Introduction to JavaScript, functions, DOM
- 1. Module-5 Introduction to JavaScript: Functions, DOM, Forms, and Event Handlers
- 2. Module 5: Introduction to JavaScript: Functions, DOM, Forms, and Event Handlers
- 3. History of Javascript • HTML’s first version, designed by Tim Berners-Lee from 1989 to 1991, was fairly static in nature. • Except for link jumps with the a element, web pages simply displayed content, and the content was fixed. • In 1995, the dominant browser manufacturer was Netscape, and one of its employees, Brendan Eich, thought that it would be useful to add dynamic functionality to web pages. • So he designed the JavaScript programming language, which adds dynamic functionality to web pages when used in conjunction with HTML. • For example, JavaScript provides the ability to update a web page’s content when an event occurs, such as when a user clicks a button. • It also provides the ability to retrieve a user’s input and process that input. • It took Eich only 10 days in May 1995 to implement the JavaScript programming language—a truly remarkable feat. • Marc Andreessen, one of Netscape’s founders, originally named the new language Mocha and then LiveScript. • But for marketing purposes, Andreessen really wanted the name JavaScript.
- 4. History of Javascript • In December 1995, Andreessen got his wish when Netscape obtained a trademark license from Java manufacturer, Sun Microsystems, and LiveScript’s name was changed to JavaScript. • Unfortunately, many, many people over the years have made the mistake of assuming that JavaScript is the same as Java or very close to it. • Don’t be fooled by the name—JavaScript is not all that similar to Java. • Other browser manufacturers support their own versions of JavaScript. • For their Internet Explorer and Edge browsers, Microsoft uses JScript. • For their Chrome browser, Google uses the V8 JavaScript Engine. • Fortunately, all the browser manufacturers attempt to follow the ECMAScript standard, so for most tasks, programmers can write one version of their code and it will work for all the different browsers. Note: ECMA Script or ES is a trademarked scripting language made by ECMA International. The European Computer Manufacture Association or ECMA is used for client-side scripting for the worldwide web.
- 5. The HTML <script> Tag • The HTML <script> tag is used to define a client-side script (JavaScript). • The <script> element either contains script statements, or it points to an external script file through the src attribute. • Common uses for JavaScript are image manipulation, form validation, and dynamic changes of content. • To select an HTML element, JavaScript most often uses the document.getElementById() method. • Statements can be terminated with a semicolon
- 6. Uses of JavaScript • Provide alternative to server-side programming • Servers are often overloaded • Client processing has quicker reaction time • JavaScript can work with forms • JavaScript can interact with the internal model of the web page (Document Object Model) • JavaScript is used to provide more complex user interface than plain forms with HTML/CSS can provide Dr. Asha S Manek
- 7. Event-Driven Computation • Users actions, such as mouse clicks and key presses, are referred to as events • The main task of most JavaScript programs is to respond to events • For example, a JavaScript program could validate data in a form before it is submitted to a server • Caution: It is important that crucial validation be done by the server. It is relatively easy to bypass client-side controls • For example, a user might create a copy of a web page but remove all the validation code. Dr. Asha S Manek
- 8. JavaScript in XHTML • Directly embedded <script type=“text/javascript”> <!-- …Javascript here… --> </script> • Indirect reference <script type=“text/javascript” src=“tst_number.js”/> • This is the preferred approach Dr. Asha S Manek
- 9. Hello World Web Page Fig 5.1: Initial display and what happens after the user clicks the button on the Hello web page
- 10. Buttons • There are different types of buttons, each with its own syntax.,here’s its syntax: <input type="button" value="button-label" onclick="click-event-handler"> • The input element’s most common attributes—type, value, and onclick. • The input element is used for different types of user input, and its type attribute specifies which type of user input. More formally, the type attribute specifies the type of control that’s being implemented, where a control is a user input entity such as a button, text control, or checkbox. • The input element’s value attribute specifies the button’s label. If you don’t provide a value attribute, the button will have no label. • The input element’s onclick attribute specifies the JavaScript instructions that the JavaScript engine executes when the user clicks the button. • Clicking the button is considered to be an event, so the onclick attribute’s JavaScript code is known as an event handler.
- 11. Functions • A function in JavaScript is similar to a mathematical function. A mathematical function receives arguments, performs a calculation, and returns an answer. Ex:sin(x) • The syntax for calling a function: function function-name(zero-or-more-parameters-separated-by- commas) { statement-1; statement-2; … last-statement; } And here’s the displayHello function definition from the Hello web page: • Function definitions should be placed (1) in a script container in the web page’s head container or (2) in an external JavaScript file.
- 12. Variables • Before you use a variable in JavaScript code, use var to declare the variable in a declaration statement, the word var is a keyword. For example: var name; var careerGoals; • In the Hello web page’s function. Here’s the function’s first statement: var msg; • The msg variable will hold a string that forms a message. • The variable will be allowed to hold the type of values like —numbers, strings, and so on. • The variable’s type is determined dynamically by the type of the value that’s assigned into the variable. For example: name = "Mia Hamm"; careerGoals = 158; • JavaScript is known as a loosely typed language, or a dynamically typed language, which means not to declare a variable’s data type explicitly, and assign different types of values into a variable at different times during the execution of a program.
