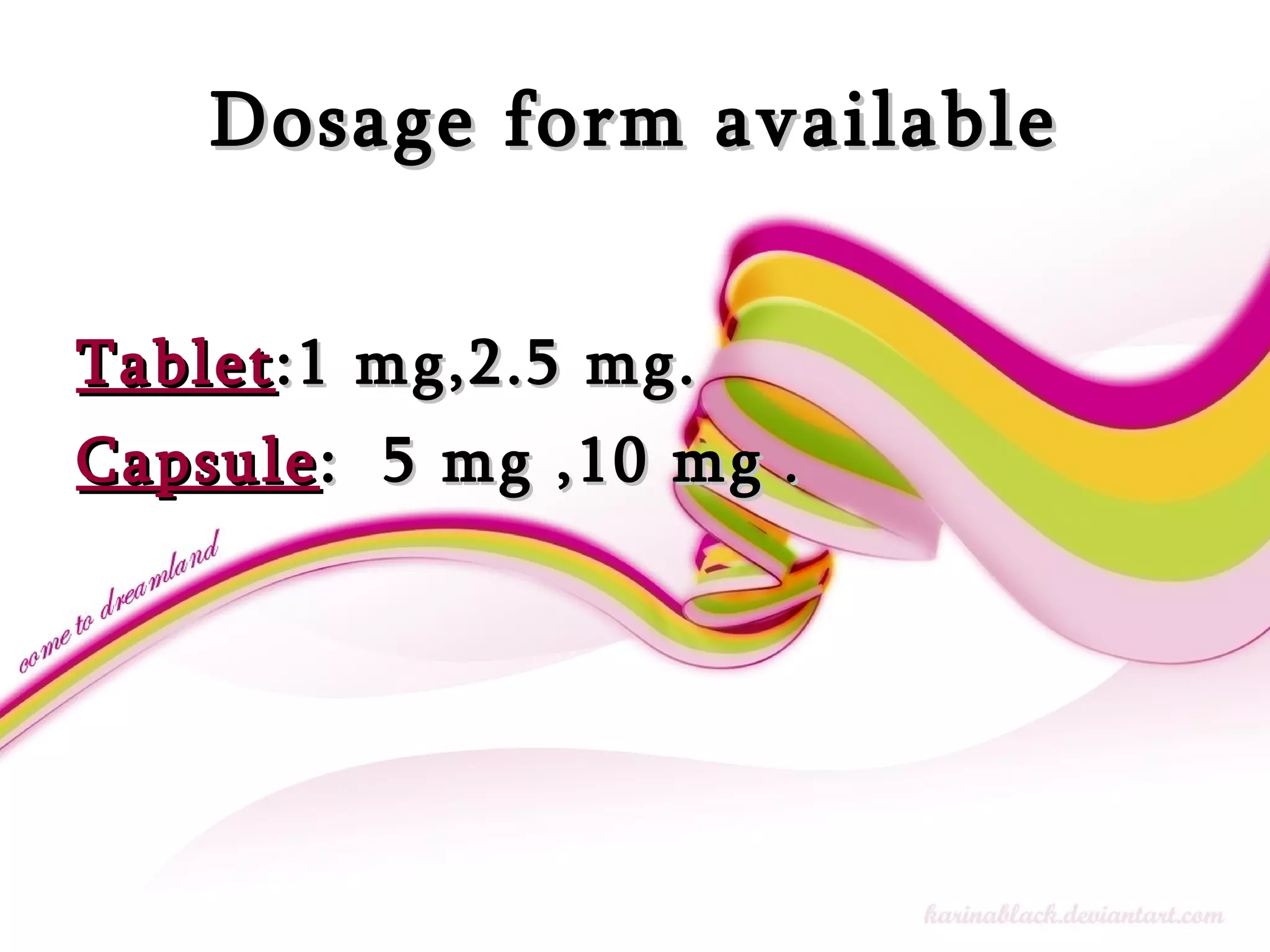
Bromocriptine is an antiparkinson and antidiabetic drug that works by stimulating dopamine receptors in the brain. It is also used to treat hyperprolactinemia and acromegaly. It has a rapid onset of around 1-2 hours, is highly protein bound, and primarily metabolized by the liver via CYP3A4 enzymes. Common side effects include dizziness, nausea, and hypotension. It can interact with other drugs that are CYP3A4 inhibitors or substrates, as well as ergot alkaloids, dopamine antagonists, and medications with vasoconstrictive effects. Initial dosing is usually at bedtime to reduce potential central nervous system side effects