C Programming Language Part 7
0 likes511 views
The document discusses functions in C programming. It defines a function as a block of code that performs a specific task. Some key points: - Functions allow breaking a program into smaller and reusable parts. The main() function is required in every C program. - Functions are declared with a return type, name, and parameters. They are defined with a block of code enclosed in curly braces. - Functions can be called from other functions and can call themselves recursively. However, a function cannot be defined within another function. - By default, C uses call-by-value to pass arguments to functions. This means changes to parameters do not affect the original arguments. Call-by-reference uses
1 of 23






















Ad
Recommended
C Programming Language Step by Step Part 2



C Programming Language Step by Step Part 2Rumman Ansari The document summarizes a simple "Hello World" program in C and explains its key parts. The program consists of a preprocessor command to include the stdio.h library, a main function where execution begins, and a printf statement to display "Hello World". It also describes how to save the code as a .c file, compile it using gcc to generate an executable, and run the executable to display the output.
C Programming Language Part 6



C Programming Language Part 6Rumman Ansari Loops allow code to be executed repeatedly. The main loop types are while, for, and do-while loops. While and do-while loops test the condition at the beginning or end of the loop respectively. For loops allow code to be executed a specific number of times. Loops can be nested by placing one loop inside another. Break and continue statements control the flow of loops. Break exits the current loop while continue skips to the next iteration. Though goto can provide unconditional jumps, its use is discouraged due to reducing code readability.
C Programming Language Part 4



C Programming Language Part 4Rumman Ansari The document discusses different types of operators in C programming language including arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, and assignment operators. It provides examples of each operator and their functions. Arithmetic operators are used to perform mathematical calculations. Relational operators compare values. Logical operators combine conditional statements. Bitwise operators work at the bit level on binary representations of numbers. Assignment operators assign values from right operands to left operands.
C Programming Language Part 9



C Programming Language Part 9Rumman Ansari The document contains 5 code snippets demonstrating the use of various C functions:
1) A program that calculates the sum of 1/n from n=1 to 10 using a cast to convert n to a float.
2) A program that gets a single character input and prints a message based on the input.
3) A program that tests if a character is a letter, digit or other character using isalpha and isdigit functions.
4) A program that converts a character to uppercase if lowercase and vice versa using islower, toupper, tolower.
5) A program that converts a character to lowercase if uppercase and vice versa using isupper, tolower, toupper.
C Programming Language Part 8



C Programming Language Part 8Rumman Ansari The document discusses arrays in C programming. It explains that arrays consist of contiguous memory locations and how to declare and initialize one-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays. It provides examples of accessing array elements, finding the sum and transpose of 2D arrays, and multiplying two matrices using nested for loops. The document is a reference for working with different types of arrays through examples of common array operations in C.
C Programming Language Step by Step Part 5



C Programming Language Step by Step Part 5Rumman Ansari The document discusses operators precedence and associativity in C programming language. It provides a table that lists C operators in order of precedence from highest to lowest. It also shows the associativity of each operator. The document then provides several code examples to demonstrate how operators precedence works in expressions evaluation in C.
C programming function



C programming functionargusacademy This document discusses user-defined functions in C programming. It provides examples of functions with and without parameters and return values. It also demonstrates call by value and call by reference methods. The key points covered are:
1) User-defined functions allow programmers to define reusable blocks of code to perform tasks.
2) Functions can receive input from parameters and return outputs through return values.
3) Parameters passed by value are copied into the function, so changes made inside the function do not affect the original variables.
4) Parameters passed by reference allow the function to modify the original variables.
1 introducing c language



1 introducing c languageMomenMostafa This document provides an overview of the C programming language course contents which includes data types, operators, control statements, functions, arrays, pointers, input/output and string functions. It also discusses the seven steps of programming, C strengths such as efficiency and portability, weaknesses like not being object-oriented, and provides simple C program examples and explanations.
Expressions using operator in c



Expressions using operator in cSaranya saran C provides various built-in operators to manipulate data and variables. These operators can be classified as arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment, conditional, and special operators. Arithmetic operators perform basic math operations like addition and subtraction. Relational operators compare values. Logical operators combine conditional statements. Bitwise operators perform manipulations at the bit level. Assignment operators assign values. Conditional operators provide an if-else statement in a single line. Precedence and associativity determine the order of evaluation for expressions containing multiple operators.
Decision making and branching



Decision making and branchingSaranya saran The document discusses different types of selection and looping structures in C programming such as if-else statements, switch statements, while loops, for loops, and nested loops. It provides syntax examples and sample code to demonstrate if-else ladders, nested if statements, while, do-while and for loops. Examples include calculating grades based on marks, finding roots of quadratic equations, Fibonacci series, swapping values and reversing numbers.
C Programming Language Part 11



C Programming Language Part 11Rumman Ansari The document provides information on strings in C programming language. It discusses that strings are arrays of characters terminated by a null character. It shows examples of declaring and initializing strings, reading strings from users, and printing strings. It also provides examples of using standard string functions like strcpy(), strcat(), strlen() etc. Further examples demonstrate finding frequency of characters in a string, counting vowels, consonants, digits and whitespaces, and removing non-alphabet characters from a string.
7 functions



7 functionsMomenMostafa The document discusses functions in C programming. It provides examples of defining functions with parameters and return types, calling functions by passing arguments, using header files to declare functions, and recursion. It shows functions being defined and called to perform tasks like calculating factorials, displaying prices based on hotel rates and nights, and converting numbers to binary. Functions allow breaking programs into smaller, reusable components.
How c program execute in c program 



How c program execute in c program Rumman Ansari The C program executes as follows:
1. A text editor is used to write the C program code and save it as a file with a .c extension.
2. A compiler converts the C source code into machine-readable object code.
3. The object code is executed by the CPU, which follows the program's instructions step-by-step to carry out the desired operations and output.
Introduction to Computer and Programing - Lecture 04



Introduction to Computer and Programing - Lecture 04hassaanciit Here are the errors in the given C statements:
(a) int = 314.562 * 150 ;
- Left side of = operator should be a variable name, not a data type.
(b) name = ‘Ajay’ ;
- ‘Ajay’ is a string, it needs to be enclosed in " " for a character variable or ' ' for a string variable.
(c) varchar = ‘3’ ;
- varchar is not a valid data type in C.
(d) 3.14 * r * r * h = vol_of_cyl ;
- Left side of = operator should be a variable name.
(e) k = ( a
Concepts of C [Module 2]![Concepts of C [Module 2]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/conceptsofcm2-p1-150416080853-conversion-gate02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Concepts of C [Module 2]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/conceptsofcm2-p1-150416080853-conversion-gate02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Concepts of C [Module 2]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/conceptsofcm2-p1-150416080853-conversion-gate02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Concepts of C [Module 2]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/conceptsofcm2-p1-150416080853-conversion-gate02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Concepts of C [Module 2]Abhishek Sinha It is an attempt to make the students of IT understand the basics of programming in C in a simple and easy way. Send your feedback for rectification/further development.
88 c-programs



88 c-programsLeandro Schenone This document is the table of contents for a book on C programming. It lists 88 example C programs that are intended to teach C concepts in an evolutionary manner. The programs cover basics like input/output, variables, data types, operators, loops, conditional statements, arrays, functions, pointers, structures, file I/O and more. The programs are presented from simplest to more complex to help programmers learn each new element of the C language.
Core programming in c