- 13. Identifiers • An identifier is the technical term for a program component’s name—the name of a function. • In the Hello web page, displayHello was the identifier for the function name, and msg was the identifier for a variable. • Rules : 1) Identifiers must consist entirely of letters, digits, dollar signs ($), and/or underscore (_) characters. 2) The first character must not be a digit. • Coding-convention rules are narrower than the preceding rules. Coding conventions suggest that you use letters and digits only, not dollar signs or underscores. • All letters should be lowercase except the first letter in the second word, third word, and so on, few examples: firstName, message, daysInMonth • Coding conventions suggest that you use descriptive words for your identifiers.
- 14. Assignment Statements and Objects • The magic behind how the web page replaces the initial message with “Hello, world!” when the user clicks the button. • The assignment operator (=) assigns the value at the right into a variable at the left. • Each object has a set of related properties, plus a set of behaviors. A property is an attribute of an object. • A behavior is a task that the object can perform. The document object contains properties like the web page’s type. • There’s also an object associated with the entire web page, and that object’s name is document. • To access an object’s property, specify the object name, a dot, and then the property name. ex: document.doctype • One of the document object’s behaviors is its ability to retrieve an element using the element’s id value. The HTML5 standard says that an id attribute’s value must be unique for a particular web page. • In JavaScript (and many other programming languages, as well), an object’s behaviors are referred to as methods. • To call an object’s method, you specify the object name, a dot, the method name, and then parentheses around any arguments you want to pass to the method • To retrieve an element, the document object uses its getElemementById method.
- 15. • Behind the scenes, all of the elements in a web page are represented as objects. When a browser loads the Hello web page, the browser software generates objects for the head element, the body element, the h3 element, and so on. • After msg gets the h3 element’s object, that object gets updated with this assignment statement: msg.outerHTML = "<h1>Hello, world!</h1>"; • Note msg.outerHTML. All element objects have an outerHTML property, which stores the element’s code, including the element’s start and end tags.
- 16. Document Object Model • The Document Object Model, which is normally referred to as the DOM, models all of the parts of a web page document as nodes in a node tree. A node tree is similar to a directory tree. • it shows web page elements that include other elements (and text and attributes). • Each node represents either • (1) an element, • (2) a text item that appears between an element’s start and end tags, Or • (3) an attribute within one of the elements.
- 17. • The DOM provides different ways to access the nodes in the node tree. Here are three common techniques: • 1. Retrieve the node tree’s root by using document (for the document object) in code and then use the root object as a starting point in traversing down the tree. • 2. Retrieve the node that the user just interacted with (e.g. a button that was clicked) and use that node object as a starting point in traversing up or down the tree. • 3. Retrieve a particular element node by calling the document object’s getElementById method with the element’s id value as an argument.
- 18. Forms and How They’re Processed: Client-Side Versus Server-Side • A form is a mechanism for grouping input controls (e.g., buttons, text controls, and checkboxes) within a web page. • To make forms useful, you need to read the user’s input, process it, and display the results. And to do all that, you need JavaScript. • With server-side processing, the form input values are transmitted across the Internet to the server computer. The server then does the calculations and transmits the answers back to the client computer. • With client-side processing, there’s no need to go back and forth across the Internet with user input and generated results. After the web page downloads, the client computer does all the work. Therefore, client-side processing tends to be faster. • Use client-side processing for relatively simple web pages.
- 19. On the other hand, there are several reasons why server-side processing is sometimes preferable: • When the calculations require a lot of programming code. • When the calculations require the use of large amounts of data, which usually means using a database. • When the code is proprietary. • When the inputs and/or calculation results need to be shared by other users. • When user information needs to be processed securely behind the scenes on the server.For example, credit card numbers and passwords should be processed on the server side.
- 20. form Element • the form element, which is in charge of grouping a form’s controls. Here’s a template for the form element’s syntax: <form> label text-box, list-box, check-box, etc. label text-box, list-box, check-box, etc. ... submit-button </form> • The following code implements a form with two text controls and a submit button: <form> First Name: <input type="text" id="first" size="15"><br> Last Name: <input type="text" id="last" size="15"><br><br> <input type="button" value="Generate Email" onclick="generateEmail(this.form);"> </form>
- 21. Reasons to use a form element: • Forms can lead to faster JavaScript processing of the input elements. • Forms provide support for being able to check user input to make sure it follows a particular format. That’s called input validation. • Forms provide the ability to add a reset button to assign all the form controls to their original values. • To implement a reset button, specify reset for the type attribute, like as follows: <input type="reset" value="Reset">
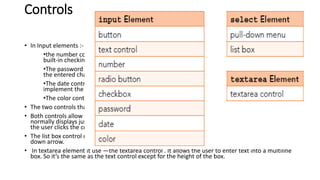
- 22. Controls • In Input elements :- •the number control provides a mechanism for users to enter a number for input, and it has built-in checking to make sure the input is a properly formatted number. •The password control allows the user to enter text into a box where, to help with privacy, the entered characters are obscured. Typically, that means the characters display as bullets. •The date control allows the user to enter a month-day-year value for a date. Most browsers implement the date control with a drop-down calendar where the user picks a date from it. •The color control enables the user to select a color from a color picker tool. • The two controls that use the select element—the pull-down menu and list box controls. • Both controls allow the user to select an item(s) from a list of items. The pull-down menu control normally displays just one item at a time from the list and displays the rest of the list only after the user clicks the control’s down arrow. • The list box control displays multiple list items simultaneously without requiring the user to click a down arrow. • In textarea element it use —the textarea control . It allows the user to enter text into a multiline box. So it’s the same as the text control except for the height of the box.
