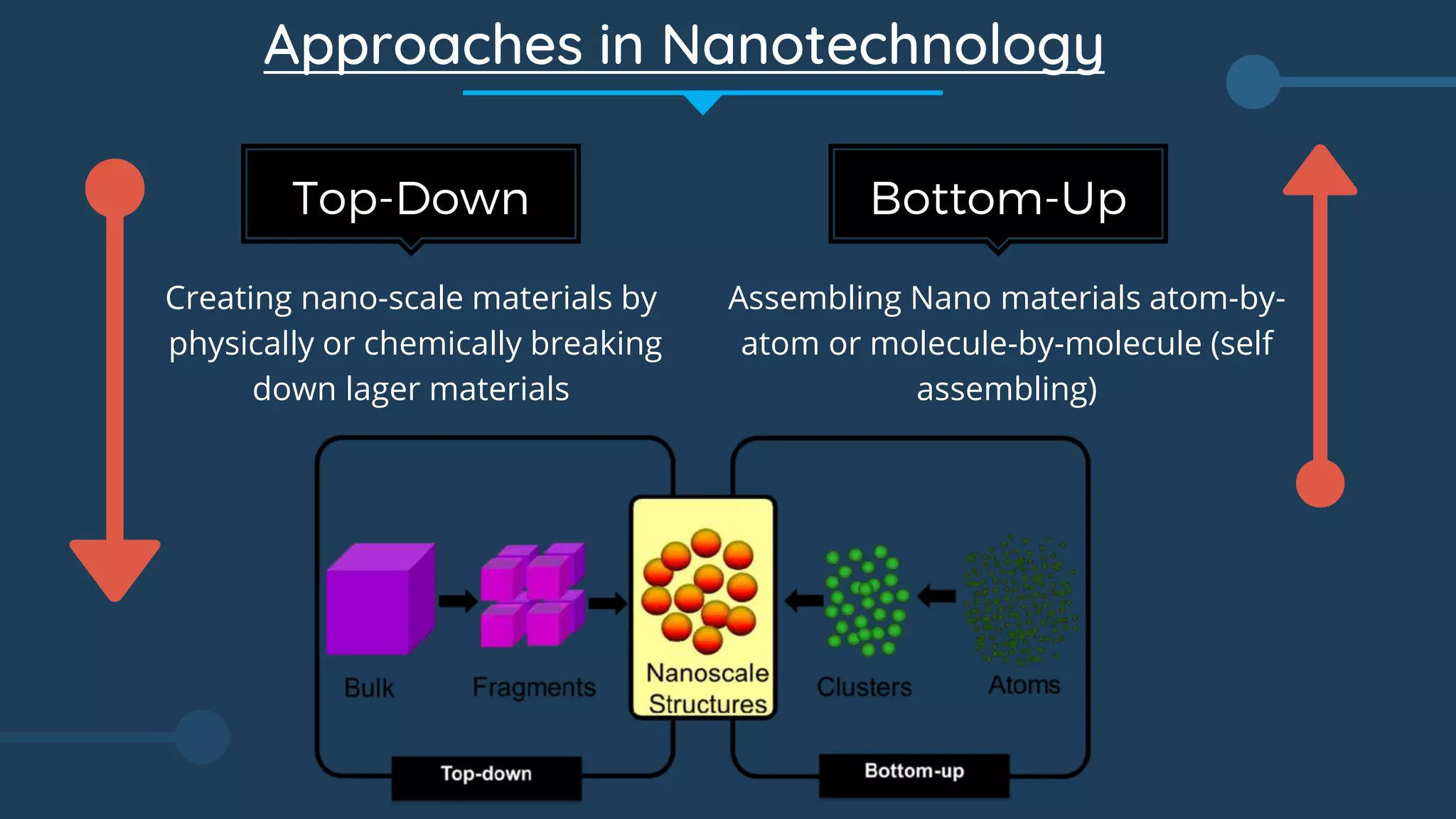
The document discusses the evolution and applications of nanotechnology in electronics and various fields such as medicine, materials science, and engineering. It highlights the unique properties of nanoscale materials, potential advancements in drug delivery, and the future of nanorobotics while also addressing the associated risks and ethical concerns. The conclusion emphasizes the transformative potential of nanotechnology in creating stronger, lighter, and more efficient materials alongside significant advancements in computing capabilities.