Core programming in cRahul Pandit This C program takes in an integer from the user and converts it to its binary equivalent. It uses bitwise operators like right shift and AND to extract each bit and check if it is 1 or 0. A loop shifts the number by 31, 30, 29 ... 1, 0 bits and ANDs it with 1 each time to extract the bits, printing 1 for each bit that is 1 and 0 for each bit that is 0, effectively converting the decimal number to its 32-bit binary representation.
Input output statement in C



Input output statement in CMuthuganesh S The document discusses input/output functions in C programming. It describes the scanf() function for input, which reads data from variables using format specifiers in a control string. It also describes printf() for output, which prints values to the screen using format specifiers. Additional functions getchar() and putchar() are discussed for reading and writing single characters respectively.
C lab-programs



C lab-programsTony Kurishingal 1. The document contains code for 8 programming experiments involving algorithms for calculating simple and compound interest, determining Armstrong and Fibonacci numbers, finding the roots of a quadratic equation, matrix operations, and sorting arrays.
2. The algorithms are presented step-by-step and the C code to implement each algorithm is included and commented.
3. Sample inputs and outputs are provided for each program to demonstrate its functionality.
Mesics lecture 5 input – output in ‘c’



Mesics lecture 5 input – output in ‘c’eShikshak 1. There are two main ways to handle input-output in C - formatted functions like printf() and scanf() which require format specifiers, and unformatted functions like getchar() and putchar() which work only with characters.
2. Formatted functions allow formatting of different data types like integers, floats, and strings. Unformatted functions only work with characters.
3. Common formatted functions include printf() for output and scanf() for input. printf() outputs data according to format specifiers, while scanf() reads input and stores it in variables based on specifiers.
Functions and pointers_unit_4



Functions and pointers_unit_4MKalpanaDevi The document discusses functions in C programming. It defines what a function is and explains why functions are used to avoid duplicating code and make programs easier to design, understand and maintain. It describes the different types of functions like pre-defined and user-defined functions. It also covers function prototypes, parameters, return values, recursion, library functions and pointers.
Simple c program



Simple c programRavi Singh This document contains 14 C program examples that print various pyramid patterns. The programs demonstrate basic C programming concepts like loops, conditional statements, functions and demonstrate printing patterns using characters, numbers or both. Each program includes the code, comments on purpose and author. The output displayed below each program code verifies the pattern printed. Overall the document serves as a learning resource for basic C programming and pattern printing techniques.
Programming in C [Module One]![Programming in C [Module One]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/programmingincchapterone-150312070001-conversion-gate01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Programming in C [Module One]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/programmingincchapterone-150312070001-conversion-gate01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Programming in C [Module One]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/programmingincchapterone-150312070001-conversion-gate01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Programming in C [Module One]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/programmingincchapterone-150312070001-conversion-gate01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Programming in C [Module One]Abhishek Sinha A step to fulfill the desire of the students who wish to learn Programming from scratch...
Chapter One - Concept of C
Practical write a c program to reverse a given number



Practical write a c program to reverse a given numberMainak Sasmal This document contains code snippets for various C programming problems and their solutions. Some of the problems addressed include:
1. Writing programs to reverse a number, check if a number is palindrome, and find the smallest of three numbers.
2. Programs to calculate the sum of a series, find the average of numbers, and count vowels and consonants in a string.
3. Additional examples show how to determine prime numbers, calculate the sum of a squared series, find the largest number in an array, and calculate factorials.
4. Other solutions demonstrate checking if a number is odd or even, determining if a character is a vowel, checking for a leap year, and calculating the highest common
Input And Output



Input And OutputGhaffar Khan The document discusses input and output functions in C programming. It describes getchar() and putchar() for character input/output, printf() and scanf() for formatted input/output, and gets() and puts() for string input/output. It provides examples of using these functions to read input from the keyboard and display output to the screen.
Input Output Management In C Programming



Input Output Management In C ProgrammingKamal Acharya This document discusses input/output functions in C programming, including printf() and scanf(). It explains how to use format specifiers like %d, %f, %s with printf() to output variables of different types. It also covers escape sequences like \n, \t that control formatting. Scanf() uses similar format specifiers to read input from the keyboard into variables. The document provides examples of using printf() and scanf() with different format specifiers and modifiers.
C programming



C programmingSamsil Arefin I am telling about basic c such as variable,constant,operators,decison making,loops,switch,break and continue,function,call by value ,call by reference and recursion.In this pdf i give some practice problems too.
week-10x



week-10xKITE www.kitecolleges.com The C program takes a binary number as input, finds its 2's complement by scanning from right to left and complementing all bits after the first 1, and prints the 2's complement as output. It first checks that the input is a valid binary number, then calls a complement() function that reverses the string, complements each bit, and handles carrying for adjacent bits.
C Programming Language Step by Step Part 1



C Programming Language Step by Step Part 1Rumman Ansari This document provides an overview of the C programming language. It discusses the history and development of C, starting with predecessors like ALGOL-60 and BCPL in the 1960s and 1970s. C was created in the early 1970s and the first C compiler was released in 1978. Since then, C has become widely used for system programming and is foundational to many other languages like C++ and Java. The document outlines some key advantages of C, like its efficiency and ability to handle low-level tasks. It also provides brief descriptions of common C programming concepts.
Introduction to Basic C programming 02



Introduction to Basic C programming 02Wingston This presentation offers complete basic users a simple guide to the C programming Language in a practical manner
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Expressions using operator in c



Expressions using operator in cSaranya saran C provides various built-in operators to manipulate data and variables. These operators can be classified as arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment, conditional, and special operators. Arithmetic operators perform basic math operations like addition and subtraction. Relational operators compare values. Logical operators combine conditional statements. Bitwise operators perform manipulations at the bit level. Assignment operators assign values. Conditional operators provide an if-else statement in a single line. Precedence and associativity determine the order of evaluation for expressions containing multiple operators.
Decision making and branching



Decision making and branchingSaranya saran The document discusses different types of selection and looping structures in C programming such as if-else statements, switch statements, while loops, for loops, and nested loops. It provides syntax examples and sample code to demonstrate if-else ladders, nested if statements, while, do-while and for loops. Examples include calculating grades based on marks, finding roots of quadratic equations, Fibonacci series, swapping values and reversing numbers.
C Programming Language Part 11



C Programming Language Part 11Rumman Ansari The document provides information on strings in C programming language. It discusses that strings are arrays of characters terminated by a null character. It shows examples of declaring and initializing strings, reading strings from users, and printing strings. It also provides examples of using standard string functions like strcpy(), strcat(), strlen() etc. Further examples demonstrate finding frequency of characters in a string, counting vowels, consonants, digits and whitespaces, and removing non-alphabet characters from a string.
7 functions



7 functionsMomenMostafa The document discusses functions in C programming. It provides examples of defining functions with parameters and return types, calling functions by passing arguments, using header files to declare functions, and recursion. It shows functions being defined and called to perform tasks like calculating factorials, displaying prices based on hotel rates and nights, and converting numbers to binary. Functions allow breaking programs into smaller, reusable components.
How c program execute in c program 



