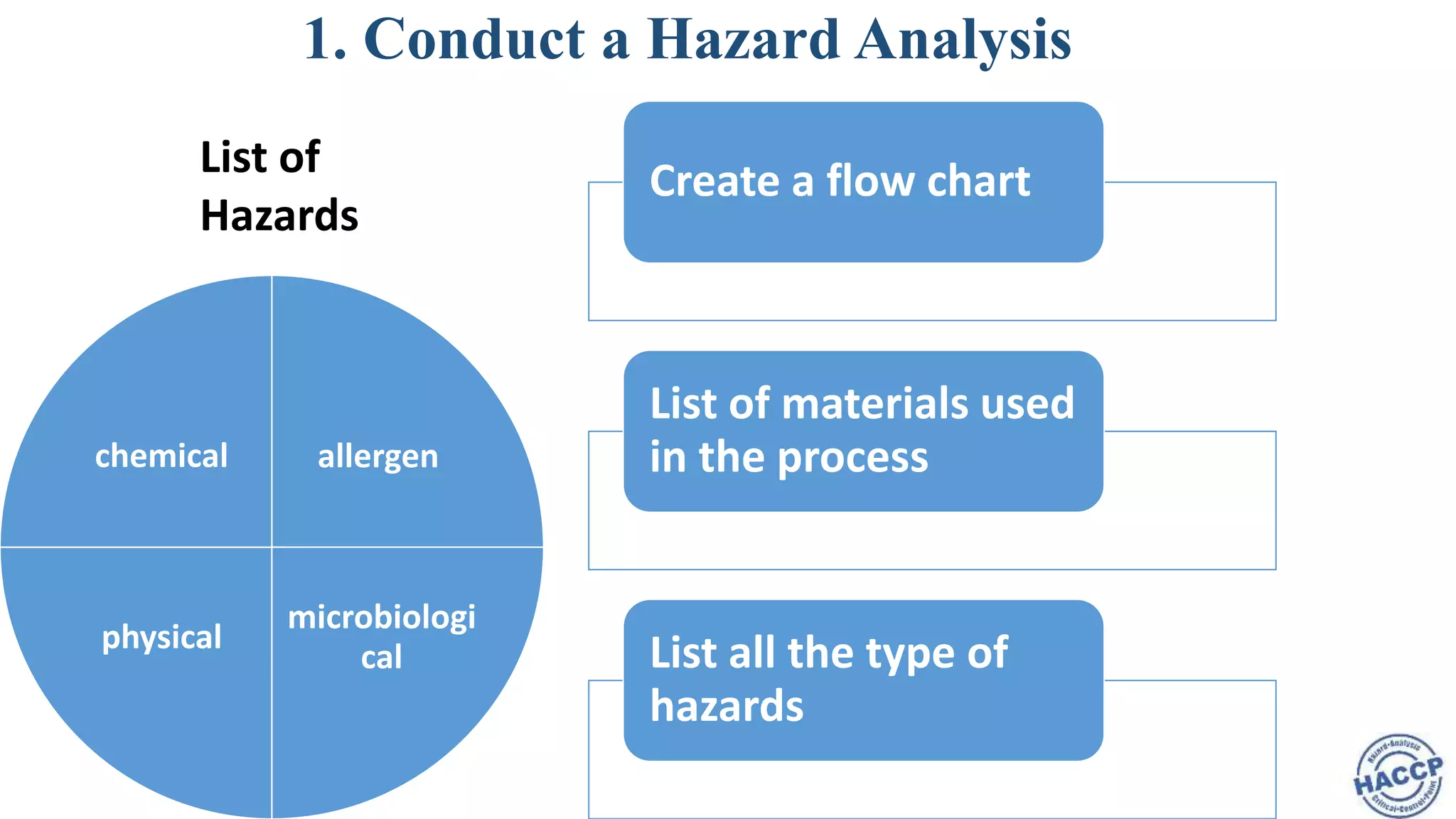
HACCP, or Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, is a systematic approach to ensuring food safety by addressing biological, chemical, and physical hazards during production processes. Initially developed for the space program in the late 1950s, it emphasizes identifying hazards, establishing critical control points, and implementing monitoring systems to ensure product safety and quality. The seven principles of HACCP guide the development and application of this internationally recognized safety system across various sectors, including meats, dairy, and restaurants.