Chapter 7 - Data Link Control Protocols 9e
- 1. Data Link Control Protocols CEN 220/CIS 192 Advanced Data Communications and Networking Data and Computer Communications, W. Stallings 9/E, Chapter 7
- 2. Data Link Control Protocols “Great and enlightened one,” said Ten-teh, as soon as his stupor was lifted, “has this person delivered his message competently, for his mind was still a seared vision of snow and sand and perchance his tongue has stumbled?” “Bend your ears to the wall,” replied the Emperor, “and be assured.” —Kai Lung's Golden Hours, Earnest Bramah
- 3. Data Link Control Protocols When sending data, to achieve control, a layer of logic is added above the physical layer data link control or a data link control protocol To manage exchange of data over a link: frame synchronization flow control error control addressing control and data link management
- 4. Flow Control Ensure sending entity does not overwhelm receiving entity prevent buffer overflow Influenced by: transmission time • time taken to emit all bits into medium propagation time • time for a bit to traverse the link Assumption is all frames are successfully received with no frames lost or arriving with errors
- 5. Model of Frame Transmission
- 6. Stop and Wait Simplest form of flow control Works well for a message sent in a few large frames stop and wait becomes inadequate if large block of data is split into small frames by source
- 7. Stop and Wait Link Utilization
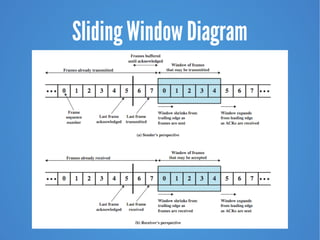
- 8. Sliding Windows Flow Control Allows multiple numbered frames to be in transit receiver has buffer W long transmitter sends up to W frames without ACK ACK includes number of next frame expected sequence number is bounded by size of field (k) • frames are numbered modulo 2k • giving max window size of up to 2k – 1 receiver can ACK frames without permitting further transmission (Receive Not Ready) must send a normal acknowledge to resume If have full-duplex link, can piggyback acks
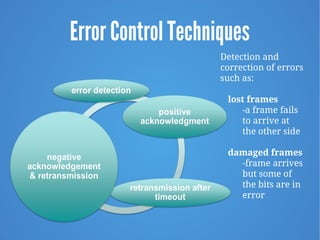
- 11. Error Control Techniques Detection and correction of errors such as: lost frames -a frame fails to arrive at the other side damaged frames -frame arrives but some of the bits are in error
- 12. Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) Collective name for error control mechanisms Effect of arq is to turn an unreliable data link into a reliable one Versions of arq are: stop-and-wait go-back-N selective-reject
- 13. Stop and Wait ARQ Source transmits single frame Waits for ack • no other data can be sent until destination’s reply arrives If frame received is damaged, discard it transmitter has timeout if no ACK within timeout, retransmit If ack is damaged, transmitter will not recognize transmitter will retransmit receiver gets two copies of frame use alternate numbering and ACK0 / ACK1
- 14. Stop and Wait ARQ
- 15. Go-Back-N ARQ Most commonly used error control Based on sliding-window Use window size to control number of outstanding frames If no error, ack as usual If error, reply with rejection destination will discard that frame and all future frames until frame in error is received correctly transmitter must go back and retransmit that frame and all subsequent frames
- 16. Go Back N - Handling Damaged frame error in frame i so receiver rejects frame i transmitter retransmits frames from i Lost frame frame i lost and either • transmitter sends i+1 and receiver gets frame i+1 out of sequence and rejects frame i • or transmitter times out and sends ACK with P bit set which receiver responds to with ACK i transmitter then retransmits frames from i
- 17. Go Back N - Handling
- 18. Selective-Reject (ARQ) Also called selective retransmission Only rejected frames are retransmitted Subsequent frames are accepted by the receiver and buffered Minimizes retransmission Receiver must maintain large enough buffer More complex logic in transmitter less widely used Useful for satellite links with long propagation delays
- 20. High Level Data Link Control (HDLC)
- 22. HDLC Frame Structure uses synchronous transmission transmissions are in the form of frames single frame format used
- 23. Flag Fields and Bit Stuffing Delimit frame at both ends with 01111110 Receiver hunts for flag sequence to synchronize Bit stuffing used to avoid confusion with data containing flag sequence 01111110 0 inserted after every sequence of five 1s if receiver detects five 1s it checks next bit if next bit is 0, it is deleted (was stuffed bit) if next bit is 1 and seventh bit is 0, accepted as flag if sixth and seventh bits 1, sender is indicating abort
- 24. Address Field Identifies secondary station that transmitted or will receive frame Usually 8 bits long May be extended to multiples of 7 bits leftmost bit indicates if is the last octet (1) or not (0) Address 11111111 allows primary to broadcast
- 25. Control Field Different frame types Information - data transmitted to user (next layer up) • flow and error control piggybacked on information frames Supervisory - ARQ when piggyback is not used Unnumbered - supplementary link control functions First 1-2 bits of control field identify frame type
- 26. Control Field Use of poll/final (p/f) bit depends on context In command frame p bit set to 1 to solicit (poll) response from peer In response frame f bit set to 1 to indicate response to soliciting command Sequence number usually 3 bits can extend to 8 bits as shown below
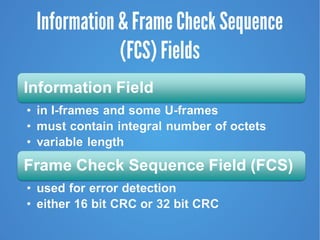
- 27. Information & Frame Check Sequence (FCS) Fields
- 28. HDLC Operation Consists of exchange of i-frames, s-frames and u-frames Involves three phases
- 31. Summary Data link protocols – frame synchronization – flow control ● stop-and-wait, sliding window ● ACK frame ● error control – lost frame, damaged frame – stop-and-wait, go-back-N, selective-reject ARQs HDLC – NRM, ABM,ARM