How c program execute in c program Rumman Ansari The C program executes as follows:
1. A text editor is used to write the C program code and save it as a file with a .c extension.
2. A compiler converts the C source code into machine-readable object code.
3. The object code is executed by the CPU, which follows the program's instructions step-by-step to carry out the desired operations and output.
Introduction to Computer and Programing - Lecture 04



Introduction to Computer and Programing - Lecture 04hassaanciit Here are the errors in the given C statements:
(a) int = 314.562 * 150 ;
- Left side of = operator should be a variable name, not a data type.
(b) name = ‘Ajay’ ;
- ‘Ajay’ is a string, it needs to be enclosed in " " for a character variable or ' ' for a string variable.
(c) varchar = ‘3’ ;
- varchar is not a valid data type in C.
(d) 3.14 * r * r * h = vol_of_cyl ;
- Left side of = operator should be a variable name.
(e) k = ( a
Concepts of C [Module 2]![Concepts of C [Module 2]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/conceptsofcm2-p1-150416080853-conversion-gate02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Concepts of C [Module 2]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/conceptsofcm2-p1-150416080853-conversion-gate02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Concepts of C [Module 2]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/conceptsofcm2-p1-150416080853-conversion-gate02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Concepts of C [Module 2]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/conceptsofcm2-p1-150416080853-conversion-gate02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Concepts of C [Module 2]Abhishek Sinha It is an attempt to make the students of IT understand the basics of programming in C in a simple and easy way. Send your feedback for rectification/further development.
88 c-programs



88 c-programsLeandro Schenone This document is the table of contents for a book on C programming. It lists 88 example C programs that are intended to teach C concepts in an evolutionary manner. The programs cover basics like input/output, variables, data types, operators, loops, conditional statements, arrays, functions, pointers, structures, file I/O and more. The programs are presented from simplest to more complex to help programmers learn each new element of the C language.
Core programming in c



Core programming in cRahul Pandit This C program takes in an integer from the user and converts it to its binary equivalent. It uses bitwise operators like right shift and AND to extract each bit and check if it is 1 or 0. A loop shifts the number by 31, 30, 29 ... 1, 0 bits and ANDs it with 1 each time to extract the bits, printing 1 for each bit that is 1 and 0 for each bit that is 0, effectively converting the decimal number to its 32-bit binary representation.
Input output statement in C



Input output statement in CMuthuganesh S The document discusses input/output functions in C programming. It describes the scanf() function for input, which reads data from variables using format specifiers in a control string. It also describes printf() for output, which prints values to the screen using format specifiers. Additional functions getchar() and putchar() are discussed for reading and writing single characters respectively.
C lab-programs



C lab-programsTony Kurishingal 1. The document contains code for 8 programming experiments involving algorithms for calculating simple and compound interest, determining Armstrong and Fibonacci numbers, finding the roots of a quadratic equation, matrix operations, and sorting arrays.
2. The algorithms are presented step-by-step and the C code to implement each algorithm is included and commented.
3. Sample inputs and outputs are provided for each program to demonstrate its functionality.
Mesics lecture 5 input – output in ‘c’



Mesics lecture 5 input – output in ‘c’eShikshak 1. There are two main ways to handle input-output in C - formatted functions like printf() and scanf() which require format specifiers, and unformatted functions like getchar() and putchar() which work only with characters.
2. Formatted functions allow formatting of different data types like integers, floats, and strings. Unformatted functions only work with characters.
3. Common formatted functions include printf() for output and scanf() for input. printf() outputs data according to format specifiers, while scanf() reads input and stores it in variables based on specifiers.
Functions and pointers_unit_4



Functions and pointers_unit_4MKalpanaDevi The document discusses functions in C programming. It defines what a function is and explains why functions are used to avoid duplicating code and make programs easier to design, understand and maintain. It describes the different types of functions like pre-defined and user-defined functions. It also covers function prototypes, parameters, return values, recursion, library functions and pointers.
Simple c program



Simple c programRavi Singh This document contains 14 C program examples that print various pyramid patterns. The programs demonstrate basic C programming concepts like loops, conditional statements, functions and demonstrate printing patterns using characters, numbers or both. Each program includes the code, comments on purpose and author. The output displayed below each program code verifies the pattern printed. Overall the document serves as a learning resource for basic C programming and pattern printing techniques.
Programming in C [Module One]![Programming in C [Module One]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/programmingincchapterone-150312070001-conversion-gate01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Programming in C [Module One]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/programmingincchapterone-150312070001-conversion-gate01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Programming in C [Module One]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/programmingincchapterone-150312070001-conversion-gate01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Programming in C [Module One]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/programmingincchapterone-150312070001-conversion-gate01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Programming in C [Module One]Abhishek Sinha A step to fulfill the desire of the students who wish to learn Programming from scratch...
Chapter One - Concept of C
Practical write a c program to reverse a given number



Practical write a c program to reverse a given numberMainak Sasmal This document contains code snippets for various C programming problems and their solutions. Some of the problems addressed include:
1. Writing programs to reverse a number, check if a number is palindrome, and find the smallest of three numbers.
2. Programs to calculate the sum of a series, find the average of numbers, and count vowels and consonants in a string.
3. Additional examples show how to determine prime numbers, calculate the sum of a squared series, find the largest number in an array, and calculate factorials.
4. Other solutions demonstrate checking if a number is odd or even, determining if a character is a vowel, checking for a leap year, and calculating the highest common
Input And Output



Input And OutputGhaffar Khan The document discusses input and output functions in C programming. It describes getchar() and putchar() for character input/output, printf() and scanf() for formatted input/output, and gets() and puts() for string input/output. It provides examples of using these functions to read input from the keyboard and display output to the screen.
Input Output Management In C Programming



Input Output Management In C ProgrammingKamal Acharya This document discusses input/output functions in C programming, including printf() and scanf(). It explains how to use format specifiers like %d, %f, %s with printf() to output variables of different types. It also covers escape sequences like \n, \t that control formatting. Scanf() uses similar format specifiers to read input from the keyboard into variables. The document provides examples of using printf() and scanf() with different format specifiers and modifiers.
C programming



C programmingSamsil Arefin I am telling about basic c such as variable,constant,operators,decison making,loops,switch,break and continue,function,call by value ,call by reference and recursion.In this pdf i give some practice problems too.
week-10x



week-10xKITE www.kitecolleges.com The C program takes a binary number as input, finds its 2's complement by scanning from right to left and complementing all bits after the first 1, and prints the 2's complement as output. It first checks that the input is a valid binary number, then calls a complement() function that reverses the string, complements each bit, and handles carrying for adjacent bits.
Viewers also liked (17)
C Programming Language Step by Step Part 1



C Programming Language Step by Step Part 1Rumman Ansari This document provides an overview of the C programming language. It discusses the history and development of C, starting with predecessors like ALGOL-60 and BCPL in the 1960s and 1970s. C was created in the early 1970s and the first C compiler was released in 1978. Since then, C has become widely used for system programming and is foundational to many other languages like C++ and Java. The document outlines some key advantages of C, like its efficiency and ability to handle low-level tasks. It also provides brief descriptions of common C programming concepts.
Introduction to Basic C programming 02



Introduction to Basic C programming 02Wingston This presentation offers complete basic users a simple guide to the C programming Language in a practical manner
C Programming Language Part 5



C Programming Language Part 5Rumman Ansari The document discusses operators precedence and associativity in C programming language. It provides a table that lists C operators in order of precedence from highest to lowest. It also shows the associativity of each operator. The document then provides several code examples to demonstrate how operators precedence works in expressions evaluation in C.
Basic c programming and explanation PPT1



Basic c programming and explanation PPT1Rumman Ansari This document provides an introduction to a basic C programming "Hello World" example and explanations of the code. It includes the short program which prints "Hello World" with comments explaining each line of code. It also explains key elements like including standard input/output, the main function, using printf to display output, and returning 0 at the end of the main function.
My first program in c, hello world !



