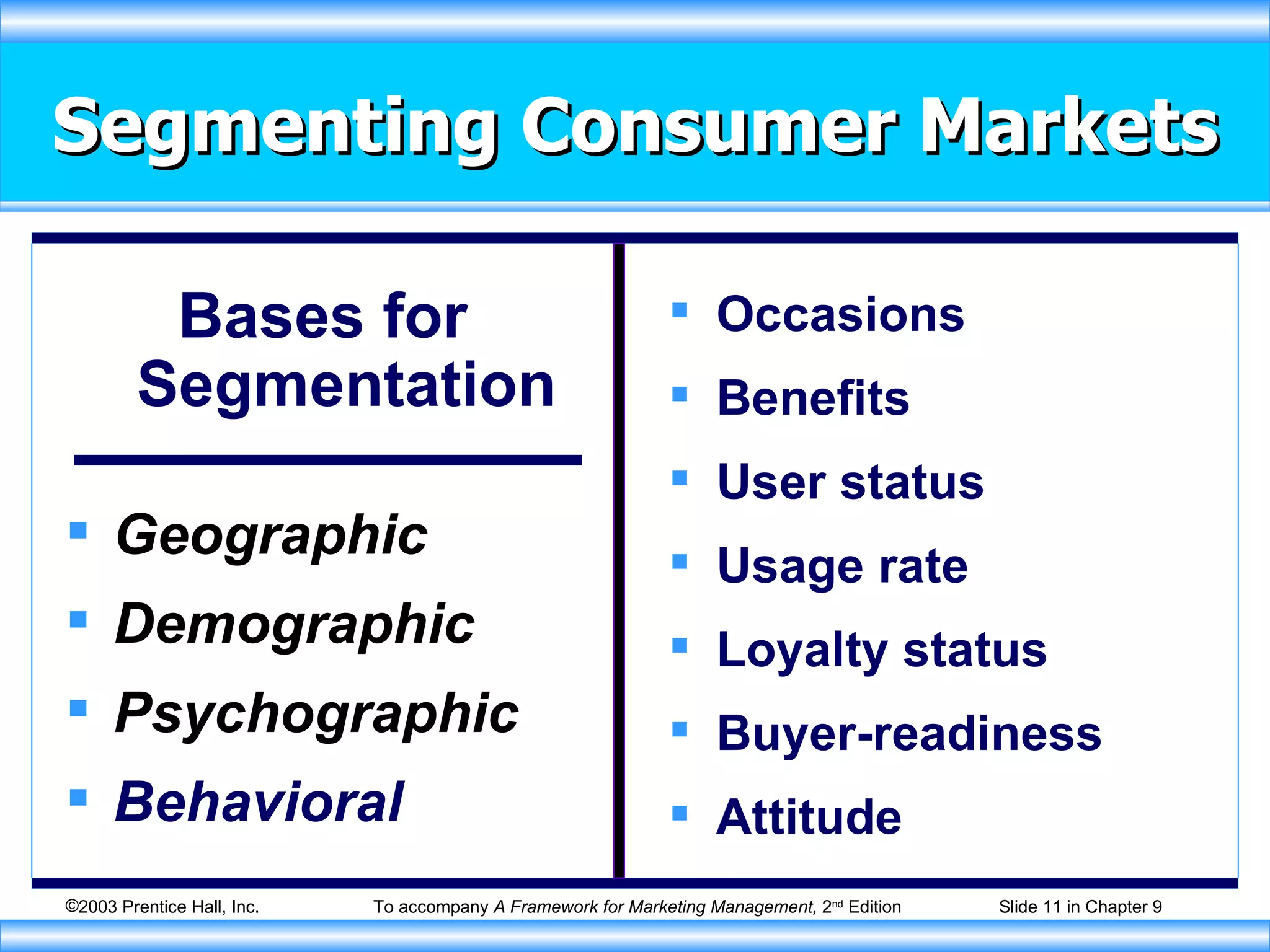
This document discusses market segmentation and target marketing. It explains that companies identify distinct customer groups, select one or more segments to target, and position their product to appeal to the target segment. The document outlines various ways to segment markets, such as by geography, demographics, psychographics, and behavior. It also discusses criteria for evaluating segment attractiveness and different strategies for selecting target markets, such as concentrating on a single segment or pursuing multiple segments.