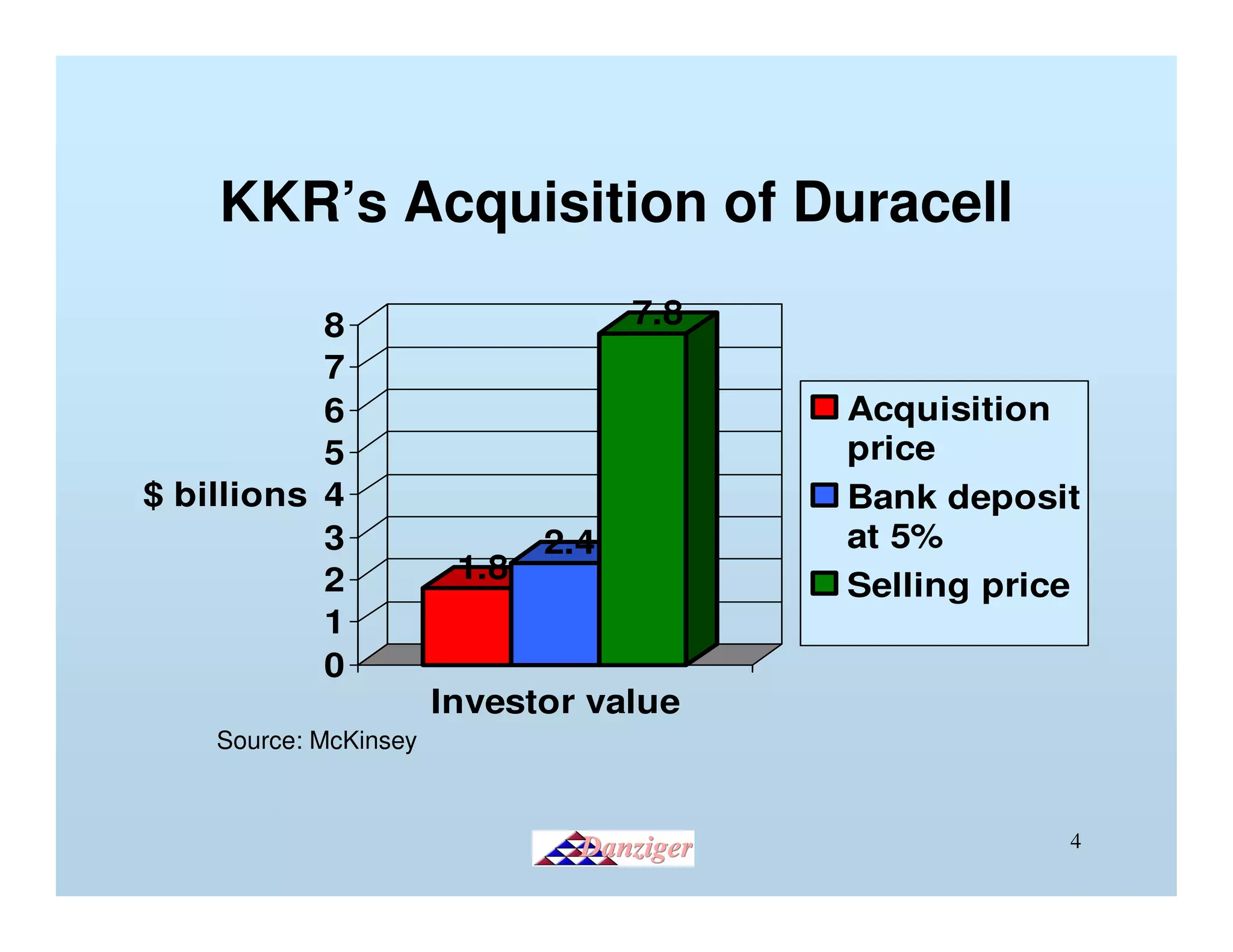
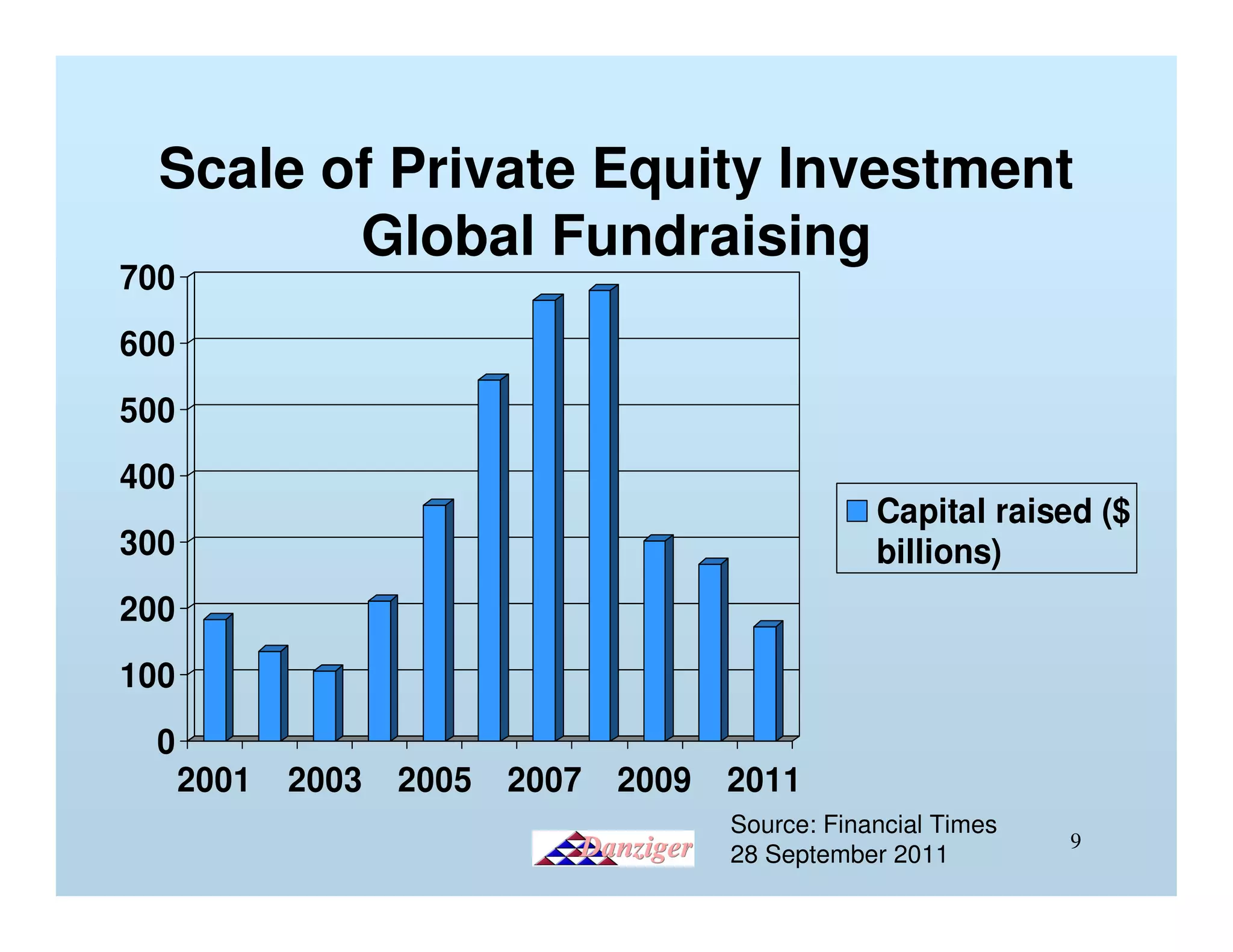
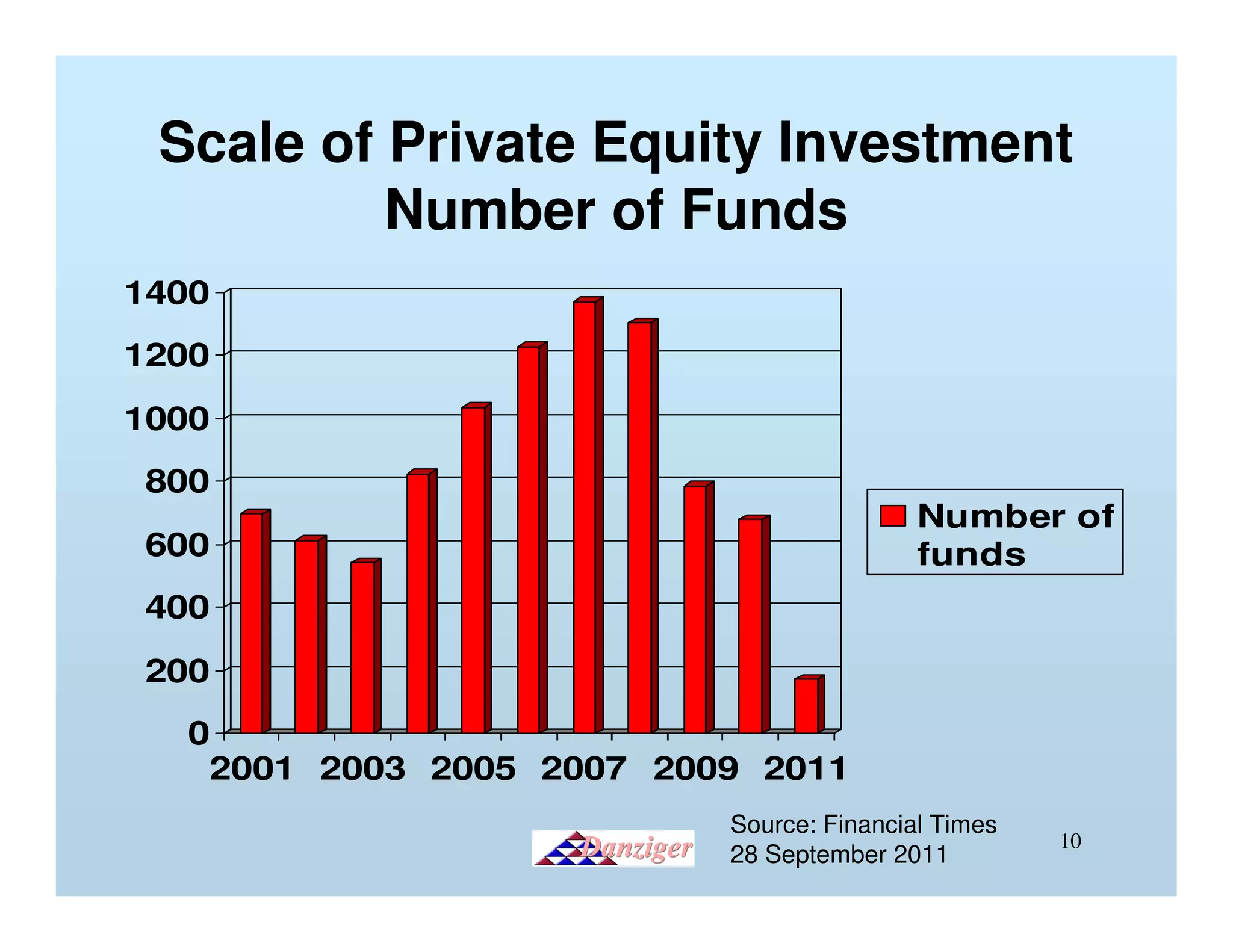
This document provides an introduction to private equity, detailing its definition, distinctions from other investment models, and its impact on corporate performance and investor returns. It highlights the global scale of private equity investments, with a focus on wealth creation and corporate buyouts, supported by statistics and case studies. The presentation emphasizes the operational improvements and efficiency gains realized through private equity strategies.