My first program in c, hello world !Rumman Ansari The document discusses a simple "Hello World" C program. It includes the source code, which prints "Hello World" using the printf function. It explains that a C program consists of preprocessor commands, comments, functions, variables, and statements/expressions. It then breaks down the parts of the "Hello World" program, noting that #include is a preprocessor command that includes the stdio.h header file, main is the starting function, /*...*/ are comments, printf is a function that displays the message, and return 0 terminates main and returns a value of 0.
Medicaid organization profile



Medicaid organization profileAnurag Byala This document provides information about Medicaid Systems, an Indian company established in 1987 that designs, develops, and manufactures electrophysiology and neurodiagnosis medical equipment. The company has a annual turnover of $2.95 million, manufactures over 96 models of products, and has over 15,500 products sold, serving over 4,580 customers. It focuses on quality and continuous improvement through practices like Kaizen and has a young workforce of 73 employees across 10 locations in India.
C programming tutorial for beginners



C programming tutorial for beginnersThiyagarajan Soundhiran C was invented in 1972 by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Laboratories to implement the UNIX operating system. It is a structure oriented programming language. The C89/C90 and C99 standards were developed by the American National Standards Institute, with C99 introducing new features. C provides reliability, portability, flexibility, interactivity, and modularity. It is widely used to develop operating systems, databases, graphics packages, word processors, spreadsheets, and other applications. Embedded C is also used for features like fixed-point arithmetic and hardware addressing.
C tutorial



C tutorialChukka Nikhil Chakravarthy C language is a structured, procedural programming language developed in the early 1970s by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs. Some key points:
- C was created to develop the UNIX operating system and is still widely used for systems programming.
- Major features were derived from an earlier language called B.
- It is a middle-level language that provides low-level access to memory and hardware.
- C has been widely adopted and is one of the most popular and widely used languages, forming the basis for many other popular languages like C++ and Java. Areas where C is commonly used include operating systems, graphics applications, and compilers.
Steps for Developing a 'C' program



Steps for Developing a 'C' programSahithi Naraparaju The document outlines the three main stages of developing a C program: 1) Program design which includes problem analysis, outlining structure, algorithm development, and selecting control structures. 2) Program coding which should be readable and avoid complex logic. 3) Program testing which has two stages - human testing like code inspections, and computer-based testing using compilers and detecting run-time errors. The design stage establishes a foundation and strategy for writing the program to solve the problem. Coding then implements the design, and testing identifies any errors before the final program.
Introduction to programming with c,



Introduction to programming with c,Hossain Md Shakhawat Introduction to Programming, Introduction to C, Programming with C, How to Programming in C, Let us C
Programming in C Basics



Programming in C BasicsBharat Kalia This document provides an introduction and overview of the C programming language. It covers basic C concepts like data types, variables, operators, input/output, control flow, functions and pointers. It also compares C to Java and discusses similarities and differences between the two languages. The document is intended to teach basic C programming concepts.
Composicio Digital _Practica Pa4



Composicio Digital _Practica Pa4Marcos Baldovi En l'assignatura de Composició Digital s'estudien les tècniques que s'utilitzen en postproducció per als efectes visuals i efectes especials, per a la creació d'imatges complexes o en moviment, combinant imatges d'orígens diferents. El programari utilitzat és After Effects, Photoshop i Illustrator.
C programming basics



C programming basicsargusacademy The document discusses different programming paradigms like procedural, modular, and object-oriented programming. It also provides a brief history of the C language, noting it was developed in the 1970s and derived from B and BCPL. The document lists some features of C like it being a middle-level language, case-sensitive, using compilers, and teaching basic programming skills.
Aviation catalog



Aviation catalogclockworkalpha vintage park vintage park restaurants vintage engagement rings vintage pearl vintage clothing vintage air vintage dresses vintage wedding dresses vintage park apartments vintage car wash vintage park vintage park restaurants vintage engagement rings vintage pearl vintage clothing vintage air vintage dresses vintage wedding dresses vintage park apartments vintage car wash vintage air vintage apartments vintage airstream vintage ads vintage aprons vintage appliance company vintage arcade games
Ad
Similar to C Programming Language Part 7 (20)
Detailed concept of function in c programming



Detailed concept of function in c programminganjanasharma77573 Detailed concept of function in c programming
CH.4FUNCTIONS IN C (1).pptx



CH.4FUNCTIONS IN C (1).pptxsangeeta borde This document discusses functions in C programming. It defines a function as a self-contained block of statements that performs a specific task. Functions have a unique name, receive values from the calling program, may return a value, and are independent and reusable. There are two types of functions: predefined/standard library functions and user-defined functions. The document outlines the advantages of using functions and modular design. It also explains function declarations, definitions, parameters, scope, and how to define and call user-defined functions in C using both call-by-value and call-by-reference parameter passing.
CH.4FUNCTIONS IN C_FYBSC(CS).pptx



CH.4FUNCTIONS IN C_FYBSC(CS).pptxSangeetaBorde3 The shared ppt contains the syllabus for the C Programming subject Ch no 4-Functions in C. It is helpful for FYBSC(CS) students
UNIT3.pptx



UNIT3.pptxNagasaiT The document discusses C functions. Some key points:
1. Functions allow breaking code into reusable chunks that perform specific tasks. The main() function is required in every C program.
2. Functions are declared with a return type, name, and parameters. Definitions include the function body.
3. Standard library functions like strcat() and memcpy() are pre-defined for common tasks.
4. Functions are called by name and pass arguments by value or reference. Parameters allow customizing a function's behavior.
5. Recursion allows a function to call itself, enabling solutions to problems like factorials and Fibonacci sequences.
programlama fonksiyonlar c++ hjhjghjv jg



programlama fonksiyonlar c++ hjhjghjv jguleAmet jhhkj jhghjvjh yughjbhjnbhjgn ghjgjhvgcaisuriouorim easiopipo easpiiopiar easporiwporiopwiw wroprieowp rerwo eiwo ri eowpir riewporwir ewi ropw ieopirwopriaerwrjfpfj afdifjeio4 4tf oefjaaeriojfo eigjd vjeroit4ueriofnvdskfreiotjf refjoierfj fdiotu 54tigjkdvnerihnfv
C functions



C functionsUniversity of Potsdam A function is a group of statements that together perform a task. Every C program has at least one function, which is main(), and all the most trivial programs can define additional functions. You can divide up your code into separate functions.
Function (rule in programming)



