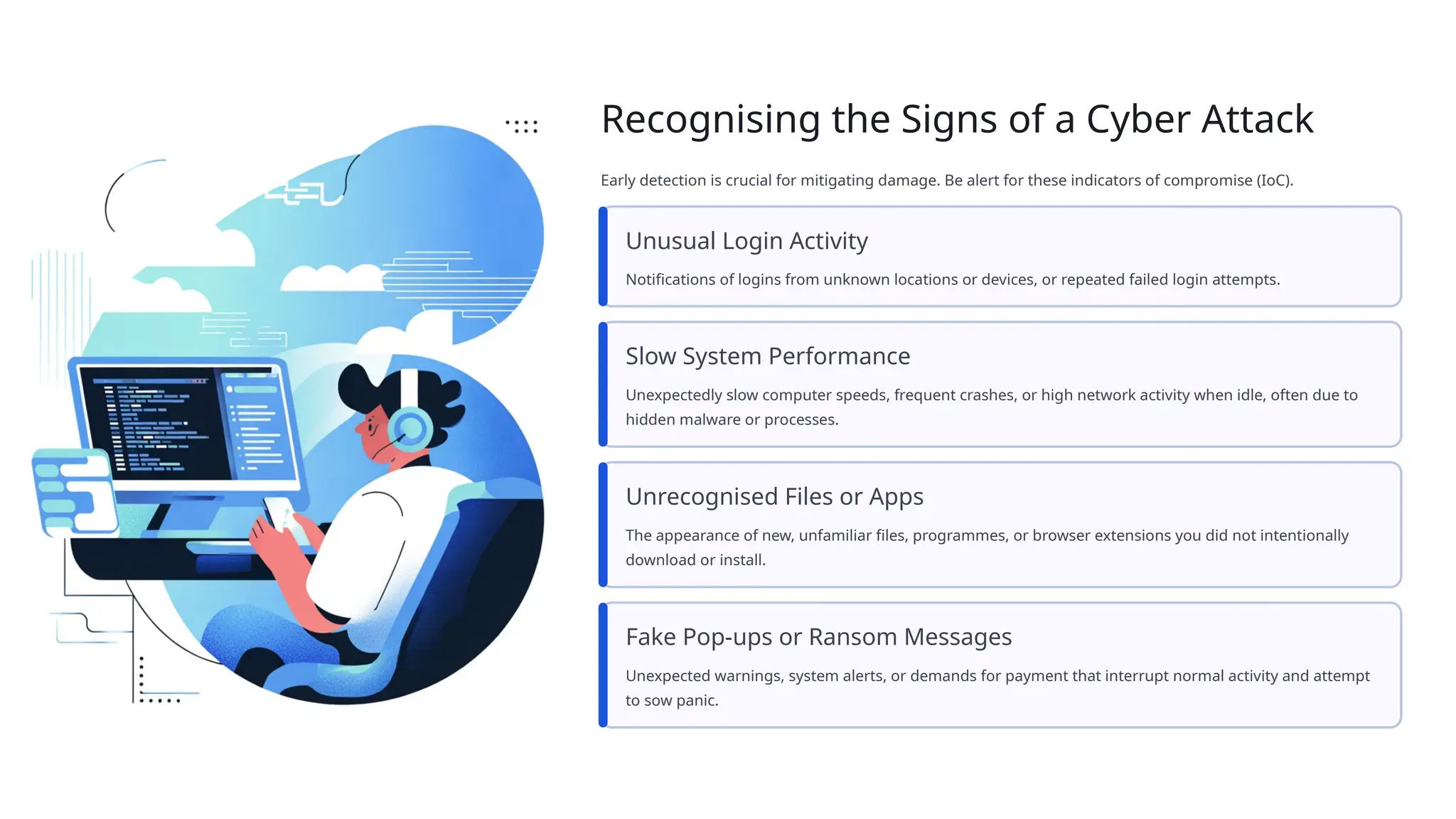
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from digital attacks. As technology advances, cyber threats like malware, phishing, ransomware, and data breaches have become more frequent and sophisticated. Modern industries rely on cybersecurity to safeguard sensitive information, maintain trust, and ensure business continuity. Preventive measures such as strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, regular updates, and employee awareness training are essential to reduce risks. Governments and organizations are also developing strict cyber laws and response teams to tackle cybercrimes effectively. With emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing, the need for stronger cybersecurity frameworks is greater than ever. Building awareness and adopting proactive defense strategies can help create a safer and more secure digital future.