Basics of MongoDB
- 1. Aishwarya Kumar Singh Software Engineer Habilelabs.io Basics of MongoDB in Windows Environment http://www.habilelabs.io
- 2. CONTENTS What is MongoDB? What is NoSQL? How is NoSQL(MongoDB) different from conventional RDBMS? Why MongoDB is important? Key features of MongoDB How to install & run MongoDB? What we get in installation package? What is JSON JSON Example Basic SQL to MongoDB Terminology Comparison Major Datatypes in MongoDB What is ObjectID (_id)? Basic CRUD operations in MongoDB Important Query methods in MongoDB Important operators RDBMS Where clause equivalents in MongoDB Where MongoDB is best suited? Excellent MongoDB learning references
- 3. WHAT IS MONGODB? • MongoDB name comes from HuMONGOus data. • According to the official website of MongoDB it is defined in the following way – MongoDB is a document database with the scalability and flexibility that you want with the querying and indexing that you need. • It is a NoSQL Database. • It is Open source and free to use. • It is a cross-platform database which works with almost every platform (Windows, mac, Linux) . • It stores data in flexible, JSON like documents.
- 4. WHAT IS NOSQL? • The mechanism of storing and retrieving the data without using the conventional way of storage i.e., inside table. • The storage mechanism adapted here is the non relational form of data. • NoSQL databases are also sometimes referred as “Not Only SQL” • Structured Query Language (SQL) adapts the conventional methods of having relations and some proper schema but NoSQL is completely different and it follows no schema. • NoSQL databases are divided in the following parts: • Document databases: used to store semi-structured data as documents (MongoDB, ArangoDB, RethinkDB, CouchDB). Data is represented as a JSON document. • Graph stores: used to store the information about the network of the data (Neo4J, GraphBase, WhiteDB) • Key-value stores: Data is stored in the form of key-value pairs. They are the simplest NoSQL Databases (Redis, DynamoDB, Riak, Berkeley DB). • Wide-column stores: It uses tables, rows and columns but the names and formats of the columns can vary from row to row in the same table (Cassandra and HBase).
- 5. HOW NOSQL IS DIFFERENT FROM CONVENTIONAL RDBMS? • SQL databases are table based databases whereas NoSQL databases are document based, key-value pairs, graph databases or wide-column stores. • SQL databases have predefined schema whereas NoSQL databases have dynamic schema for unstructured data. • SQL databases are vertically scalable whereas the NoSQL databases are horizontally scalable. • SQL databases are not best suited for hierarchal data storage whereas NoSQL is best suited for it. RDBMS (SQL) NoSQL Base Table (rows and columns) Document, key-value pairs, graph and wide-column stores Schema Predefined Dynamic Scalability Vertical Horizontal Category Relational Non-relational or Distributed Big Data Preference Preferred Not preferred Complex Query Preference Preferred Not preferred Hierarchical Data Storage Preference Not preferred Preferred
- 6. WHY MONGODB IS IMPORTANT ? • MongoDB is important in many aspects and some of those major points are as follows: 1. It is document oriented and does not need the row and column format of the data. 2. It gives high performance. 3. It is dynamic in nature where you don’t need to predefine a schema like in conventional RDBMS. 4. There is no concept of Joins in MongoDB instead it has $lookup aggregation operator in versions >=3.2. There is a mongoose alternative as well which is called as populate() that is used to reference documents in other collections. 5. MongoDB stores data in JSON format which allows to send the data in whatever form you want.
- 7. KEY FEATURES OF MONGODB ? 1. Data is stored in BSON and presented in JSON. 2. Server-side JavaScript is supported (JavaScript expressions and functions). 3. Document oriented database where there are no tables and no row-based data. 4. NoSQL, where there is no schema. Documents can have different structures. Documents can be embedded. This is specifically designed for horizontal scaling. 5. By default, there is a primary key (_id), which is an auto-generated field for every document. 6. Sharding is supported which is very much essential for horizontal scaling and replication. 7. It has automatic load balancing configurations. 8. Fault Tolerance is natively built in MongoDB.
- 8. HOW TO INSTALL & RUN MONGODB ?
- 9. HOW TO INSTALL & RUN MONGODB ? • To install the MongoDB you need to visit the download section of the official website. Visit the following link: https://www.mongodb.com/download- center/community. Select the version, OS and the package there and then click download. • After download is completed double click the file (e.g.:- mongodb-win32-x86_64- 2008plus-ssl-3.4.5-signed.msi). This will start the installation. • Go through all the steps. Simply click next on each step and at the last step click on Finish button. This will install the MongoDB on your system. RUNNING THE MONGODB IN SYSTEM: • Create the folder C:datadb (In this case after creating the folder, you need to double click the mongod.exe file or just need to start the command line terminal and run the command mongod). To be continued…
- 10. HOW TO INSTALL & RUN MONGODB ? …in continuation • Alternatively you can create the folder at a different location and give its reference in mongo.config file. Then in mongo.bat file write the reference of the mongo.config file and run it whenever you want to start the mongodb server. • Mongo.config file has some other parameters which are described in the below image. • It comprises database path reference, log file path reference and port number reference. To be continued…
- 11. HOW TO INSTALL & RUN MONGODB ? …in continuation • The mongo.bat file will have a reference to mongo.config file. • The command written inside the mongo.bat file is: mongod -f mongo.config • It is shown in the below image. • This will allow the server to read the config file and refer the location of the database. • The default port that the mongodb server reads is 27017.