Function (rule in programming)Unviersity of balochistan quetta Functions are blocks of code that perform specific tasks in C programs. There are two types of functions - standard functions that are predefined like main(), printf(), scanf(), and user-defined functions created by the programmer. Functions can take parameters, return values, or do both. Functions can be called by value, where the value of an argument is passed, or by reference, where the address of an argument is passed, allowing the function to modify the original variable. Functions improve modularity, reusability, and code organization in C programs.
Principals of Programming in CModule -5.pdfModule-3.pdf



Principals of Programming in CModule -5.pdfModule-3.pdfanilcsbs Principals of Programming in CModule -5.pdf
Functions struct&union



Functions struct&unionUMA PARAMESWARI There are two ways to initialize a structure:
1. Initialize structure members individually when declaring structure variables:
struct point {
int x;
int y;
} p1 = {1, 2};
2. Initialize an anonymous structure and assign it to a variable:
struct point p2 = {3, 4};
Structures allow grouping of related data types together under one name. They are useful for representing records, objects, and other data aggregates. Structures can contain nested structures as members. Arrays of structures are also possible. Structures provide data abstraction by allowing access to their members using dot operator.
Presentation on Function in C Programming



Presentation on Function in C ProgrammingShuvongkor Barman The document presents information about functions in the C programming language. It discusses what a C function is, the different types of C functions including library functions and user-defined functions. It provides examples of how to declare, define, call and pass arguments to C functions. Key points covered include how functions allow dividing a large program into smaller subprograms, the ability to call functions multiple times, and how functions improve readability, debugging and reusability of code. An example program demonstrates a simple C function that calculates the square of a number.
Functions in c language 



Functions in c language tanmaymodi4 what are functions in c
importance of function in c
uses of function in c
syantax of function in c
program of function in c
Functions in c language



Functions in c languageTanmay Modi Functions - C Programming
What is a Function? A function is combined of a block of code that can be called or used anywhere in the program by calling the name. ...
Function arguments. Functions are able to accept input parameters in the form of variables. ...
Function return values
unit3 part2 pcds function notes.pdf



unit3 part2 pcds function notes.pdfJAVVAJI VENKATA RAO A function is a block of code that performs a specific task. It takes input, processes it, and returns output. There are two types of functions: library functions provided by the C language, and user-defined functions created by the programmer. Functions allow programmers to divide a large program into smaller, separate, and reusable parts of code. Functions make code more organized and modular.
CHAPTER 6



CHAPTER 6mohd_mizan This document discusses different types of functions in C programming. It provides examples of functions with no arguments and no return value, functions with arguments and no return value, functions with arguments and return value, functions with no arguments but return value, and functions that return multiple values. The examples demonstrate how to define and call each type of function.
Functions



FunctionsPragnavi Erva Functions in C allow programmers to organize code into reusable blocks. A function performs a specific task and can optionally return a value. Functions make code easier to understand, share, and isolate errors. There are different types of functions including standard library functions and user-defined functions. Functions communicate through passing arguments, returning values, and pointers. Recursion involves a function calling itself to solve smaller instances of a problem.
4. function



4. functionShankar Gangaju Functions are self-contained blocks of code that perform specific tasks. There are library functions provided by the C standard and user-defined functions created by programmers. Functions make programs clearer and easier to debug by separating code into logical units. Functions can call themselves recursively to perform repetitive tasks. Functions are defined with a return type, name, and parameters, and code is passed between functions using call-by-value parameter passing. Function prototypes declare functions before they are used.
unit_2.pptx



unit_2.pptxVenkatesh Goud The document discusses functions in C programming. It defines a function as a block of code that performs a specific task. There are two types of functions: predefined standard library functions and user-defined functions. The key aspects of a function are its declaration, definition, and call. Functions can be used to break a large program into smaller, reusable components. Parameters can be passed to functions by value or by reference. Recursion is when a function calls itself, and is used in algorithms like calculating factorials. Dynamic memory allocation allows programs to request memory at runtime using functions like malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), and free().
Functions in C



Functions in CShobhit Upadhyay The document discusses key concepts related to functions in C programming including:
- Functions take input, perform operations, and return output. The main() function is required.
- Function prototypes declare a function's name, return type, and arguments before use.
- Function definitions specify the return type, name, arguments, and function body.
- Arguments are passed by value by default, but can be passed by reference using pointers.
- Recursive functions call themselves with different argument values until a base case is reached.
- Variables can have different scopes like global, file, local, and block depending on where they are declared. Static variables retain their value between function calls.
Unit_5Functionspptx__2022_12_27_10_47_17 (1).pptx



Unit_5Functionspptx__2022_12_27_10_47_17 (1).pptxvekariyakashyap The document discusses functions in C programming. It defines what a function is and explains that functions can be used to break a large program into smaller modular pieces of code that can be reused. The key points covered include: defining functions with return types, parameters, and bodies; declaring functions; calling functions by passing arguments; and passing arguments by value vs reference. Examples are provided to demonstrate creating, calling, and passing arguments to functions. Recursion is also discussed as a special case where a function calls itself.
Ad
More from Rumman Ansari (18)
Sql tutorial



Sql tutorialRumman Ansari This document provides an overview of SQL (Structured Query Language). It discusses that SQL is used to define, manipulate, and control data in a relational database. It can define database schemas, insert, modify, retrieve, and delete data from databases. The document also provides a brief history of SQL and describes its main components like DDL, DML, and DCL. It provides examples of common SQL commands and functions. Finally, it discusses SQL Plus which is a basic Oracle utility used to interact with databases through a command line interface.
C programming exercises and solutions 



C programming exercises and solutions Rumman Ansari This document provides a list of 40 programming exercises involving arrays and matrices in C. It begins with definitions and examples of one-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays. The exercises are then listed and involve operations like adding, subtracting, multiplying matrices; sorting, searching, merging arrays; and calculating properties of matrices like transposes, diagonals, determinants. The goal is to learn how to implement and use arrays and matrices in C programming.
Java Tutorial best website



Java Tutorial best websiteRumman Ansari This tutorial provides an introduction to Java programming for beginners. Java is an object-oriented programming language originally developed by Sun Microsystems. It allows programs to be run on many different platforms without needing to be rewritten. This tutorial explains the basic concepts of Java and is intended for students learning Java programming as part of their studies in fields like computer science, IT, or engineering. Prior experience with C or C++ is recommended to help understand Java's syntax and object-oriented features, which were influenced by those languages. The target audience includes students, those looking to transition to product-based companies, and anyone passionate about coding who wants to learn Java development.
Java Questions and Answers



Java Questions and AnswersRumman Ansari This document contains a series of multiple choice questions about Java language fundamentals. There are over 30 questions covering topics like data types, arrays, keywords, object oriented concepts, and more. Each question is followed by a link to view the answer on the www.atnyla.com website. The questions are intended as a practice test to evaluate knowledge of basic Java concepts.
servlet programming



servlet programmingRumman Ansari The document contains code for three servlet programs: HelloWorld servlet that prints "Hello world", EmailServlet that takes user email as input and prints it, and FactorialServlet that calculates and displays factorial of a given number. The servlet code is written in Java and interacts with HTML pages for input/output.
C program to write c program without using main function



C program to write c program without using main functionRumman Ansari This document discusses three ways to write a C program without using the main function.
The first way uses the #define preprocessor directive to replace "begin" with "main". The second way uses the ## token merging operator in a #define to merge the characters "m", "a", "i", and "n" together. The third way uses an argumented macro to define a function called "begin" that serves the same purpose as main.
Steps for c program execution



