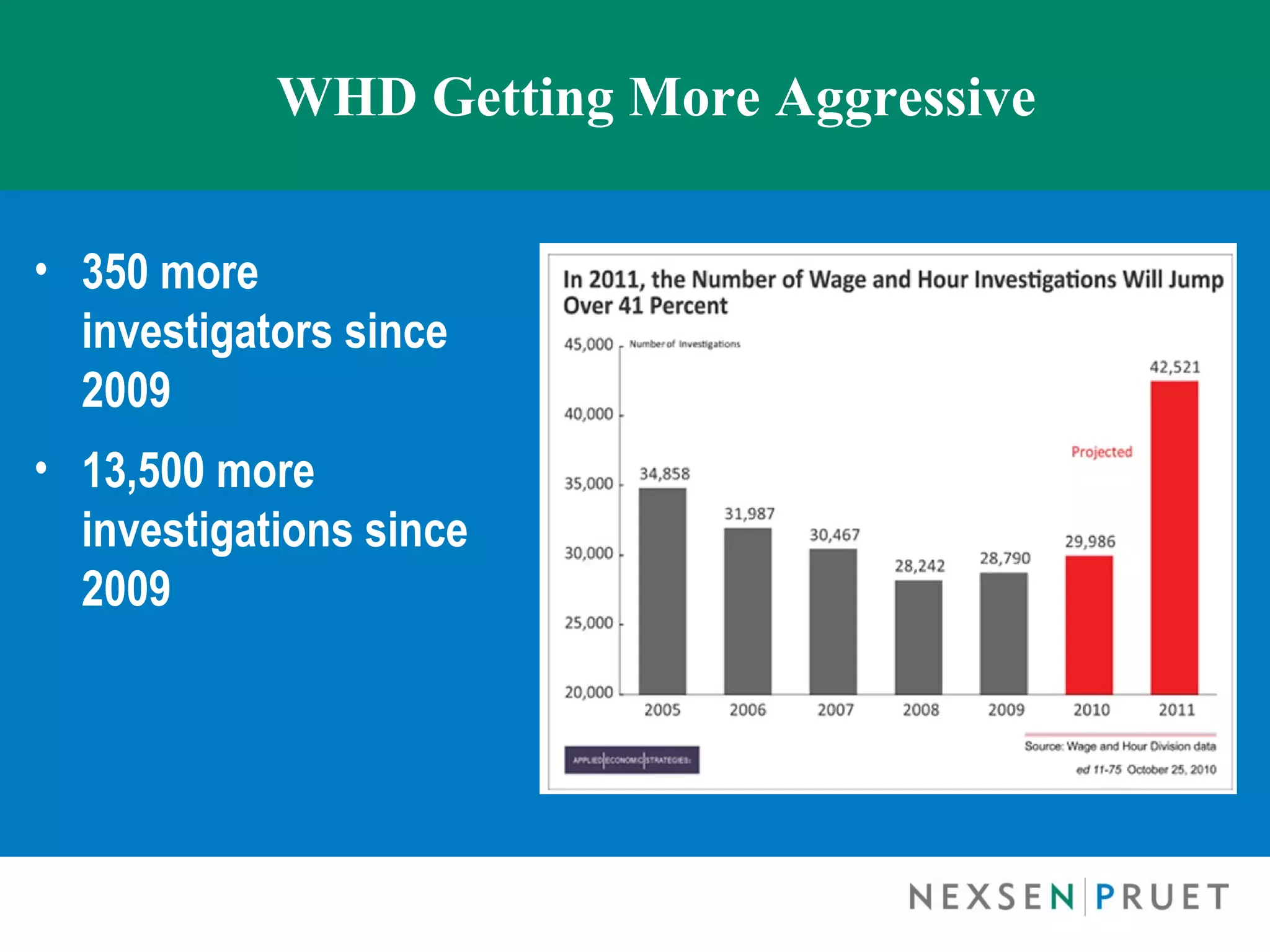
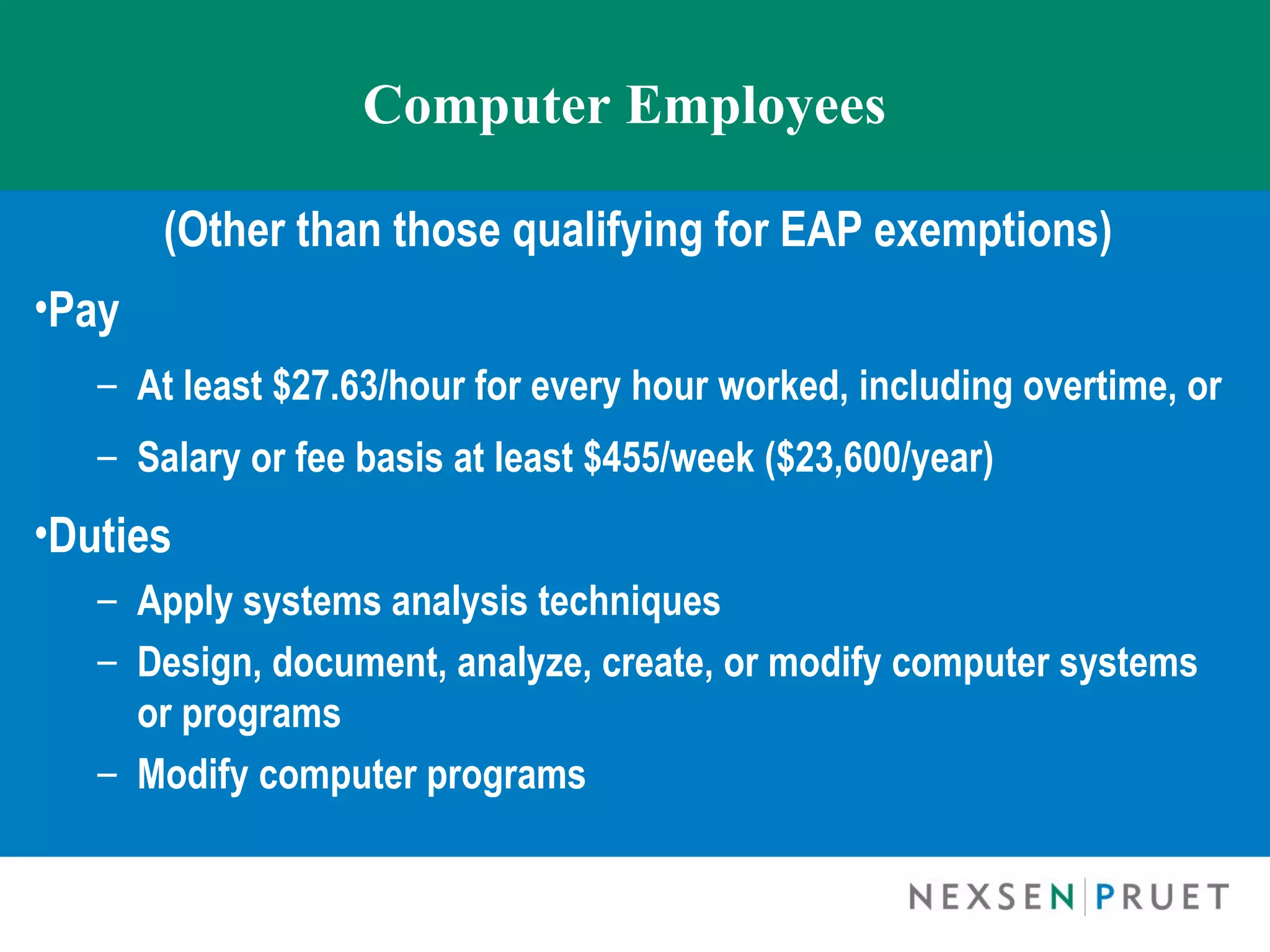
The document discusses the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), focusing on employee exemptions, particularly the 'white collar' exemptions for executive, administrative, professional, computer, and outside sales employees. It highlights the increase in FLSA litigation, cases of misclassification, and the criteria for different exemptions as well as the necessary salary basis and job duties. The document also addresses enforcement trends, including the growing number of investigations and various provisions for compliance and maintaining exempt status.

![A Dramatic Question
“To be or not to be [exempt], that is the
question [for HR Managers].”
[With apologies to] William Shakespeare](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flsaexemptornotexemptppt-13377864005095-phpapp02-120523102238-phpapp02/75/FLSA-Exempt-Or-Not-Exempt-Ppt-2-2048.jpg)