Chapter 3.pptx Oracle SQL or local Android database setup SQL, SQL-Lite, coding the database class, building and executing queries
- 1. Database in Android Android Data Managenent using SQL Lite
- 2. What is SQL lite..? ● ● SQLite is a relational database management system contained in a C programming library. In contrast to many other database management systems, SQLite is not a client–server database engine. Rather, it is embedded into the end program. SQLite is ACID-compliant and implements most of the SQL standard, using a dynamically and weakly typed SQL syntax
- 3. Origins of sql lite ● ● D. Richard Hipp designed SQLite in the spring of 2000 while working for General Dynamics on contract with the United States Navy. Hipp was designing software used aboard guided missile destroyers, which were originally based on HP-UX with an IBM Informix database back-end. SQLite began as a Tcl extension. The design goals of SQLite were to allow the program to be operated without installing a database management system or requiring a database administrator.
- 4. Why sql lite ● ● ● ● ● No server is required Object(document) based design Reqire Zero(less) Configration One machine database Multitasking database
- 5. Using SQL databases in Android Android (as well as iPhone OS) uses an embedded standalone program called sqlite3 which can be used to create a database, indices, views, Insert rows, change rows, define SQL tables, queries, triggers delete rows, run queries and administer a SQLite database file.
- 6. How to create a SQLitedatabase Open the database according to the flags OPEN_READWRITE OPEN_READONLY CREATE_IF_NECESSARY . Sets the locale of the database to the thesystem's current locale. public static SQLiteDatabase.openDatabase( Stringpath, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory, int flags ) Parameters path to database file to open and/or create factory an optional factory class that is called to instantiate a cursor when query is called, or null for default flags to control database access mode Returns the newly opened database Throws SQLiteException if the database cannot be opened
- 7. How to create a SQLitedatabase SQLiteDatabase db=this.openOrCreateDatabase ( "myfriendsDB",MODE_PRIVATE, null); where the assumed prefix for the database stored in the devices ram is: "/data/data/<CURRENT_namespace>/databases/". For instance if this app is created in a namespace called “cis493.sql1”, the full name of the newly created database will be: “/data/data/cis493.sql1/databases/myfriendsDB”. MODEcould be: MODE_PRIVATE, MODE_WORLD_READABLE, and MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE. Meaningful for apps consisting of multiples activities
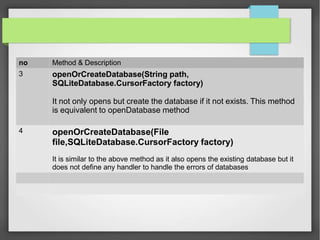
- 8. no Method & Description 1 openDatabase(String path, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory, int flags, DatabaseErrorHandler errorHandler) This method only opens the existing database with the appropriate flag mode. The common flags mode could be OPEN_READWRITE OPEN_READONLY 2 openDatabase(String path, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory, int flags) It is similar to the above method as it also opens the existing database but it does not define any handler to handle the errors of databases
- 9. no Method & Description 3 openOrCreateDatabase(String path, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory) It not only opens but create the database if it not exists. This method is equivalent to openDatabase method 4 openOrCreateDatabase(File file,SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory) It is similar to the above method as it also opens the existing database but it does not define any handler to handle the errors of databases
- 10. Executing SQL commands on the Database Action queries and Retrieval queries represent the most common operations against the database Retrieval query : typically a SQL-Select command in which a table holding a number of fields and rows is produced as an answer to a data request. Action query : usually performs maintenance and administrative tasks such as manipulating tables, users, environment, etc.
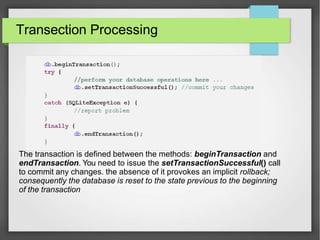
- 11. Transection Processing The transaction is defined between the methods: beginTransaction and endTransaction. You need to issue the setTransactionSuccessful() call to commit any changes. the absence of it provokes an implicit rollback; consequently the database is reset to the state previous to the beginning of the transaction
- 12. Creating a Table We will use the execSQL(…)method to manipulate SQL action queries. db.execSQL("create table tblAMIGO(" + " recIDinteger PRIMARY KEY autoincrement, " + " name text, "+ " phone text ); " );
- 13. Create table The database data types are very simple, for instance we will use: text,varchar, integer, float, numeric, date, time, timestamp, blob, boolean, and so on. 1.In general, any well-formed SQL action command (insert, delete, update, create, drop, alter, etc.) could be framed inside an execSQL(…) method. 2.You should make the call to execSQLinside of a try-catch-finally block. Be aware of potential SQLiteExceptionsituations thrown by the method.
- 14. Retrieval queries Retrieval queries are SQL-select statements. Android offers two mechanisms for phrasing SQL-select statements: 1.Raw queries take for input a syntactically correct SQL-select statement. The select query could be as complex as needed and involve any number of tables (remember that outer joins are not supported). 2.Simple queries are compact parametized select statements that operate on a single table (for developers who prefer not to use SQL).