Steps for c program executionRumman Ansari The document outlines the basic steps for C program execution:
1. Creating the program using an IDE or text editor, compiling the program using a compiler, and linking it with necessary library functions.
2. The preprocessor performs text substitution before compilation. The compiler translates source code to machine code. The linker combines object files and libraries.
3. The loader loads the machine code into memory for execution by the CPU, which performs arithmetic and logical operations to run the program.
Pointer in c program



Pointer in c programRumman Ansari A pointer in C is a variable that stores the address of another variable. It allows a program to indirectly access the memory location that a variable is stored in. Pointers are declared with a * before the variable name. The & operator returns the address of its operand and is used to initialize a pointer variable. The * operator dereferences a pointer to access the value at the address it contains.
What is token c programming



What is token c programmingRumman Ansari Tokens are the basic building blocks of C language that are combined to write C programs. There are six types of tokens: keywords, identifiers, constants, strings, special symbols, and operators. A C program consists of various tokens, where a token can be a keyword, identifier, constant, string literal, special symbol, or operator. For example, the statement "printf("welcome here\n");" contains five tokens - printf, (, "welcome here\n", ), and ;.
What is identifier c programming



What is identifier c programmingRumman Ansari Identifiers are names given to variables, functions, and other user-defined items in a program to uniquely identify them. Identifiers must be different from keywords and other identifiers. They can include letters, digits, and underscores but must begin with a letter or underscore. Common examples of identifiers are variable and function names like roll_no and average. Identifiers are case-sensitive and allow programmers to reference specific program elements like variables during execution.
What is keyword in c programming



What is keyword in c programmingRumman Ansari Keywords are predefined reserved words in C that have special meanings and cannot be used as variable or constant names. Some common keywords include int, float, if, else, while, and return. Keywords are used to define variables and functions and control program flow. This document provides examples of how keywords like int and float declare variable types and return is used to exit a function. It also lists all the keywords allowed in the ANSI C standard.
Type casting in c programming



Type casting in c programmingRumman Ansari Type casting is converting a variable from one data type to another. It is done explicitly using a cast operator like (type_name). It is best to cast to a higher data type to avoid data loss as casting to a lower type may truncate the value. There are two types of casting in C - implicit casting which happens automatically during assignment, and explicit casting which requires a cast operator. Implicit casting is done when assigning a value to a compatible type while explicit casting is needed when types are incompatible.
C Programming Language Step by Step Part 3



C Programming Language Step by Step Part 3Rumman Ansari This document summarizes different data types in C including integer, floating point, character, and void types. It describes the storage size and value range for each type. It also provides examples of defining, initializing, and printing variables of each type. Constants and literals in C are also discussed along with two ways to define constants using the #define preprocessor or const keyword.
C Programming



C ProgrammingRumman Ansari The document contains code snippets and flowcharts for C programming problems including calculating the area of a triangle, finding the average of three numbers, checking if a number is less than 10, converting Celsius to Fahrenheit, solving a quadratic equation, checking if a year is a leap year, swapping values of two variables, adding and multiplying matrices, adding numbers, finding the largest of three numbers using arrays, printing numbers using do-while and while loops, finding the largest and smallest of three numbers, adding two numbers with call by value, evaluating factorial without and with recursion.
Tail recursion



Tail recursionRumman Ansari Tail recursion is when a recursive call is the last thing executed by a function. This allows the call stack to reuse stack frames rather than building up the call stack, avoiding stack overflow issues. A tail recursive function calculates results as it goes rather than waiting to return from recursive calls. This optimization makes tail recursive functions more efficient than regular recursive functions in terms of speed and memory usage.
Tail Recursion in data structure



Tail Recursion in data structureRumman Ansari Tail recursion is a type of recursion where the recursive call is the last thing executed by the function. This allows the compiler to optimize recursion by reusing the stack frame rather than allocating a new one for each recursive call. The key advantage is that tail recursive functions can process recursive problems of any size without overflowing the stack. Some examples show how a factorial function can be written iteratively using tail recursion, avoiding wasting memory on multiple stack frames.
Spyware manual



Spyware manualRumman Ansari This document discusses different types of spyware, how it works, and its impacts. It defines spyware as programs installed without permission that can monitor internet activity and send information to third parties. Spyware is classified into different categories like malware, adware, tracking cookies, and keyloggers that can steal personal data. The document traces the early history of the term spyware in 1995 and provides examples of well-known spyware programs like Gator and Cydoor. It also describes how spyware infects computers and the security risks to users, before discussing techniques to prevent spyware infections.
Linked list



Linked listRumman Ansari The document discusses the disadvantages of arrays and advantages of linked lists. Arrays are static structures that cannot be easily extended or reduced for the data set, and maintaining new insertions and deletions in arrays is expensive. Linked lists are dynamic data structures where each element is a separate object that can grow and shrink on demand. While linked lists allow for easier insertion and deletion and more efficient memory utilization compared to arrays, directly accessing individual elements requires traversing from the head, unlike arrays.
Recently uploaded (20)
Pruebas y Solucion de problemas empresariales en redes de Fibra Optica



Pruebas y Solucion de problemas empresariales en redes de Fibra OpticaOmarAlfredoDelCastil FLUKE
Pruebas y Solucion de problemas
empresariales en redes de Fibra Optica
Tesia Dobrydnia - A Leader In Her Industry



Tesia Dobrydnia - A Leader In Her IndustryTesia Dobrydnia Tesia Dobrydnia brings her many talents to her career as a chemical engineer in the oil and gas industry. With the same enthusiasm she puts into her work, she engages in hobbies and activities including watching movies and television shows, reading, backpacking, and snowboarding. She is a Relief Senior Engineer for Chevron and has been employed by the company since 2007. Tesia is considered a leader in her industry and is known to for her grasp of relief design standards.
MODULE 5 BUILDING PLANNING AND DESIGN SY BTECH ACOUSTICS SYSTEM IN BUILDING



MODULE 5 BUILDING PLANNING AND DESIGN SY BTECH ACOUSTICS SYSTEM IN BUILDINGDr. BASWESHWAR JIRWANKAR : Introduction to Acoustics & Green Building -
Absorption of sound, various materials, Sabine’s formula, optimum reverberation time, conditions for good acoustics Sound insulation:
Acceptable noise levels, noise prevention at its source, transmission of noise, Noise control-general considerations
Green Building: Concept, Principles, Materials, Characteristics, Applications
"The Enigmas of the Riemann Hypothesis" by Julio Chai



