scaling as your startup grows for less than $100/month before credits. We will discuss AWS Budgets, Cost Explorer, architect priorities, and the importance of having flexible, optimized Infrastructure as Code. We will wrap everything up discussing opportunities where to save with AWS services such as S3, EC2, Load Balancers, Lambda Functions, RDS, and many others.
TimeSeries Machine Learning - PyData London 2025



TimeSeries Machine Learning - PyData London 2025Suyash Joshi Timeseries Machine Learning - forecasting and anomaly detection with InfluxDB
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...



Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...NTT DATA Technology & Innovation Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL?
(POSETTE: An Event for Postgres 2025)
June 11, 2025
Shinya Kato
NTT DATA Japan Corporation
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure AI Foundations



Oracle Cloud Infrastructure AI FoundationsVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Oracle Cloud Infrastructure AI Foundations
Enabling BIM / GIS integrations with Other Systems with FME



Enabling BIM / GIS integrations with Other Systems with FMESafe Software Jacobs has successfully utilized FME to tackle the complexities of integrating diverse data sources in a confidential $1 billion campus improvement project. The project aimed to create a comprehensive digital twin by merging Building Information Modeling (BIM) data, Construction Operations Building Information Exchange (COBie) data, and various other data sources into a unified Geographic Information System (GIS) platform. The challenge lay in the disparate nature of these data sources, which were siloed and incompatible with each other, hindering efficient data management and decision-making processes.
To address this, Jacobs leveraged FME to automate the extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) of data between ArcGIS Indoors and IBM Maximo. This process ensured accurate transfer of maintainable asset and work order data, creating a comprehensive 2D and 3D representation of the campus for Facility Management. FME's server capabilities enabled real-time updates and synchronization between ArcGIS Indoors and Maximo, facilitating automatic updates of asset information and work orders. Additionally, Survey123 forms allowed field personnel to capture and submit data directly from their mobile devices, triggering FME workflows via webhooks for real-time data updates. This seamless integration has significantly enhanced data management, improved decision-making processes, and ensured data consistency across the project lifecycle.
PyData - Graph Theory for Multi-Agent Integration



PyData - Graph Theory for Multi-Agent Integrationbarqawicloud Graph theory is a well-known concept for algorithms and can be used to orchestrate the building of multi-model pipelines. By translating tasks and dependencies into a Directed Acyclic Graph, we can orchestrate diverse AI models, including NLP, vision, and recommendation capabilities. This tutorial provides a step-by-step approach to designing graph-based AI model pipelines, focusing on clinical use cases from the field.
Viral>Wondershare Filmora 14.5.18.12900 Crack Free Download



Viral>Wondershare Filmora 14.5.18.12900 Crack Free DownloadPuppy jhon ➡ 🌍📱👉COPY & PASTE LINK👉👉👉 ➤ ➤➤ https://drfiles.net/
Wondershare Filmora Crack is a user-friendly video editing software designed for both beginners and experienced users.
Developing Schemas with FME and Excel - Peak of Data & AI 2025



Developing Schemas with FME and Excel - Peak of Data & AI 2025Safe Software When working with other team members who may not know the Esri GIS platform or may not be database professionals; discussing schema development or changes can be difficult. I have been using Excel to help illustrate and discuss schema design/changes during meetings and it has proven a useful tool to help illustrate how a schema will be built. With just a few extra columns, that Excel file can be sent to FME to create new feature classes/tables. This presentation will go thru the steps needed to accomplish this task and provide some lessons learned and tips/tricks that I use to speed the process.
No-Code Workflows for CAD & 3D Data: Scaling AI-Driven Infrastructure



No-Code Workflows for CAD & 3D Data: Scaling AI-Driven InfrastructureSafe Software When projects depend on fast, reliable spatial data, every minute counts.
AI Clearing needed a faster way to handle complex spatial data from drone surveys, CAD designs and 3D project models across construction sites. With FME Form, they built no-code workflows to clean, convert, integrate, and validate dozens of data formats – cutting analysis time from 5 hours to just 30 minutes.
Join us, our partner Globema, and customer AI Clearing to see how they:
-Automate processing of 2D, 3D, drone, spatial, and non-spatial data
-Analyze construction progress 10x faster and with fewer errors
-Handle diverse formats like DWG, KML, SHP, and PDF with ease
-Scale their workflows for international projects in solar, roads, and pipelines
If you work with complex data, join us to learn how to optimize your own processes and transform your results with FME.
Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean account J...



Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean account J...angelo60207 Prevent infrastructure costs from becoming a significant line item on your startup’s budget! Serial entrepreneur and software architect Angelo Mandato will share his experience with AWS Activate (startup credits from AWS) and knowledge on how to architect a lean and mean AWS account ideal for budget minded and bootstrapped startups. In this session you will learn how to manage a production ready AWS account capable of scaling as your startup grows for less than $100/month before credits. We will discuss AWS Budgets, Cost Explorer, architect priorities, and the importance of having flexible, optimized Infrastructure as Code. We will wrap everything up discussing opportunities where to save with AWS services such as S3, EC2, Load Balancers, Lambda Functions, RDS, and many others.
“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...



