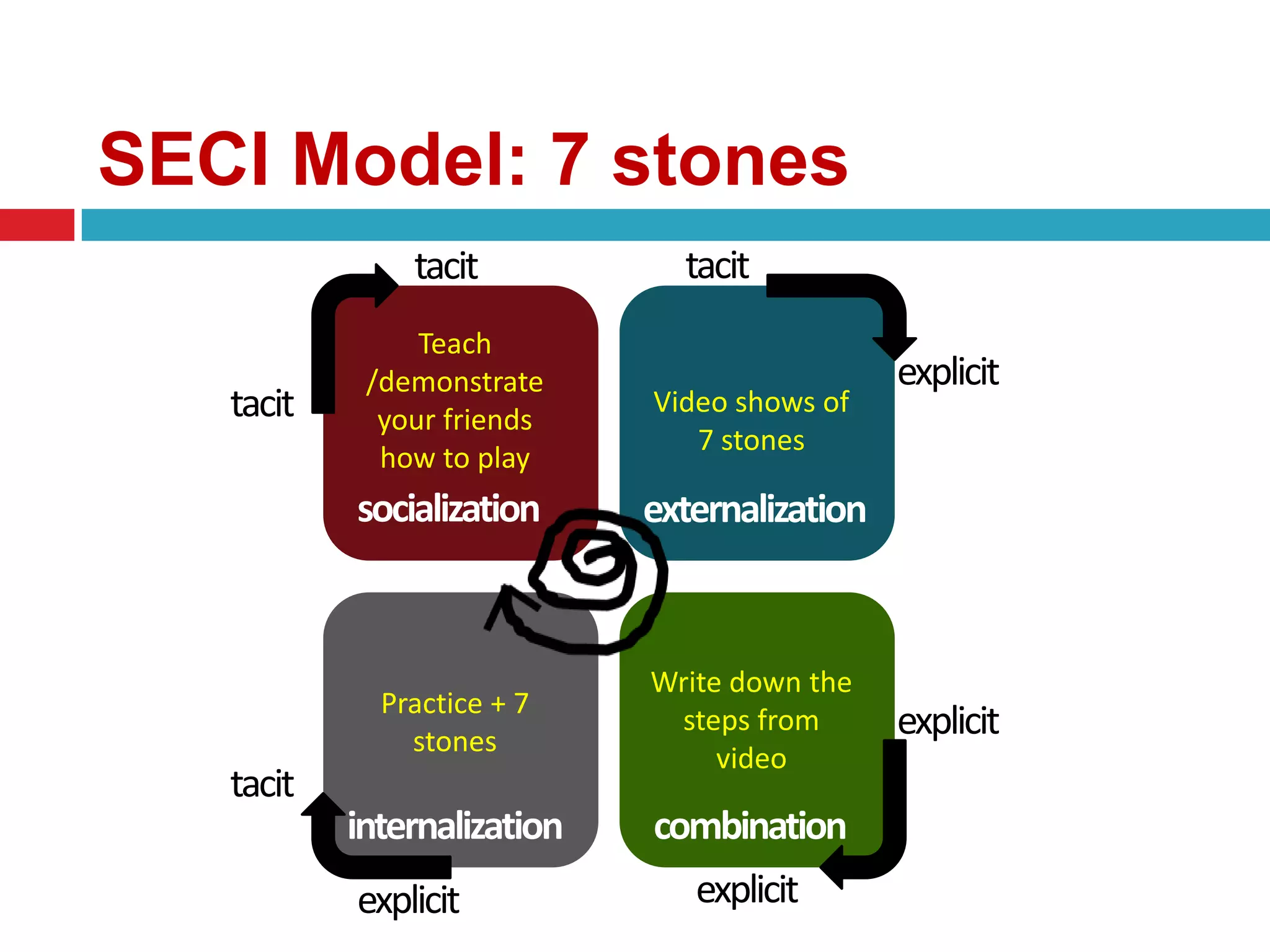
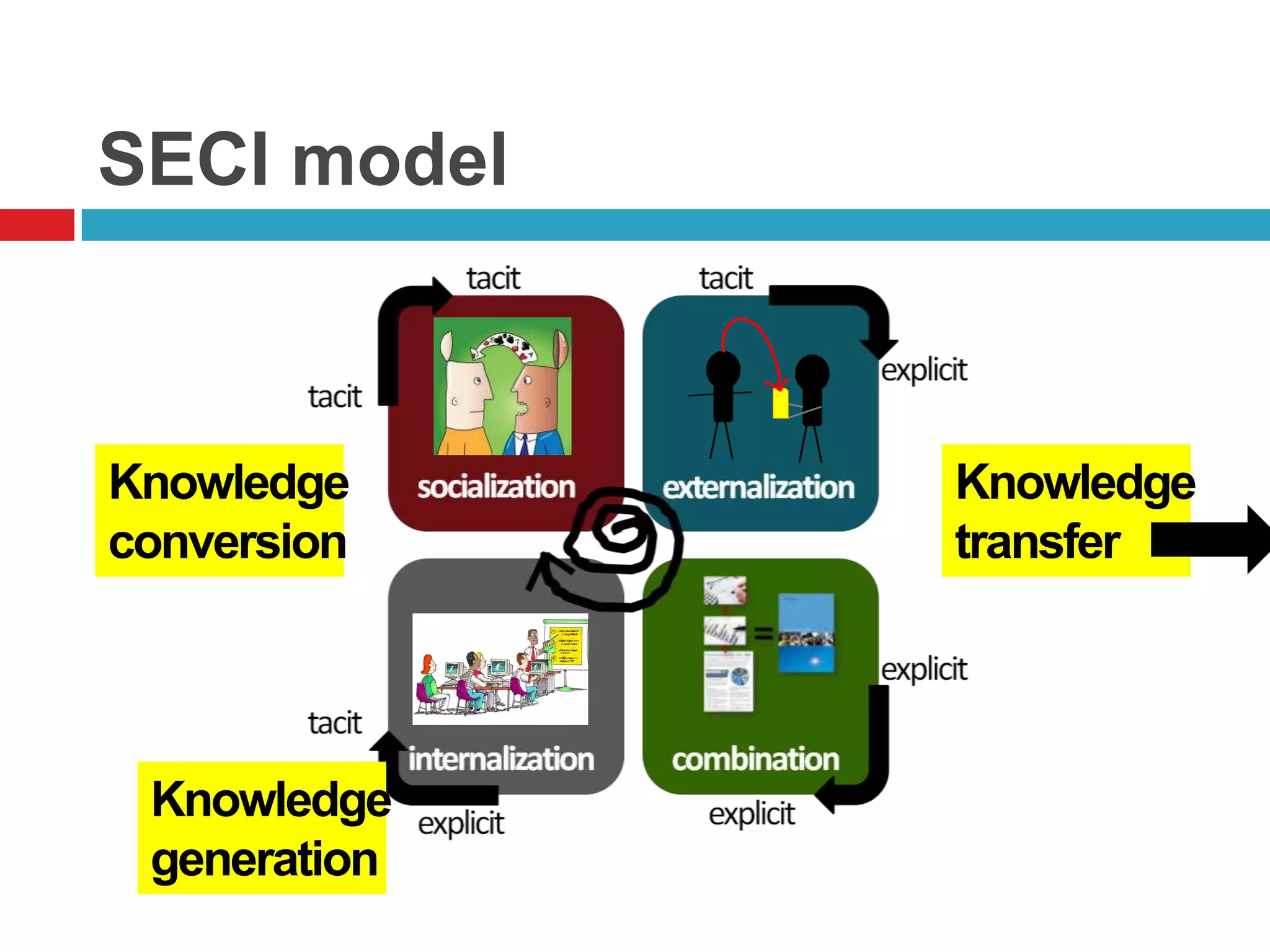
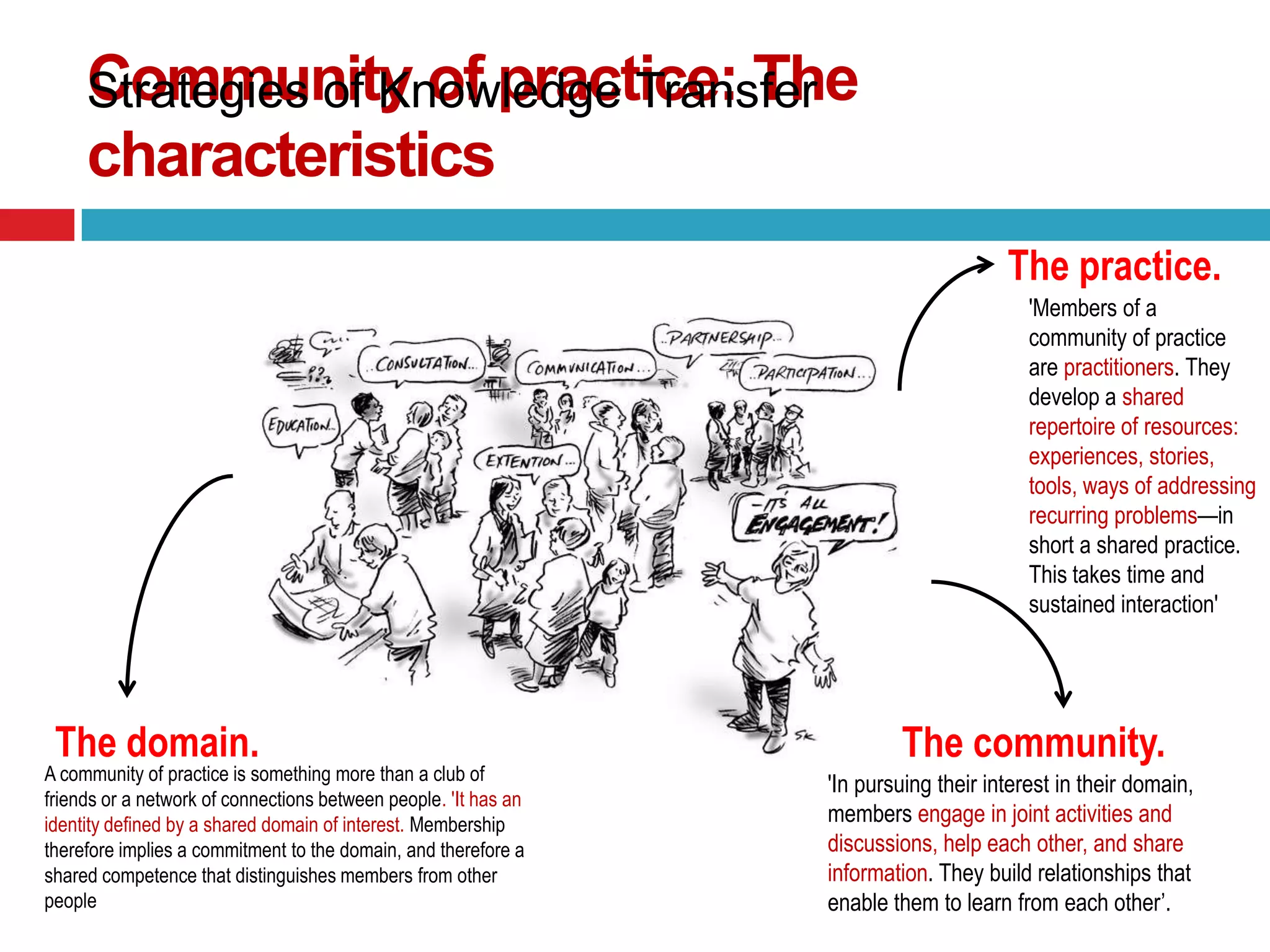
The document discusses different types of knowledge and strategies for knowledge transfer. It describes explicit knowledge as being easily codified and communicated, while tacit knowledge is difficult to articulate and usually learned through demonstration. The SECI model of knowledge conversion is introduced, which shows how knowledge is transformed between its tacit and explicit forms through socialization, externalization, combination, and internalization. Common strategies for knowledge transfer discussed include best practices, communities of practice, and electronic technologies. The goal of knowledge transfer is facilitating organizational learning by sharing what is learned in one part of an organization with other parts.