"The Enigmas of the Riemann Hypothesis" by Julio ChaiJulio Chai In the vast tapestry of the history of mathematics, where the brightest minds have woven with threads of logical reasoning and flash-es of intuition, the Riemann Hypothesis emerges as a mystery that chal-lenges the limits of human understanding. To grasp its origin and signif-icance, it is necessary to return to the dawn of a discipline that, like an incomplete map, sought to decipher the hidden patterns in numbers. This journey, comparable to an exploration into the unknown, takes us to a time when mathematicians were just beginning to glimpse order in the apparent chaos of prime numbers.
Centuries ago, when the ancient Greeks contemplated the stars and sought answers to the deepest questions in the sky, they also turned their attention to the mysteries of numbers. Pythagoras and his followers revered numbers as if they were divine entities, bearers of a universal harmony. Among them, prime numbers stood out as the cornerstones of an infinite cathedral—indivisible and enigmatic—hiding their ar-rangement beneath a veil of apparent randomness. Yet, their importance in building the edifice of number theory was already evident.
The Middle Ages, a period in which the light of knowledge flick-ered in rhythm with the storms of history, did not significantly advance this quest. It was the Renaissance that restored lost splendor to mathe-matical thought. In this context, great thinkers like Pierre de Fermat and Leonhard Euler took up the torch, illuminating the path toward a deeper understanding of prime numbers. Fermat, with his sharp intuition and ability to find patterns where others saw disorder, and Euler, whose overflowing genius connected number theory with other branches of mathematics, were the architects of a new era of exploration. Like build-ers designing a bridge over an unknown abyss, their contributions laid the groundwork for later discoveries.
9aeb2aae-3b85-47a5-9776-154883bbae57.pdf



9aeb2aae-3b85-47a5-9776-154883bbae57.pdfRishabhGupta578788 Certification of participation for the tata crucibal campus quiz 2024
Software Engineering Project Presentation Tanisha Tasnuva



Software Engineering Project Presentation Tanisha Tasnuvatanishatasnuva76 Software Engineering Presentation.
Air Filter Flat Sheet Media-Catalouge-Final.pdf



Air Filter Flat Sheet Media-Catalouge-Final.pdf FILTRATION ENGINEERING & CUNSULTANT This presentation provides a detailed overview of air filter testing equipment, including its types, working principles, and industrial applications. Learn about key performance indicators such as filtration efficiency, pressure drop, and particulate holding capacity. The slides highlight standard testing methods (e.g., ISO 16890, EN 1822, ASHRAE 52.2), equipment configurations (such as aerosol generators, particle counters, and test ducts), and the role of automation and data logging in modern systems. Ideal for engineers, quality assurance professionals, and researchers involved in HVAC, automotive, cleanroom, or industrial filtration systems.
Digital Crime – Substantive Criminal Law – General Conditions – Offenses – In...



Digital Crime – Substantive Criminal Law – General Conditions – Offenses – In...ManiMaran230751 Digital Crime – Substantive Criminal Law – General Conditions – Offenses – Investigation Methods for
Collecting Digital Evidence – International Cooperation to Collect Digital Evidence.
ISO 4020-6.1- Filter Cleanliness Test Rig Catalogue.pdf



ISO 4020-6.1- Filter Cleanliness Test Rig Catalogue.pdf FILTRATION ENGINEERING & CUNSULTANT ISO 4020-6.1 – Filter Cleanliness Test Rig: Precision Testing for Fuel Filter Integrity
Explore the design, functionality, and standards compliance of our advanced Filter Cleanliness Test Rig developed according to ISO 4020-6.1. This rig is engineered to evaluate fuel filter cleanliness levels with high accuracy and repeatability—critical for ensuring the performance and durability of fuel systems.
🔬 Inside This Presentation:
Overview of ISO 4020-6.1 testing protocols
Rig components and schematic layout
Test methodology and data acquisition
Applications in automotive and industrial filtration
Key benefits: accuracy, reliability, compliance
Perfect for R&D engineers, quality assurance teams, and lab technicians focused on filtration performance and standard compliance.
🛠️ Ensure Filter Cleanliness — Validate with Confidence.
Introduction of Structural Audit and Health Montoring.pptx



Introduction of Structural Audit and Health Montoring.pptxgunjalsachin Introduction to Structural Audit - Introduction, Objectives, Bye-laws, Importance, Various Stages involved, Visual inspection: scope, coverage, limitations, Factors to be keenly observed. Investigation Management, Aspects of audit of Masonry buildings, RC frame buildings, Steel Structures
UNIT-1-PPT-Introduction about Power System Operation and Control



UNIT-1-PPT-Introduction about Power System Operation and ControlSridhar191373 Power scenario in Indian grid – National and Regional load dispatching centers –requirements of good power system - necessity of voltage and frequency regulation – real power vs frequency and reactive power vs voltage control loops - system load variation, load curves and basic concepts of load dispatching - load forecasting - Basics of speed governing mechanisms and modeling - speed load characteristics - regulation of two generators in parallel.
Video Games and Artificial-Realities.pptx



Video Games and Artificial-Realities.pptxHadiBadri1 🕹️ #GameDevs, #AIteams, #DesignStudios — I’d love for you to check it out.
This is where play meets precision. Let’s break the fourth wall of slides, together.
Software Developer Portfolio: Backend Architecture & Performance Optimization



Software Developer Portfolio: Backend Architecture & Performance Optimizationkiwoong (daniel) kim In-depth technical portfolio of a Backend Developer (2+ years) specializing in high-performance ERP systems. Details C# expertise in multi-layered caching (Memory, SSDB, DB), custom ORM development with Expression Trees, advanced connection pooling (Stack-based, PgBouncer), and efficient CSV/XML serialization solutions.
Highway Engineering - Pavement materials



Highway Engineering - Pavement materialsAmrutaBhosale9 Bituminous binders are sticky, black substances derived from the refining of crude oil. They are used to bind and coat aggregate materials in asphalt mixes, providing cohesion and strength to the pavement.
ISO 4548-7 Filter Vibration Fatigue Test Rig Catalogue.pdf



ISO 4548-7 Filter Vibration Fatigue Test Rig Catalogue.pdf FILTRATION ENGINEERING & CUNSULTANT This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of a specialized test rig designed in accordance with ISO 4548-7, the international standard for evaluating the vibration fatigue resistance of full-flow lubricating oil filters used in internal combustion engines.
Key features include:
Proposed EPA Municipal Waste Combustor Rule



Proposed EPA Municipal Waste Combustor RuleAlvaroLinero2 Florida Section AWMA Presentation on Proposed EPA Municipal Waste Combustor Rule. Reviews EPA procedures to set standards and pitfalls.
Kevin Corke Spouse Revealed A Deep Dive Into His Private Life.pdf