“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...Edge AI and Vision Alliance For the full video of this presentation, please visit: https://www.edge-ai-vision.com/2025/06/state-space-models-vs-transformers-for-ultra-low-power-edge-ai-a-presentation-from-brainchip/
Tony Lewis, Chief Technology Officer at BrainChip, presents the “State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit.
At the embedded edge, choices of language model architectures have profound implications on the ability to meet demanding performance, latency and energy efficiency requirements. In this presentation, Lewis contrasts state-space models (SSMs) with transformers for use in this constrained regime. While transformers rely on a read-write key-value cache, SSMs can be constructed as read-only architectures, enabling the use of novel memory types and reducing power consumption. Furthermore, SSMs require significantly fewer multiply-accumulate units—drastically reducing compute energy and chip area.
New techniques enable distillation-based migration from transformer models such as Llama to SSMs without major performance loss. In latency-sensitive applications, techniques such as precomputing input sequences allow SSMs to achieve sub-100 ms time-to-first-token, enabling real-time interactivity. Lewis presents a detailed side-by-side comparison of these architectures, outlining their trade-offs and opportunities at the extreme edge.
Azure vs AWS Which Cloud Platform Is Best for Your Business in 2025



Azure vs AWS Which Cloud Platform Is Best for Your Business in 2025Infrassist Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...



Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...NTT DATA Technology & Innovation
“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...