- 15. RawQuery Cursor c1 = db.rawQuery( "select count(*) as Total from Student", null); The rawQuery contains a select-statement that counts the rows in the table Student. 2.The result of this count is held in a table having only one row and one column. The column is called “Total”. 3.The cursor c1will be used to traverse the rows (one!) of the resulting table. 4.Fetching a row using cursor c1 requires advancing to the next record in the answer set. 5.Later the (singleton) field total must be bound to a local Java variable
- 16. Cursors Android cursor s are used to gain (random) access to tables produced by SQL select statements. Cursors primarily provide one row-at-the-time operations on a table. Cursors include several types of operator 1.Positional awareness operators (isFirst(), isLast(), isBeforeFirst(), isAfterLast()), 2.Record Navigation (moveToFirst(), moveToLast(), moveToNext(), moveToPrevious(), move(n)) 3. Field extraction (getInt, getString, getFloat, getBlob, getDate, etc.) 4.Schema inspection (getColumnName, getColumnNames, getColumnIndex, getColumnCount, getCount)
- 18. Cursors provide READ_ONLYaccess to records. 2.Early versions of the Android SDK included cursor commands to sequentially modify records. Those operators have been deprecated in Release 1.0. 3.Methods such as cursor.updateInt(...)and cursor.deleteRow(...)are not valid anymore. 4.Instead use an action SQL command in an execSQL(...)method .
- 19. ParametizedRawQuery String mySQL= "select count(*) as Total " + " from Student" + " where recID> ?" + " and name = ?"; String [] args= {"114337", "Dipak"}; Cursor c1 = db.rawQuery (mySQL, args);
- 20. Simple Querie Simple queries can only retrieve data from a single table.(non-joining ) it is an template The method’s signature has a fixed sequence of seven arguments representing: 1.the table name, 2.the columns to be retrieved, 3.the search condition (where-clause), 4.arguments for the where-clause, 5.the group-by clause, 6.having-clause, and 7.the order-by clause.
- 21. example
- 22. SQL Action Queries insert into student values ( ‘Macarena’, ‘555-1234’); update student set name = ‘Maria Macarena’ where phone = ‘555-1234’; delete from where phone = ‘555-1234’; create table Temp ( column1 int, column2 text, column3 date ); drop table Temp;
- 23. Action queries
- 24. Insert Operator public long insert (String table, String nullColumnHack, ContentValues values)
- 25. Insertion ● ● execSQL(String sql, Object[ ] bindArgs) This method not only insert data , but also used to update or modify already existing data in database using bind arguments
- 26. update Operator public int update ( String table, ContentValues values, String whereClause, String[ ] whereArgs) Parameters table : values : the table to update in a map <name,value> from column names to new column values. null is a valid value that will be translated to NULL. whereClause : the optional WHERE clause to apply when updating. Passing null will update all rows. Returns : the number of rows affected
- 27. delete Operator public int delete( String table, String whereClause , String[ ] whereArgs) Parameters table the table to delete from whereClause the optional WHERE clause to apply when deleting. Passing null will delete all rows. Returns the number of rows affected if a whereClauseis passed in, 0 otherwise. To remove all rows and get a count pass "1" as the whereClause
















![ParametizedRawQuery
String mySQL= "select count(*) as Total "
+ " from Student"
+ " where recID> ?"
+ " and name = ?";
String [] args= {"114337", "Dipak"};
Cursor c1 = db.rawQuery (mySQL, args);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3-240319074916-17e1041c/85/Chapter-3-pptx-Oracle-SQL-or-local-Android-database-setup-SQL-SQL-Lite-coding-the-database-class-building-and-executing-queries-19-320.jpg)





![Insertion
●
●
execSQL(String sql, Object[ ] bindArgs)
This method not only insert data , but also used to update
or modify already existing data in database using bind
arguments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3-240319074916-17e1041c/85/Chapter-3-pptx-Oracle-SQL-or-local-Android-database-setup-SQL-SQL-Lite-coding-the-database-class-building-and-executing-queries-25-320.jpg)
![update Operator
public int update ( String table,
ContentValues values,
String whereClause, String[ ] whereArgs)
Parameters
table :
values :
the table to update in
a map <name,value> from column names to new column values.
null is a valid value that will be translated to NULL.
whereClause : the optional WHERE clause to apply when updating.
Passing null will update all rows.
Returns : the number of rows affected](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3-240319074916-17e1041c/85/Chapter-3-pptx-Oracle-SQL-or-local-Android-database-setup-SQL-SQL-Lite-coding-the-database-class-building-and-executing-queries-26-320.jpg)
![delete Operator
public int delete( String table, String whereClause , String[ ] whereArgs)
Parameters
table the table to delete from
whereClause the optional WHERE clause to apply when deleting. Passing
null will delete all rows.
Returns the number of rows affected if a whereClauseis passed in,
0 otherwise.
To remove all rows and get a count pass "1" as the whereClause](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3-240319074916-17e1041c/85/Chapter-3-pptx-Oracle-SQL-or-local-Android-database-setup-SQL-SQL-Lite-coding-the-database-class-building-and-executing-queries-27-320.jpg)