Java programming Introduction | Java basic architecture
- 1. Fundamental of Java Programming Introduction to Java
- 2. Introduction to Java Java is a general purpose object oriented Programming language. It is developed by Sun Microsystems of USA in 1991. Its original name was Oak given by James Gosling, who is one of the inventors of the language. Java was initially Developed for Softwares for Consumer Electronics Devices like TVs, VCRs, and others.
- 3. The father of Java – James Gosling
- 4. Introduction to Java Java has taken the most popular languages of that time i.e. C and C++ as base by considering its various features and removing their limitations. With this they have develop a most simple, reliable, portable and powerful language.
- 5. History of Java Year Development 1990 Sun Microsystems decided to develop a special software for consumer electronics devices. A Team has been formed to undertake this task. James Gosling was the head of that team. 1991 The team announce a new language called “Oak” 1992 The team known as “Green Project” team, have demonstrated the use of language on a list of home appliances. 1993 World Wide Web (WWW) has given support to Green Project Team and they have started thinking for development of Web Applets 1994 A new Web browser called HotJava has been developed by the Team to run applets. 1995 Oak was rename to Java due to some legal problems. 1996 Sun release Java Development Kit 1.0 (JDK 1.0)
- 6. History of Java Year Development 1997 Sun release JDK 1.1 1998 Sun release Java 2 with JDK 1.2 1999 Sun release J2SE and J2EE 2000 JDK 1.3 2002 JDK 1.4 2004 JDK 1.5 2006 JDK 1.6
- 7. Features to Java Java has various features which makes it simple, secure and compact. They are as follows: (1) Compiled and Interpreted (2) Platform Independent and Portable (3) Object Oriented (4) Secure (5) Distributed (6) Familiar, Simple and Small (7) Multithreaded and Interactive (8) High Performance (9) Dynamic and Extensible
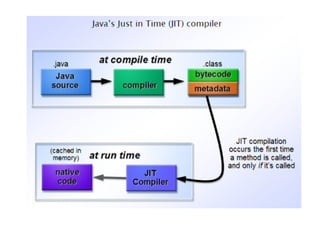
- 8. Features to Java (1) Compiled and Interpreted : •Usually a computer language is either compiled or interpreted. But java combines both the approaches. First java compiler translates the source code into byte code instructions. •Bytecodes are not machine instructions so in second stage, Java Interpreter generates machine code and execute the code. So we can say that java is Compiler and Interpreter.
- 9. Java Program Source Code Java Compiler Virtual Machine Byte Code Virtual Machine Byte Code Phase – I (Compilation) Java Interpreter Output Phase – II (Interpretation)
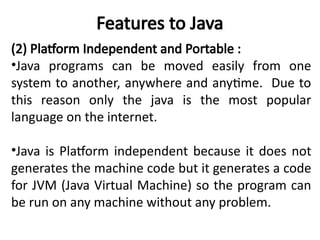
- 10. Features to Java (2) Platform Independent and Portable : •Java programs can be moved easily from one system to another, anywhere and anytime. Due to this reason only the java is the most popular language on the internet. •Java is Platform independent because it does not generates the machine code but it generates a code for JVM (Java Virtual Machine) so the program can be run on any machine without any problem.
- 11. Features to Java (3) Object Oriented : Java is pure Object Oriented Programming Language. Almost everything in java is an object. All programs, codes and data always resides inside the objects and classes.
- 12. Features to Java (4) Secure : Java is a secure language. It has compile time and run time checking for data types. On the other hand java provides the assurance that no viruses will be communicated with applets. One more thing is java does not support pointers so no question of memory address to user.
- 13. Features to Java (5) Distributed : Java is a language developed for distributed language for creating application on networks. It has ability to share both – data and programs. This will allow the programmers at various remote locations to work together on a single project.
- 14. Features to Java (6) Simple, Small and Familiar : Java is simple language because many of the features are from C and C++. Again it removes problems from C and C++. Java is small language because it consist of only Six packages. It is familiar because it looks like C++. In other words we can say “Java is simplified version of C++”.
- 15. Features to Java (7) Multithreaded and Interactive : Multithreading means handling multiple tasks simultaneously. Means that we can do more then one work at a time. E.g. listening music is one work and download from internet is another work is the example of Multithreading. Through java we can develop programs for interactive systems like cellphones, lcds etc.
- 16. Features to Java (8) High Performance : •The performance of Java is quite impressive because it uses compilation and interpretation both. It gives a very much high performance to the java programs. •Java architecture has also reduce the overheads which also improves the performance.
- 17. Features to Java (9) Dynamic and Extensible: Java is dynamic language. It is capable of creating new classes, methods and objects. Java supports functions written in C or C++ also. This is known as native code. This native code will bind with the code dynamically. Java is Extensible because we can define our own classes also which can be added to the pure java language.
- 18. Comparison between C and Java (1) Java does not have struct and union (2) Java does not have pointers (3) Java does not have sizeof or typedef (4) Java does not have preprocessors like #include, #define etc. (5) Java has new operator instanceof (6) Java has various features of OOP which are not there in C
- 19. Comparison between C++ and Java (1) Java does not support Operator Overloading (2) Java does not have template classes (3) Java does not support multiple inheritance instead of that it uses interface (4) Java does not support global variable declaration (5) Java does not use destructor instead of that it uses finalize() method (6) There are no header files in java
- 20. C++ Summary of C, C++ and Java C Java
- 21. Process of Building and Running Java Application Text Editor Java Source Code javac (Compiler) Java class file java (Interpreter) Java Program Output
- 22. JAVA ENVIRONMENT
- 23. Three Components • JDK - Java Development Kit • JVM – Java Virtual Machine • JRE – Java Runtime Environment
- 24. JDK • Writing Java applets and applications needs development tools like JDK. • Java developers are initially presented with two JDK tools, java and javac. • Both are run from the command prompt. • It's easy for both new and experienced programmers to get started.
- 25. JDK Architecture
- 26. JRE • JRE is an acronym for Java Runtime Environment. • It is also written as Java RTE. • The Java Runtime Environment is a set of software tools • It physically exists. • It contains a set of libraries + other files that JVM uses at runtime.
- 27. JRE Architecture
- 28. JVM • Java compiler produces code for a Virtual Machine known as Java Virtual Machine. • JVM converts Java byte code into machines language. • JVM is a engine that provides runtime environment to drive the Java Code or applications.
- 33. Popular Java Editors • To write your Java programs, you will need a text editor. There are even more sophisticated IDEs available in the market. − • Notepad − On Windows machine, you can use any simple text editor like Notepad (Recommended for this tutorial), TextPad. • Netbeans − A Java IDE that is open-source and free which can be downloaded from https://www.netbeans.org/index.html. • Eclipse − A Java IDE developed by the eclipse open-source community and can be downloaded from https://www.eclipse.org/.