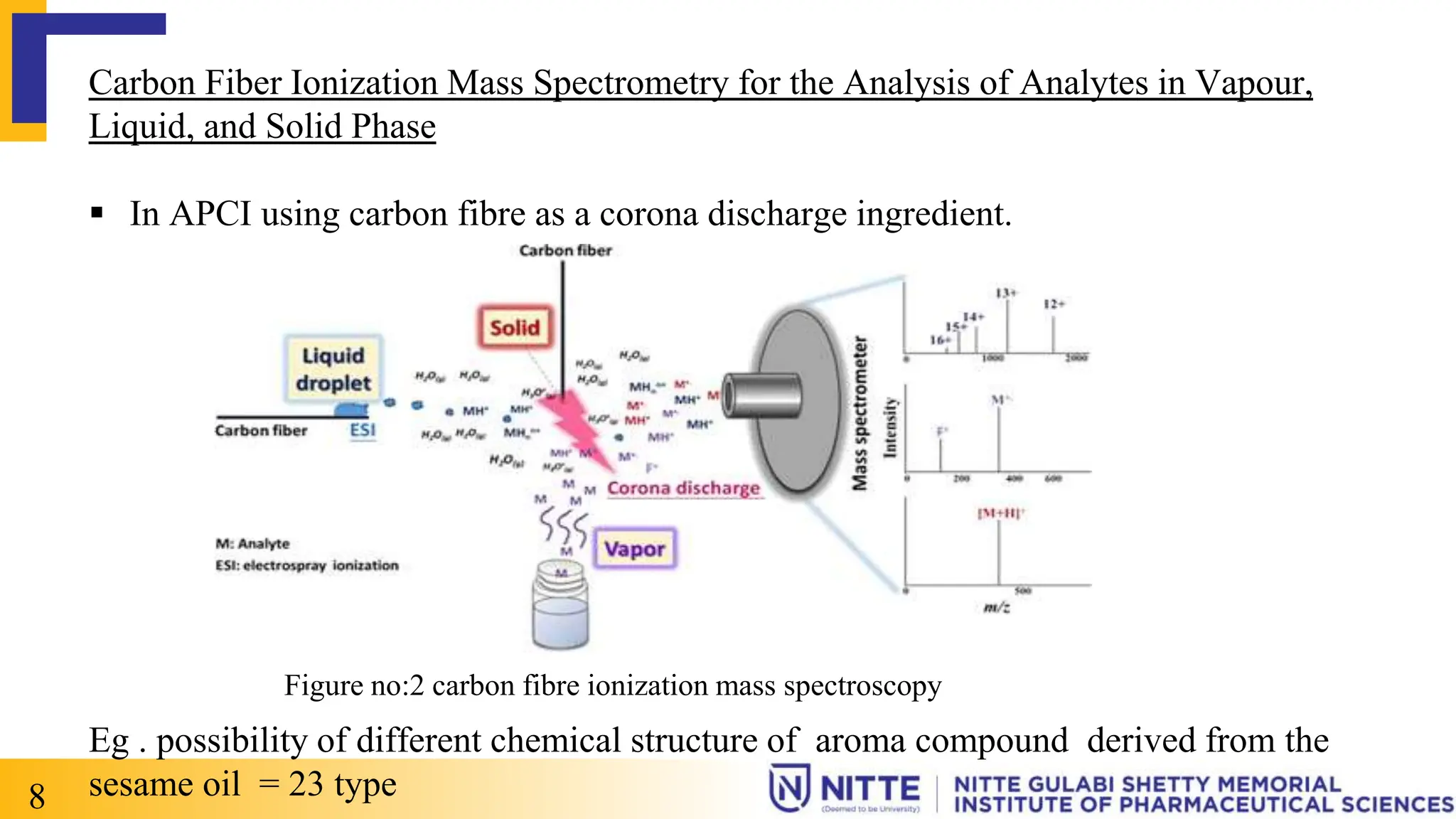
Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) is a soft ionization technique that uses corona discharge to ionize analyte molecules from a vapor. In APCI, the sample is vaporized and mixed with solvent vapor before entering the ionization source. The solvent vapor is ionized by corona discharge, and these ions then initiate gas-phase ion-molecule reactions with analyte molecules to form protonated or deprotonated molecular ions. APCI works well for moderately polar to non-polar compounds with molecular weights up to 1,500 Da, producing predominantly singly-charged ions. Applications include analysis of drugs, pesticides, and other small molecule compounds by LC-MS.