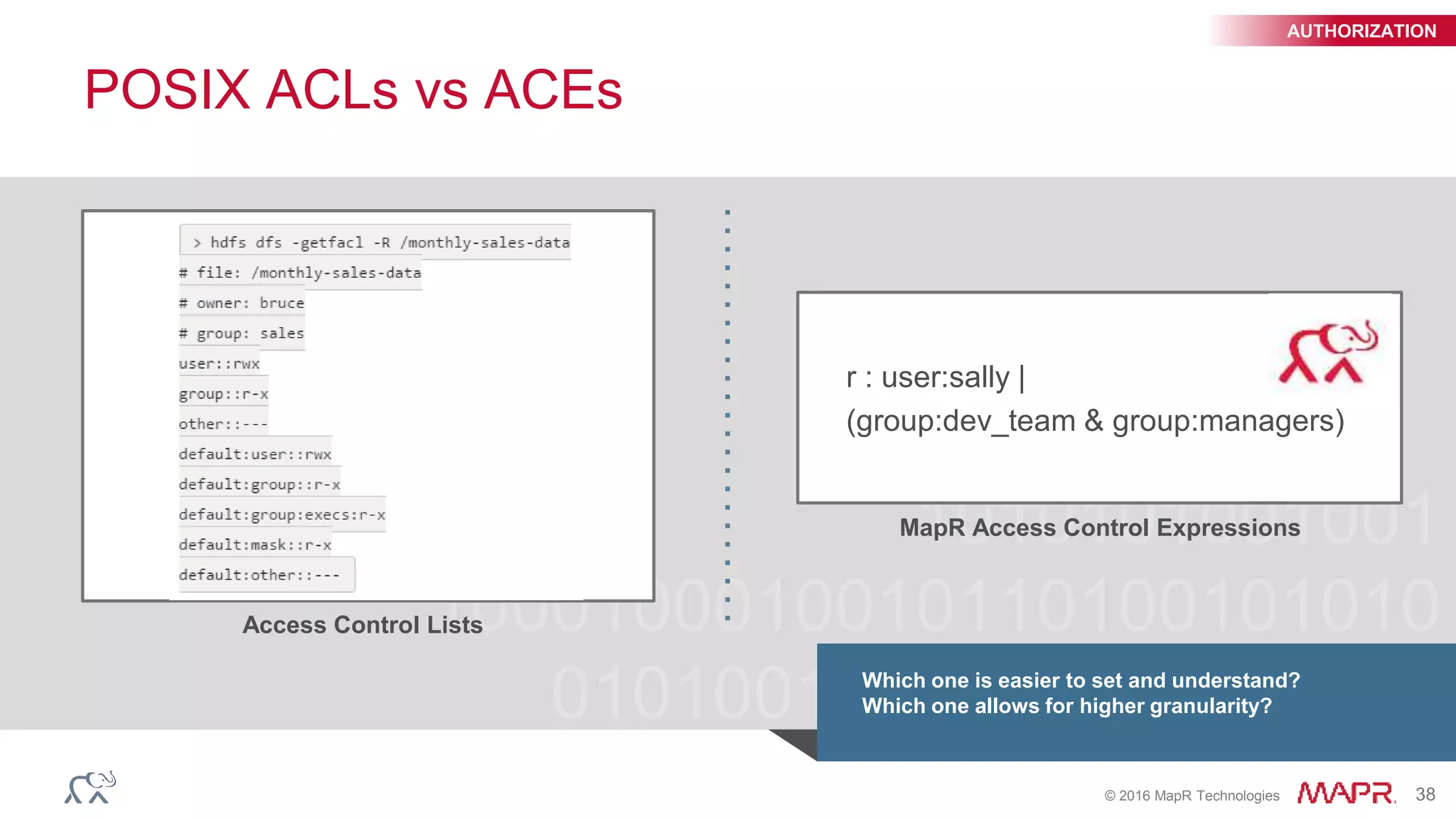
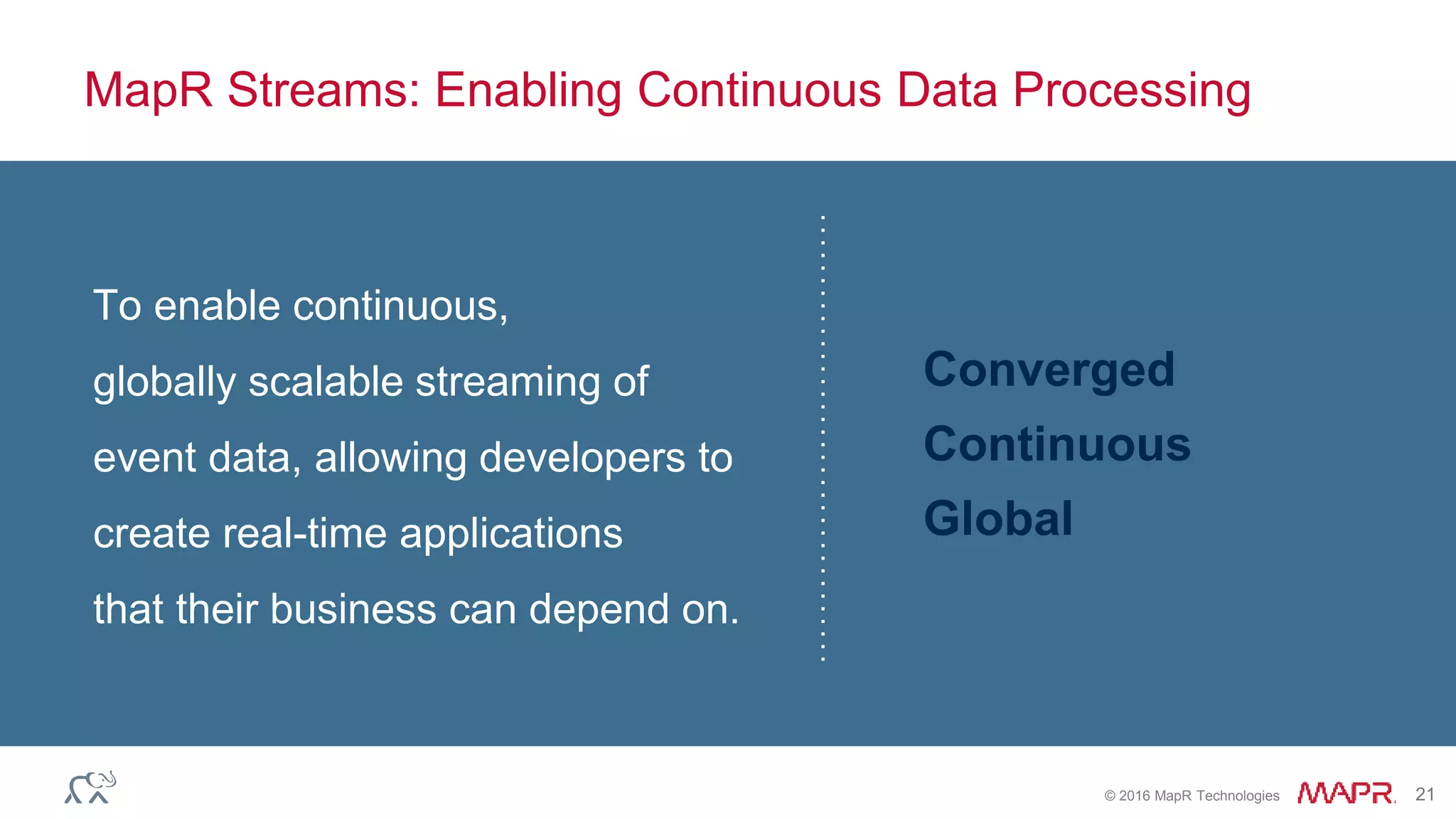
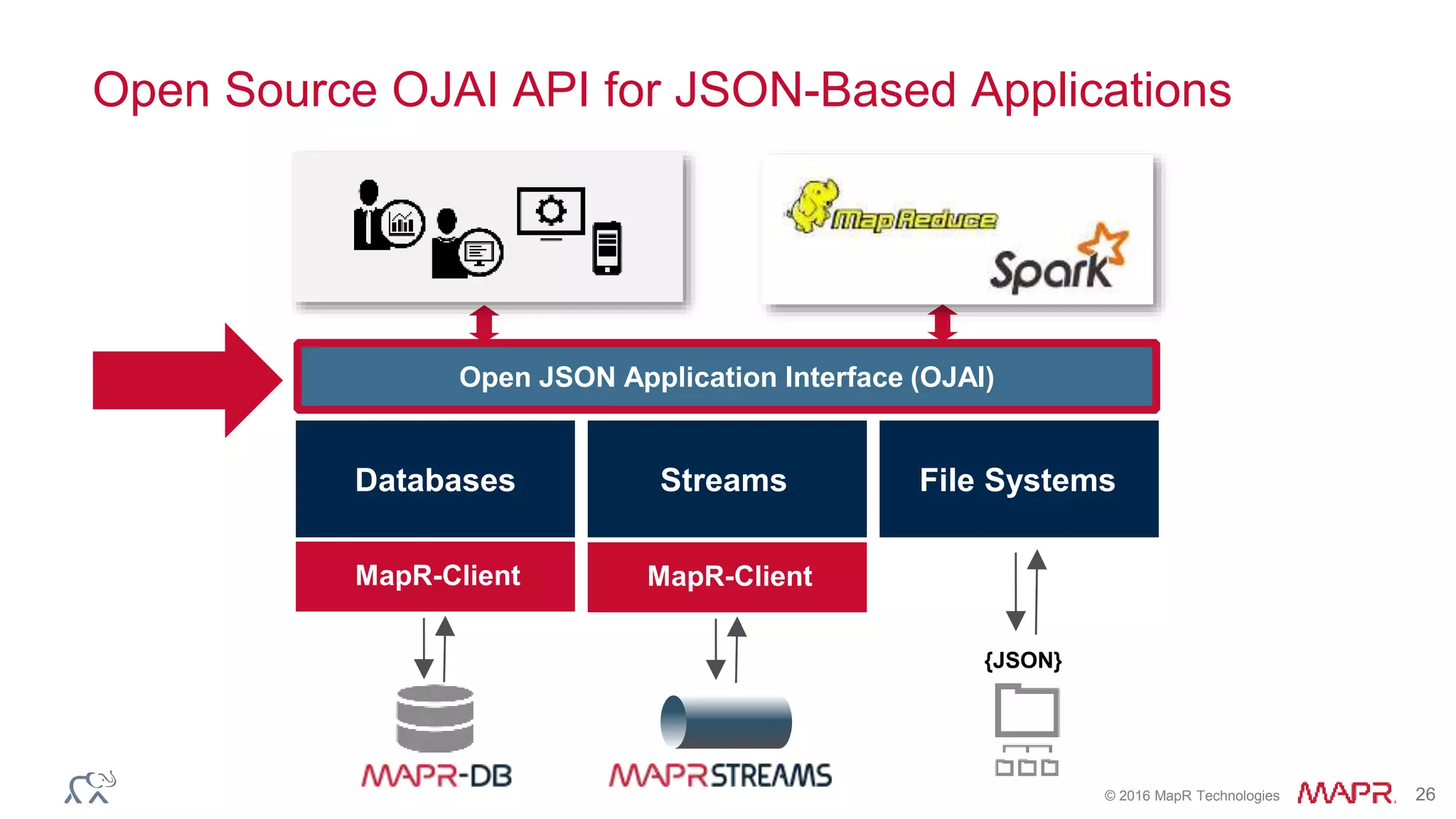
The document outlines key updates and features of the MapR Converged Data Platform with version 5.2, including improvements to cluster monitoring through the Spyglass initiative, support for real-time streaming via MapR Streams, and development capabilities with MapR-DB and OJAI API. It emphasizes enhanced data security through Access Control Expressions (ACEs) and the integration of SQL with JSON data via Apache Drill. The presentation provides an overview of system capabilities, ecosystem updates, and tools to streamline big data management.























