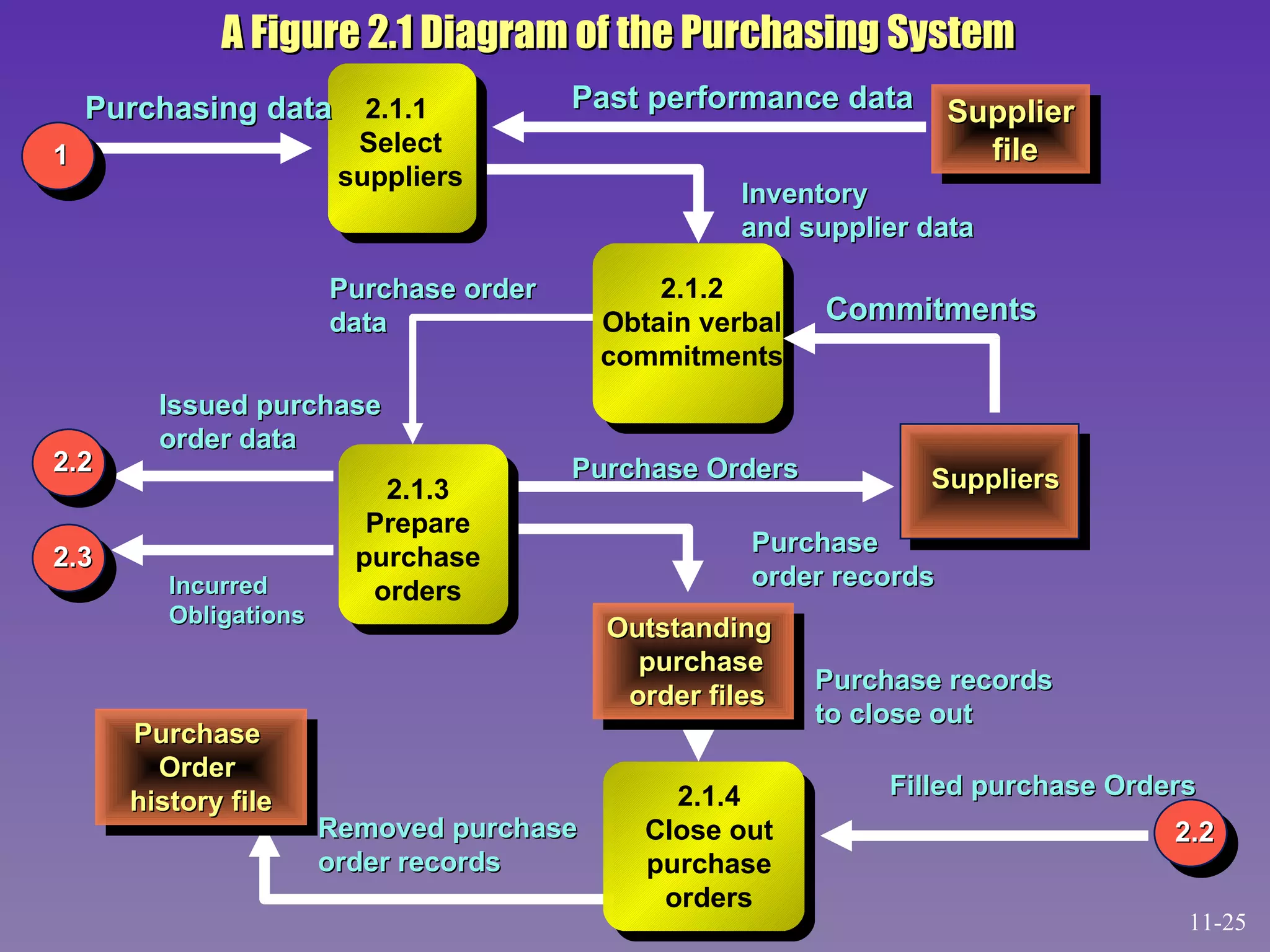
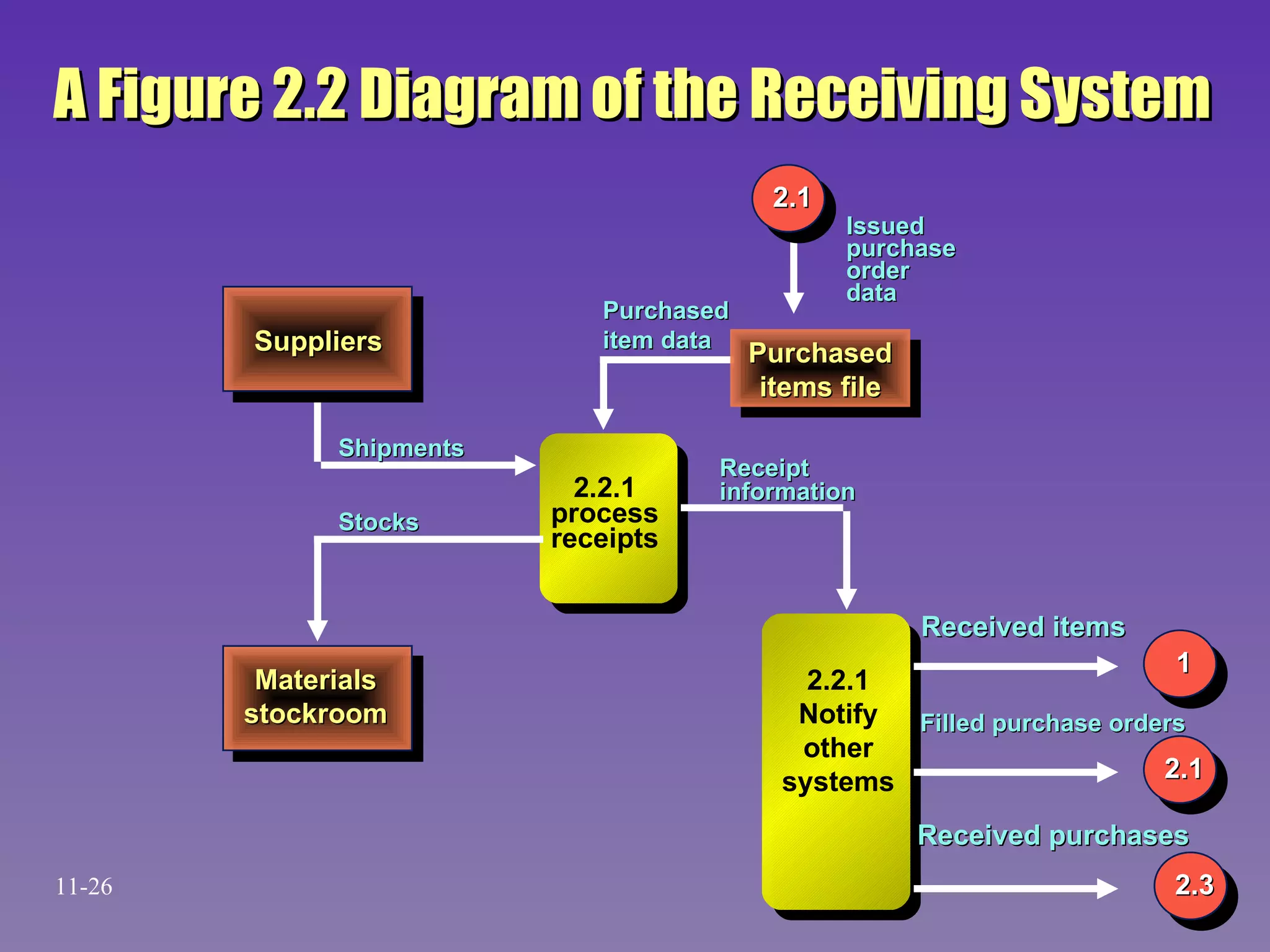
The document discusses accounting information systems (AIS) and their components. It describes how an AIS gathers data on a firm's activities, transforms that data into useful information, and makes it available to internal and external users. It also provides examples of AIS subsystems, including order entry, inventory, billing, accounts receivable, purchasing, receiving, and accounts payable systems. Additionally, it notes that an AIS performs necessary tasks using standard procedures, focuses on detailed historical data, and provides a foundation for other management information systems.





![2. Manipulate data Classify (use codes) Sort Calculate Summarize Data Processing Tasks [cont.] 11-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11-100209001437-phpapp01/75/Chap11-6-2048.jpg)
![3. Store data Describes each transaction Represents most of the database Data Processing Tasks [cont.] 11-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11-100209001437-phpapp01/75/Chap11-7-2048.jpg)
![4. Document preparation Triggers By an action By a time schedule Hardcopy or on-screen Data Processing Tasks [cont.] 11-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11-100209001437-phpapp01/75/Chap11-8-2048.jpg)