- 23. Text Control • the text control as a box that a user can enter text into. • template for the text control’s syntax: <input type="text" id="text-box-identifier" placeholder="user-entry-description" size="box-width" maxlength="maximum-typed-characters"> Ex: <input type="text" id="ssn" placeholder="#########" size="9" maxlength="9">
- 24. Accessing a Form’s Control Values • The elements property is a collection of things, and in JavaScript, to access an element within a collection, use []’s. • To access the controls that are within a form, we use the form object’s elements property. The elements property holds a collection of controls, where a collection is a group of items that are of the same type. To access a control within the elements collection, you put quotes around the control’s id value and surround the quoted value with []’s. • After retrieving the control, there’s still one more step need to access the control’s value property. ex: form.elements["first"].value
- 25. <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="author" content="John Dean"> <title>Email Address Generator</title> <script> // This function generates an email address. function generateEmail(form) { document.getElementById("email").innerHTML = form.elements["first"].value + form.elements["last"].value + "@pesce.ac.in"; form.reset(); form.elements["first"].focus(); } // end generateEmail </script> </head> <body> <h3> Enter your first and last names and then click the button. </h3> <form> First Name: <input type="text" id="first" size="15" autofocus> <br> Last Name: <input type="text" id="last" size="15"> <br><br> <input type="button" value="Generate Email" onclick="generateEmail(this.form);"> <p id="email"></p> </body> </form> </html>
- 26. JavaScript Object Properties and HTML Element Attributes : • Text control element attributes: type, placeholder, size, maxlength, value, autofocus, disabled, readonly • Here are the corresponding JavaScript properties for a text control element object: type, placeholder, size, maxLength, value, autofocus, disabled, readOnly Control Elements’ innerHTML Property: • The outerHTML property It accesses the control element’s code, including its start and end tags. • The innerHTML property accesses the content within the control element’s code, not including its start and end tags. • Retrieve the p element’s object and then use its innerHTML property, like as follows: document.getElementById("email").innerHTML EX:
- 27. reset and focus Methods • The form object’s reset method reassigns the form’s controls to their original values. • If suppose web page has no value attributes for its text controls, the reset method call assigns empty strings to the text controls, thereby blanking them out. ex: form.reset(); • An element object calls the focus method, the browser puts the focus on the element’s control if it’s possible to do so. For text control elements, like the first-name text control retrieved in the preceding code,putting the focus on it means the browser positions the cursor in the text control. ex: form.elements["first"].focus();






















![Accessing a Form’s Control Values
• The elements property is a collection of things, and in JavaScript, to
access an element within a collection, use []’s.
• To access the controls that are within a form, we use the form
object’s elements property. The elements property holds a collection
of controls, where a collection is a group of items that are of the same
type. To access a control within the elements collection, you put
quotes around the control’s id value and surround the quoted value
with []’s.
• After retrieving the control, there’s still one more step need to access
the control’s value property.
ex: form.elements["first"].value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-5-240622141518-1b5d2597/85/Introduction-to-JavaScript-functions-DOM-24-320.jpg)
![<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="author" content="John Dean">
<title>Email Address Generator</title>
<script>
// This function generates an email address.
function generateEmail(form) {
document.getElementById("email").innerHTML
= form.elements["first"].value +
form.elements["last"].value + "@pesce.ac.in";
form.reset();
form.elements["first"].focus();
} // end generateEmail
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h3>
Enter your first and last names and then click the
button.
</h3>
<form>
First Name:
<input type="text" id="first" size="15" autofocus>
<br>
Last Name:
<input type="text" id="last" size="15">
<br><br>
<input type="button" value="Generate Email"
onclick="generateEmail(this.form);">
<p id="email"></p>
</body>
</form>
</html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-5-240622141518-1b5d2597/85/Introduction-to-JavaScript-functions-DOM-25-320.jpg)

![reset and focus Methods
• The form object’s reset method reassigns the form’s controls to their
original values.
• If suppose web page has no value attributes for its text controls, the reset
method call assigns empty strings to the text controls, thereby blanking
them out.
ex: form.reset();
• An element object calls the focus method, the browser puts the focus on
the element’s control if it’s possible to do so. For text control elements, like
the first-name text control retrieved in the preceding code,putting the
focus on it means the browser positions the cursor in the text control.
ex: form.elements["first"].focus();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-5-240622141518-1b5d2597/85/Introduction-to-JavaScript-functions-DOM-27-320.jpg)