“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...Edge AI and Vision Alliance
Angular2 with TypeScript
- 1. -Rohit Kumar @rbdharnia -Manish Kapoor @kapoormanish_89 Angular2 with TypeScript
- 2. Agenda TypeScript • What is TypeScript • Installation • Hello World!! • Features • Demos – Types – Class – Inheritance – Interface Angular2 • Why angular 2? • Angular 2 quick start application • Angular 2 architecture • Navigation and Routing
- 6. TypeScript ○ Implements ECMA 6 Specification. ○ Has types(number, string, boolean, any) ○ Better Support for OOP(Classes, Interfaces, Inheritance, Enum) ○ Optional typing(Duck typing) ○ Functions(Optional parameters, default parameters) ○ Module System (Exporting & Importing modules) Features:
- 11. TypeScript Exercises!! 1. Hello World! 2. Create a method with multiple parameters. 3. Create a method with default parameters. 4. Create a method with optional parameters. 5. Create a class with name “Person” and fields ‘firstName’ and ‘lastName’. 6. Add a funtion print() in the class which prints firstName and secondName 7. Create a constructor. 8. Create another class Employee which extends Person 9. Add another field ‘employeeCode’ and method print() . This method should override the method of base class
- 13. Angular 2 Agenda • Why angular 2? • Angular 2 quick start application • Angular 2 architecture • Navigation and Routing
- 14. Why Angular2 • Simple, but Not Simplistic • Web component oriented architecture • Mobile First • Better Foundations (DI, Router, Components) • Speed & Performance • Productivity
- 15. Angular 2 Quick Start Step 1: Create and configure the project A. Create the project folder B. Add package definition and configuration files C. Install packages
- 16. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 17. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 18. No need to add configuration yourself, just clone and checkout to branch ‘master’. [email protected]:rohitbishnoi/angular2- quickstart.git
- 19. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 20. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 21. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 22. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 23. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 24. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 25. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 26. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 27. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 28. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 29. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 30. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 31. Angular 2 Quick Start
- 33. Architecture Overview 1. Modules a. Angular apps are modular b. Generally we assemble our application from many modules c. Block of code dedicated to a single purpose d. A module exports some value, typically a class. e. Modules are optional, but it is highly recommended.
- 34. Architecture Overview 2. Components a. A component controls a portion of screen, we could call it a view. b. We define components application logic inside a class. c. Class interacts with view through its API.
- 36. Architecture Overview 3. Templates a. We define a component's view with its companion template. b. A form of html that tells Angular how to render the component. c. Most of the time it looks like regular html … and then it get a bit strange. d. See the example on next page.
- 38. Templates continued.. Let's write some code now • Create a ToDoListComponent • It will have 2 variables, todos list and a selectedTodo • Bootstrap todo list • Create a template todo-list-component.html • Display a list of bootstrapped todos. Hint: use directives option in AppComponent config metadata to make it aware about ToDoListComponent. directives: [TodoListComponent]
- 39. Templates continued.. <li *ngFor="let todo of todos" (click)="selectTodo(todo)"> {{todo}} </li> What is *ngFor and (click) in above code snippet ?
- 40. Templates continued.. Template Syntax • Html • Interpolations {{selectedTodo}}, {{2+2}} • Template Expressions [property]="expression" • Template Statements: responds to an even raised by a binding target for ex (event)="statement" • Binding Syntax: binding data value to and from the data model.
- 41. Template Syntax continued.. Data Direction Syntax Binding Type One-way from data source to view target {{expression}} [target] = "expression" bind-target = "expression" Interpolation Property Attribute Class Style One-way from view target to data source (target) = "statement" on-target = "statement" Event Two-way [(target)] = "expression" bindon-target = "expression" Two-way Binding types other than interpolation have a target name to the left of the equal sign, either surrounded by punctuation ([], ()) or preceded by a prefix (bind-, on-, bindon-).
- 42. Templates syntax continued.. Template Syntax • Built-in directives – ngClass – ngStyle – *ngIf – *ngSwitch – *ngFor example *ngFor="let hero of heroes"
- 43. Architecture Overview 4. Metadata • Metadata tell angular how to process a class. • TodoListComponent was just a class until we tell angular about it. • We tell angular that TodoListComponent is a component by attaching some metadata to it. • We attached metadata using a decorator @Component
- 44. Metadata continued.. Here are a few of the possible @Component configuration options: • selector • templateUrl • directives • providers: what the hell is that now?
- 45. Architecture Overview 4. Data Binding • You already have some idea about it now.
- 46. Exercises • Create a model class Todo with following fields – Title of string type – Priority of integer type • Create a FormComponent – It will have a list of todos – A todo object to hold currently editing todo item – A method to which add the todo item in the list – Add a template which renders form. See screenshot on next slide for reference. Hint: use ngModel to bind form elements to component variables. For eg [(ngModel)] = “currentTodo.title”
- 47. Exercises
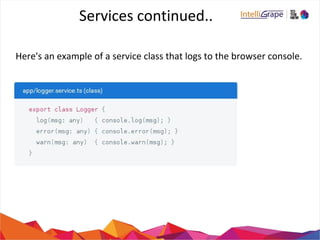
- 48. Architecture Overview 5. Services • Service is a broad category encompassing any value, function, or feature that our application needs. • A class with a narrow, well-defined purpose. It should do something specific and do it well. For example logging service, tax calculator. • There is nothing specifically Angular about services. Yet services are fundamental to any Angular application.
- 49. Services continued.. Here's an example of a service class that logs to the browser console.
- 50. Architecture Overview 5. Dependency Injection • Dependency injection is a way to supply a new instance of a class with the fully-formed dependencies it requires. Most dependencies are services. • Angular can tell which services a component needs by looking at the types of its constructor parameters. For example
- 51. Dependency Injection continued.. How it works: An injector maintains a container of service instances that it has previously created. If a requested service instance is not in the container, the injector makes one and adds it to the container before returning the service to Angular. When all requested services have been resolved and returned, Angular can call the component's constructor with those services as arguments. This is what we mean by dependency injection.
- 53. Exercises ● Create a TodoService which maintains a list of todo items. ● It will have a method to add a new Todo to the list. ● Inject TodoService in TodoListComponent and TodoFormComponent. ● TodoListComponent will just render the list as a unordered list. (ul > li) ● This list should be sorted by priority (high priority task first) . ● TodoFormComponent will be responsible for rendering the todo form and it will use service method to add todos in the list. Hint: use the following syntax to inject services while bootstraping. bootstrap(AppComponent, [BackendService, HeroService, Logger]);
- 54. Routing and Navigation ● The Angular Component Router enables navigation from one view to the next as users perform application tasks. ● Angular router is handling browser url change, forward and backward button clicks and link navigations. ● We can bind the router to links on a page and it will navigate to the appropriate application view when the user clicks a link.
- 55. Routing and Navigation Steps to configure the router ● Set the <base href="/"> in index.html ● Import ROUTER_DIRECTIVES in app component. ● Configure application routes, bootstrap application with an array of routes using the provideRouter function.
- 57. Routing and Navigation ● Register our router with bootstrap method, or inject it in bootstrap just like we do with services.
- 58. Routing and Navigation ● Add the Router Links and Router Outlet in applications AppComponent.
- 59. Routing and Navigation ● Add the Router Links and Router Outlet in applications AppComponent.
- 60. Resources • http://info.meteor.com/blog/comparing-performance-of-blaze-react-angular-meteor-and-angular-2-with- meteor • http://developer.telerik.com/featured/will-angular-2-be-a-success-you-bet/ • https://angular.io/docs/ts/latest/guide/lifecycle-hooks.html • https://angular.io/docs/ts/latest/guide/architecture.html • https://angular.io/docs/ts/latest/quickstart.html • https://angular.io/docs/ts/latest/guide/template-syntax.html • https://angular.io/docs/ts/latest/guide/router.html