![© 2016 MapR Technologies 28
JSON: Easy Variation with Documents
{
"_id" : "rp-prod132546",
"name" : "Marvel T2 Athena”,
"brand" : "Pinarello",
"category" : "bike",
"type" : "Road Bike”,
"price" : 2949.99,
"size" : "55cm",
"wheel_size" : "700c",
"frameset" : {
"frame" : "Carbon Toryaca",
"fork" : "Onda 2V C"
},
"groupset" : {
"chainset" : "Camp. Athena 50/34",
"brake" : "Camp."
},
"wheelset" : {
"wheels" : "Camp. Zonda",
"tyres" : "Vittoria Pro"
}
}
{
"_id" : "rp-prod106702",
"name" : " Ultegra SPD-SL 6800”,
"brand" : "Shimano",
"category" : "pedals",
"type" : "Components,
"price" : 112.99,
"features" : [
"Low profile design increases ...",
"Supplied with floating SH11 cleats",
"Weight: 260g (pair)"
]
}
{
"_id" : "rp-prod113104",
"name" : "Bianchi Pride Jersey SS15”,
"brand" : "Nalini",
"category" : "Jersey",
"type" : "Clothing,
"price" : 76.99,
"features" : [
"100% Polyester",
"3/4 hidden zip",
"3 rear pocket"
],
"color" : "black"
}
jerseypedalbike](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communityupgradewebinar-160921170427/75/MapR-5-2-Getting-More-Value-from-the-MapR-Converged-Community-Edition-28-2048.jpg)


![© 2016 MapR Technologies 31
Native JSON Support in MapR-DB
{
order_num: 5555,
products: [
{ product_id: 348752,
quantity: 1,
unit_price: 149.99,
total_price: 149.99
},
{ product_id: 439322,
quantity: 1,
unit_price: 99.99,
total_price: 99.99
},
{ product_id: 953923,
quantity: 1,
unit_price: 49.99,
total_price: 49.99
},
]
}
Reads/writes at element level
• Granular disk reads/writes
• Less network traffic
• Higher concurrency
Any new elements added on demand
• No predefined schemas
• Easy to store evolving data
Not all NoSQL databases treat JSON as a native data type.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communityupgradewebinar-160921170427/75/MapR-5-2-Getting-More-Value-from-the-MapR-Converged-Community-Edition-31-2048.jpg)
![© 2016 MapR Technologies 32
Leverage the Column Family Construct (Optional)
/
{a:
{a1:
{b1: "v1",
b2: [
{c1: "v1",
c2: "v2"}
]
},
a2:
{
e1: "v1",
e2: <inline jpg>
}
}
}
Column Family 1
Column Family 2
Control layout for faster data access
Different TTL requirements
Separate Table Replication settings
Specific data placement policies
Efficient ACEs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communityupgradewebinar-160921170427/75/MapR-5-2-Getting-More-Value-from-the-MapR-Converged-Community-Edition-32-2048.jpg)
![© 2016 MapR Technologies 33
Fine Grained Security for JSON Documents
{
“fname”: “John”,
“lname”: “Doe”,
“address”: “111 Main St.”,
“city”: “San Jose”,
“state”: “CA”,
“zip”: “95134”,
“credit_cards”: [
{“issuer”: “Visa”,
“number”: “4444555566667777”},
{“issuer”: “MasterCard”,
“number”: “5555666677778888”}
]
}
Entire document
Element: “fname”
Array: “credit_cards”
Sub-element in array element:
“credit_cards[*].number”
Specify different permissions levels within the document.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communityupgradewebinar-160921170427/75/MapR-5-2-Getting-More-Value-from-the-MapR-Converged-Community-Edition-33-2048.jpg)