- 12. WHAT IS THERE IN INSTALLATION PACKAGE ? • MongoDB comes with handy tools which are bundled together at a single place. Those tools are as follows: 1. mongod: Mongo demon which is the server. 2. mongo: It is a CLI based client. 3. mongos: It is a mongodb sharing routing service(Used for sharding). 4. mongostat: It is used for monitoring the Quick Overview of the running instance. 5. mongotop: It is used for monitoring the Read and Write of an instance. NOTE: 1. To start the server we just need the mongod file. 2. For the ease of learning and exploring MongoDB, you can install any MongoDB GUI tool at this point (Robo 3T, QueryAssist, NoSQLBooster, Studio 3T, MongoDB Compass, Mongo Management Studio, NoSQL Manager, NoSQL Client, Navicat for MongoDB) …to be continued
- 13. WHAT IS THERE IN INSTALLATION PACKAGE ? …in continuation mongorestore: It loads data from the Binary DB dump. bsondump & mongodump: It creates binary dump. mongooplog: It is used for the purpose of the replication from the oplog. mongoexport & mongoimport: It is used to export or import files(generally JSON & CSV). mongoperf: It is used to check the Disk IO. mongofiles: It is basically used for GridFS functionality.
- 14. WHAT IS JSON? • Before proceeding any further you must know what is JSON as MongoDB data is always represented in the JSON format. So, here are some of the essential points related to JSON. 1. JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation. It is a collection of key-value pairs. Keys must be written inside single or double quotes. Values can have any data type (Array, string, Boolean etc.) 2. JSON file must start and end with a curly brace. 3. Collection of key-value pair Various languages recognize it as an object, record, struct, dictionary, hash table, keyed list, or associative array. 4. Object is surrounded by the curly braces and key-value pairs are separated by comma. 5. Array is surrounded by square braces and each value is separated with a comma. 6. Value can be of any type string, number, object, array, true, false, null
- 15. JSON EXAMPLE { “firstName”: “John”, “lastName”: “Doe”, “age”: 25, “address”: { “streetAddress”: “221B Bakers Street”, “city”: “London”, “state”: “ENG”, “postalCode”: “200001” }, } Notice here the key-value pair form of data that is embedded inside the curly braces.
- 16. BASIC SQL TO MONGODB TERMINOLOGY COMPARISON SQL MongoDB database database table collection row document or BSON document column field index index table joins $lookup, embedded documents primary key (need to specify column or combination of column) primary key (automatically set to _id field) aggregation aggregation pipeline MongoDB MySQL Oracle Informix DB2 Database Server mongod mysqld oracle IDS DB2 Server Database Client mongo mysql sqlplus DB-Access DB2 Client Database Executables Comparison: Terminology & Concept Comparison:
- 17. MAJOR DATATYPES IN MONGODB ? 1. String 2. Integer 3. Boolean 4. Double 5. Min/Max keys 6. Arrays 7. Timestamp 8. Object 9. Null 10. Symbol 11. Date 12. ObjectID 13. Binary data 14. Code 15. Regular expression
- 18. • ObjectId in the MongoDB is same as the primary key in the conventional RDBMS. • It is by default set by MongoDB for every document that is created inside any collection. • ObjectIds are small, unique, fast to generate and ordered. • ObjectId values comprises of a 12 bytes hexadecimal number which is unique for every document. • _id: ObjectId(4 bytes timestamp, 3 bytes machine id, 2 bytes process id, • 3 bytes counter) • "_id": ObjectId("5901832c91427cac52e9ea8f") WHAT IS objectId (_id) ?