Kevin Corke Spouse Revealed A Deep Dive Into His Private Life.pdfMedicoz Clinic Kevin Corke, a respected American journalist known for his work with Fox News, has always kept his personal life away from the spotlight. Despite his public presence, details about his spouse remain mostly private. Fans have long speculated about his marital status, but Corke chooses to maintain a clear boundary between his professional and personal life. While he occasionally shares glimpses of his family on social media, he has not publicly disclosed his wife’s identity. This deep dive into his private life reveals a man who values discretion, keeping his loved ones shielded from media attention.
C Programming Language Part 7
- 2. Functions A function is a group of statements that together perform a task. Every C program has at least one function, which is main(), and all the most trivial programs can define additional functions. A function declaration tells the compiler about a function's name, return type, and parameters. A function definition provides the actual body of the function. Defining a Function: return_type function_name( parameter list ) { body of the function }
- 3. (a) C program is a collection of one or more functions. Some important case (b)A function gets called when the function name is followed by a semicolon. For example, main( ) { argentina( ) ; } (c)A function is defined when function name is followed by a pair of braces in which one or more statements may be present. For example, argentina( ) { statement 1 ; statement 2 ; statement 3 ; }
- 4. (d) Any function can be called from any other function. Even main( ) can be called from other functions. For example, main( ) { message( ) ; } message( ) { printf ( "nCan't imagine life without C" ) ; main( ) ; } (e)A function can be called any number of times. For example, main( ) { message( ) ; message( ) ; } message( ) { printf ( "nJewel Thief!!" ) ; }
- 5. (f) The order in which the functions are defined in a program and the order in which they get called need not necessarily be same. For example, main( ) { message1( ) ; message2( ) ; } message2( ) { printf ( "nBut the butter was bitter" ) ; } message1( ) { printf ( "nMary bought some butter" ) ; } Here, even though message1( ) is getting called before message2( ), still, message1( ) has been defined after message2( ). However, it is advisable to define the functions in the same order in which they are called. This makes the program easier to understand.
- 6. (g) A function can call itself. Such a process is called ‘recursion’. We would discuss this aspect of C functions later in this chapter. (h) A function can be called from other function, but a function cannot be defined in another function. Thus, the following program code would be wrong, since argentina( ) is being defined inside another function, main( ). main( ) { printf ( "nI am in main" ) ; argentina( ) { printf ( "nI am in argentina" ) ; } }
- 7. Types of C functions Library function User defined function Library function 1. main() 2. printf() 3. scanf() User defined function #include <stdio.h> void function_name(){ ................ ................ } int main(){ ........... ........... function_name(); ........... ........... }
- 8. Types of User-defined Functions in C Programming 1. Function with no arguments and no return value 2. Function with no arguments and return value 3. Function with arguments but no return value 4. Function with arguments and return value. Function with no arguments and no return value. /*C program to check whether a number entered by user is prime or not using function with no arguments and no return value*/ #include <stdio.h> void prime(); int main(){ prime(); //No argument is passed to prime(). return 0; } void prime(){ /* There is no return value to calling function main(). Hence, return type of prime() is void */ int num,i,flag=0; printf("Enter positive integer enter to check:n"); scanf("%d",&num); for(i=2;i<=num/2;++i){ if(num%i==0){ flag=1; } } if (flag==1) printf("%d is not prime",num); else printf("%d is prime",num); }
- 9. Function with no arguments but return value /*C program to check whether a number entered by user is prime or not using function with no arguments but having return value */ #include <stdio.h> int input(); int main(){ int num,i,flag = 0; num=input(); /* No argument is passed to input() */ for(i=2; i<=num/2; ++i){ if(num%i==0){ flag = 1; break; } } if(flag == 1) printf("%d is not prime",num); else printf("%d is prime", num); return 0; } int input(){ /* Integer value is returned from input() to calling function */ int n; printf("Enter positive integer to check:n"); scanf("%d",&n); return n; }
- 10. Function with arguments and no return value /*Program to check whether a number entered by user is prime or not using function with arguments and no return value */ #include <stdio.h> void check_display(int n); int main(){ int num; printf("Enter positive enter to check:n"); scanf("%d",&num); check_display(num); /* Argument num is passed to function. */ return 0; } void check_display(int n){ /* There is no return value to calling function. Hence, return type of function is void. */ int i, flag = 0; for(i=2; i<=n/2; ++i){ if(n%i==0){ flag = 1; break; } } if(flag == 1) printf("%d is not prime",n); else printf("%d is prime", n); }
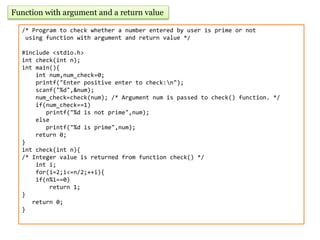
- 11. Function with argument and a return value /* Program to check whether a number entered by user is prime or not using function with argument and return value */ #include <stdio.h> int check(int n); int main(){ int num,num_check=0; printf("Enter positive enter to check:n"); scanf("%d",&num); num_check=check(num); /* Argument num is passed to check() function. */ if(num_check==1) printf("%d is not prime",num); else printf("%d is prime",num); return 0; } int check(int n){ /* Integer value is returned from function check() */ int i; for(i=2;i<=n/2;++i){ if(n%i==0) return 1; } return 0; }
- 12. void Kulut(int a,int b) { c=a+b; } int Kulut(int a,int b) { c=a+b; return 0; }
- 13. Example: /* function returning the max between two numbers */ int max(int num1, int num2) { /* local variable declaration */ int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; return result; }
- 14. Example: #include<stdio.h> void main() { printf("n I am in main"); argentina(); } void argentina() { printf("nI am in argentina n") ; }
- 15. #include<stdio.h> void main() { int c; c=max(2,3); printf("n this print is in main() %d n",c); } /* function returning the max between two numbers */ int max(int num1, int num2) { /* local variable declaration */ int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; printf("n I am in max() %d n",result); return result; } Example:
- 16. Example of a Function: #include <stdio.h> /* function declaration */ int max(int num1, int num2); int main () { /* local variable definition */ int a = 100; int b = 200; int ret; /* calling a function to get max value */ ret = max(a, b); printf( "Max value is : %dn", ret ); return 0; } /* function returning the max between two numbers */ int max(int num1, int num2) { /* local variable declaration */ int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; return result; }
- 17. #include <stdio.h> main( ) { message( ) ; message( ) ; } message( ) { printf ( "n Rahul is Thief!!n" ) ; } Example:
- 19. Function Arguments Call Type Description Call by value This method copies the actual value of an argument into the formal parameter of the function. In this case, changes made to the parameter inside the function have no effect on the argument. Call by reference This method copies the address of an argument into the formal parameter. Inside the function, the address is used to access the actual argument used in the call. This means that changes made to the parameter affect the argument.
- 20. call by value in C The call by value method of passing arguments to a function copies the actual value of an argument into the formal parameter of the function. In this case, changes made to the parameter inside the function have no effect on the argument By default, C programming language uses call by value method to pass arguments. In general, this means that code within a function cannot alter the arguments used to call the function. Consider the function swap() definition as follows. /* function returning the max between two numbers */ int max(int num1, int num2) { /* local variable declaration */ int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; return result; }
- 21. #include <stdio.h> /* function declaration */ void swap(int x, int y); int main () { /* local variable definition */ int a = 100; int b = 200; printf("Before swap, value of a : %dn", a ); printf("Before swap, value of b : %dn", b ); /* calling a function to swap the values */ swap(a, b); printf("After swap, value of a : %dn", a ); printf("After swap, value of b : %dn", b ); return 0; }
- 22. call by reference in C The call by reference method of passing arguments to a function copies the address of an argument into the formal parameter. Inside the function, the address is used to access the actual argument used in the call. This means that changes made to the parameter affect the passed argument. /* function definition to swap the values */ void swap(int *x, int *y) { int temp; temp = *x; /* save the value at address x */ *x = *y; /* put y into x */ *y = temp; /* put temp into y */ return; }
- 23. #include <stdio.h> /* function declaration */ void swap(int *x, int *y); int main () { /* local variable definition */ int a = 100; int b = 200; printf("Before swap, value of a : %dn", a ); printf("Before swap, value of b : %dn", b ); /* calling a function to swap the values. * &a indicates pointer to a ie. address of variable a and * &b indicates pointer to b ie. address of variable b. */ swap(&a, &b); printf("After swap, value of a : %dn", a ); printf("After swap, value of b : %dn", b ); return 0; }







