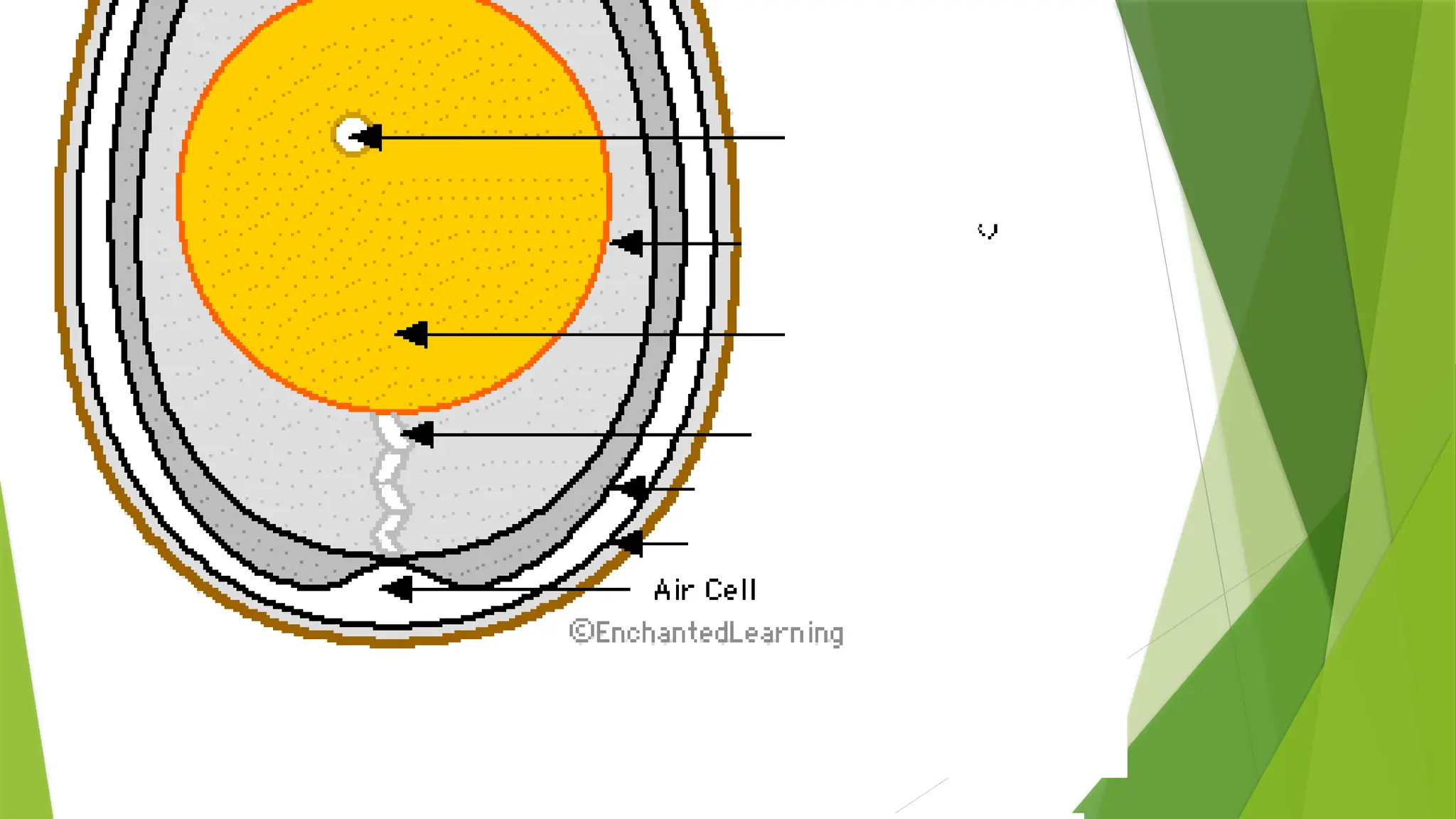
The document outlines a lesson on the composition and nutritive value of eggs, targeting students' understanding and appreciation of the topic. It includes various activities such as labeling parts of the egg and oral recitation, alongside detailed information on the egg's physical structure and nutritional components. The goal is for students to create an egg profile card and recognize the importance of egg nutrition.