- 19. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS • The basic operations in every database comprises of the following four operations: CREATE READ UPDATE DELETE • In MongoDB these four basic operations are achieved using the unique style of writing. But before actually starting with the data, you must first create a database. • In MongoDB, database is created using the use command. …to be continued
- 20. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS STARTING THE MONGODB INSTANCE IN THE TERMINAL 1. Go to the terminal and give the command mongo there so as to start the MongoDB CLI. • This will start the mongo instance in the terminal from where you can work on mongodb and fire queries. …to be continued
- 21. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS …in continuation CREATING THE DATABASE USING THE use COMMAND • Go to the terminal and write the command use <database_name> where database name will be replaced by the name of your database. This will create the database with the name which you want. • Alternatively it can be achieved by using any of the GUI tool and from there you can create the new database. But this GUI tool will first need to be connected to the host at the desired port number. …to be continued
- 22. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS The GUI tool which is shown above is QueryAssist You can Give a name to the instance from the tool. …to be continued
- 23. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS By this way you can create the database in MongoDB. Observe the note written in the Create Database Pop Up …to be continued
- 24. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS NOTE: You can ensure that your database has been created or not by using the show databases or show dbs command. The database will only appear when you have at least one collection inside it. To create a collection inside the recently created database, you must use the insert command: db.employee.insert({'name': 'John Doe', 'empId': 'HL0014’}); Now when you hit the show dbs or show databases command, it will show your database. …to be continued
- 25. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS DROPPING A DATABASE To drop a database in MongoDB you need to type the following command. db.dropDatabase() This will drop the selected database. If database is not selected then it will delete the default ‘test’ database. Now you can check through show dbs or show databases command, that your created database is dropped. You can clearly see in the picture that the habileMongo database is now not listed. It was dropped using the command above. …to be continued
- 26. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS For previous operation’s result to be visible, one must first create a collection inside it. So, let’s start with CRUD operations. CREATE For creating a collection use the following command db.createCollection(name, options) …to be continued Parameter Type Description Name String It is the name of the collection that is to be created Options Document Specifies option about the memory size and indexing. This is completely optional.
- 27. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS Options can have the following fields: …to be continued Field Type Description capped Boolean (Optional) If true, enables a capped collection. Capped collection is a fixed size collection that automatically overwrites its oldest entries when it reaches its maximum size. If you specify true, you need to specify size parameter also. autoIndexId Boolean (Optional) If true, automatically create index on _id fields. Default value is false. size number (Optional) Specifies a maximum size in bytes for a capped collection. If capped is true, then you need to specify this field also. max number (Optional) Specifies the maximum number of documents allowed in the capped collection.
- 28. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS EXAMPLE: 1. Without Options parameter – db.createCollection(‘Employees’); This will create the Employees collection. 2. With Options parameter db.createCollection(‘Employees’, {capped: true, autoIndexId: true, size: 6142800, max: 10000}); …to be continued
- 29. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS INSERT DOCUMENT For inserting the document in MongoDB collection, you need to write the following command: db.collection_name.insert(document) Where in place of collection name you can place your collection name. db.Employees.insert({‘name’: ‘John Doe’, ‘empId’: ‘HL0014’}) …to be continued
- 30. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS INSERT DOCUMENT To insert multiple documents inside a single query, you must pass an array of documents in the insert() command: db.Employees.insert([{'name': 'John Smith', 'empId': 'HL0015'},{'name': 'Dwane Simmons', 'empId': 'HL0016'}]); …to be continued
- 31. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS UPDATE For updating any document, an update() or save() method is used: db.Employees.update({'name': 'John Smith’},{$set:{'name': 'John Smith Carlos’}}); NOTE: By default mongodb will update only a single document. To update multiple documents , there is a need to set the ‘multi’ parameter to true. db.Employees.update({'name': 'John Smith’},{$set:{'name': 'John Smith Carlos’}}, {multi: true}); …to be continued
- 32. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS UPDATE Using save() method: Save method will replace the existing document with the new document passed in the save() method. db.Employees.save({"_id" : ObjectId("5bef7ca23a929140015e491f"),'name': 'John Smith Carlos', 'empId':'HL0017’}); NOTE: If Save method is used without _id, then it will update the document else it will insert a document. …to be continued
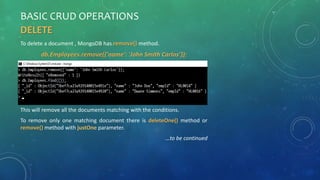
- 33. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS DELETE To delete a document , MongoDB has remove() method. db.Employees.remove({'name': 'John Smith Carlos’}); This will remove all the documents matching with the conditions. To remove only one matching document there is deleteOne() method or remove() method with justOne parameter. …to be continued
- 34. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS DELETE To delete a document , MongoDB has remove() method. db.Employees.deleteOne({'name': 'John Smith Carlos’}); The other way to delete single document is : use the findOne() method first to find the matching first document and then use remove() method. …to be continued
- 35. BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS DELETE This way you can remove a particular document from the collection. findOne() method searches all the data and returns the first matching document. You can pass the condition inside the findOne() method.m NOTE: If you don’t specify the deletion criteria (db.Employees.remove()), then it will delete all the documents inside the collection.
- 36. IMPORTANT PROJECTION & QUERY METHODS find() find() is the essential projection method which helps in selecting only the necessary data. db.Employees.find({}); findOne() This method returns the first matched document from the collection. You need to specify the condition inside the findOne() method. db.Employees.findOne({'name': 'John Smith Carlos’}); pretty() This method is used to display the text in the formatted way. …to be continued
- 37. IMPORTANT PROJECTION & QUERY METHODS distinct() distinct() is the essential method which helps in returning an array of documents that have distinct values for a specified field. db.Employees.distinct({‘name’}); isCapped() This method is used to check whether that collection is capped or not. db.Employees.isCapped(); It will return a Boolean value. If capped then true other wise false. limit() This method is used to limit the records in MongoDB. It accepts the number type argument. db.Employees.find({}).limit(2);
- 38. IMPORTANT PROJECTION & QUERY METHODS skip() This method is used to skip the number of documents. It accepts the number type argument. db.Employees.find({}).limit(1).skip(1); sort() This method is used to sort the documents in MongoDB. db.Employees.find({}).sort({‘name’: -1}); This will sort the document in descending order on the field name. …to be continued
- 39. IMPORTANT OPERATORS AND This is the operator used to query the data with AND relation. It will search the document satisfying the conditions that you pass in the query. db.Employees.find({$and: [{‘name’: ‘John Smith Carlos’}, {‘EmpId’: ‘HL0020’}]}); OR This operator is used to query the data with OR relation. It will search the document and return the result if any of the specified condition is fulfilled. db.Employees.find({$or: [{‘name’: ‘John Smith Carlos’}, {‘EmpId’: ‘HL0020’}]});
- 40. RDBMS WHERE CLAUSE EQUIVALENTS IN MONGODB Operation Syntax Example RDBMS Equivalent Equality {<key>:<value>} db.Employees.find({"name":"John Doe"}).pretty() where name = John Doe' Less Than {<key>:{$lt:<value>}} db.Employees.find({"salary":{$lt:20000}}). pretty() where salary < 20000 Less Than Equals {<key>:{$lte:<value>}} db.Employees.find({"salary":{$lte:20000}} ).pretty() where salary <= 20000 Greater Than {<key>:{$gt:<value>}} db.Employees.find({"salary":{$gt:20000}}) .pretty() where salary > 20000 Greater Than Equals {<key>:{$gte:<value>}} db.Employees.find({"salary":{$gte:20000}} ).pretty() where likes >= 20000 Not Equals {<key>:{$ne:<value>}} db.Employees.find({"salary":{$ne:20000}}) .pretty() where likes != 20000
- 41. WHERE MONGODB IS BEST SUITABLE? MongoDB is best suited for unstructured and semi-structured data such as: • Social media posts • Web pages • Emails • Medical records • Reports • Raw data from marketing researches • Scientific data
- 42. EXCELLENT MONGODB LEARNING REFERENCES • SQL to MongoDB mapping Chart https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/sql-comparison/ • What is NoSQL? https://www.mongodb.com/nosql-explained • MongoDB and MySQL Comparison https://www.mongodb.com/compare/mongodb-mysql • MongoDB Cheat Sheet https://blog.codecentric.de/files/2012/12/MongoDB-CheatSheet- v1_0.pdf • Organized Reference card – PDF file – Dzone https://dzone.com/refcardz/mongodb?chapter=1 …to be continued
- 43. EXCELLENT MONGODB LEARNING REFERENCES • Online Course Catalogue https://university.mongodb.com/courses/catalog • MongoDB resources – starter kit https://resources.mongodb.com/getting-started-with-mongodb • Brief Introduction to MongoDB by Eliot Horowitz (CTO & Co- founder of MongoDB) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EE8ZTQxa0AM
- 44. Habilelabs Pvt Ltd A premier software development company Contact Us [email protected] www.habilelabs.io FollowUs On LinkedIn






























![BASIC CRUD OPERATIONS
INSERT DOCUMENT
To insert multiple documents inside a single query, you must pass an
array of documents in the insert() command:
db.Employees.insert([{'name': 'John Smith', 'empId':
'HL0015'},{'name': 'Dwane Simmons', 'empId': 'HL0016'}]);
…to be continued](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofmongodb-181117131635/85/Basics-of-MongoDB-30-320.jpg)







![IMPORTANT OPERATORS
AND
This is the operator used to query the data with AND relation. It will
search the document satisfying the conditions that you pass in the
query.
db.Employees.find({$and: [{‘name’: ‘John Smith Carlos’},
{‘EmpId’: ‘HL0020’}]});
OR
This operator is used to query the data with OR relation. It will search
the document and return the result if any of the specified condition is
fulfilled.
db.Employees.find({$or: [{‘name’: ‘John Smith Carlos’}, {‘EmpId’:
‘HL0020’}]});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofmongodb-181117131635/85/Basics-of-MongoDB-39-320.jpg)

















































































