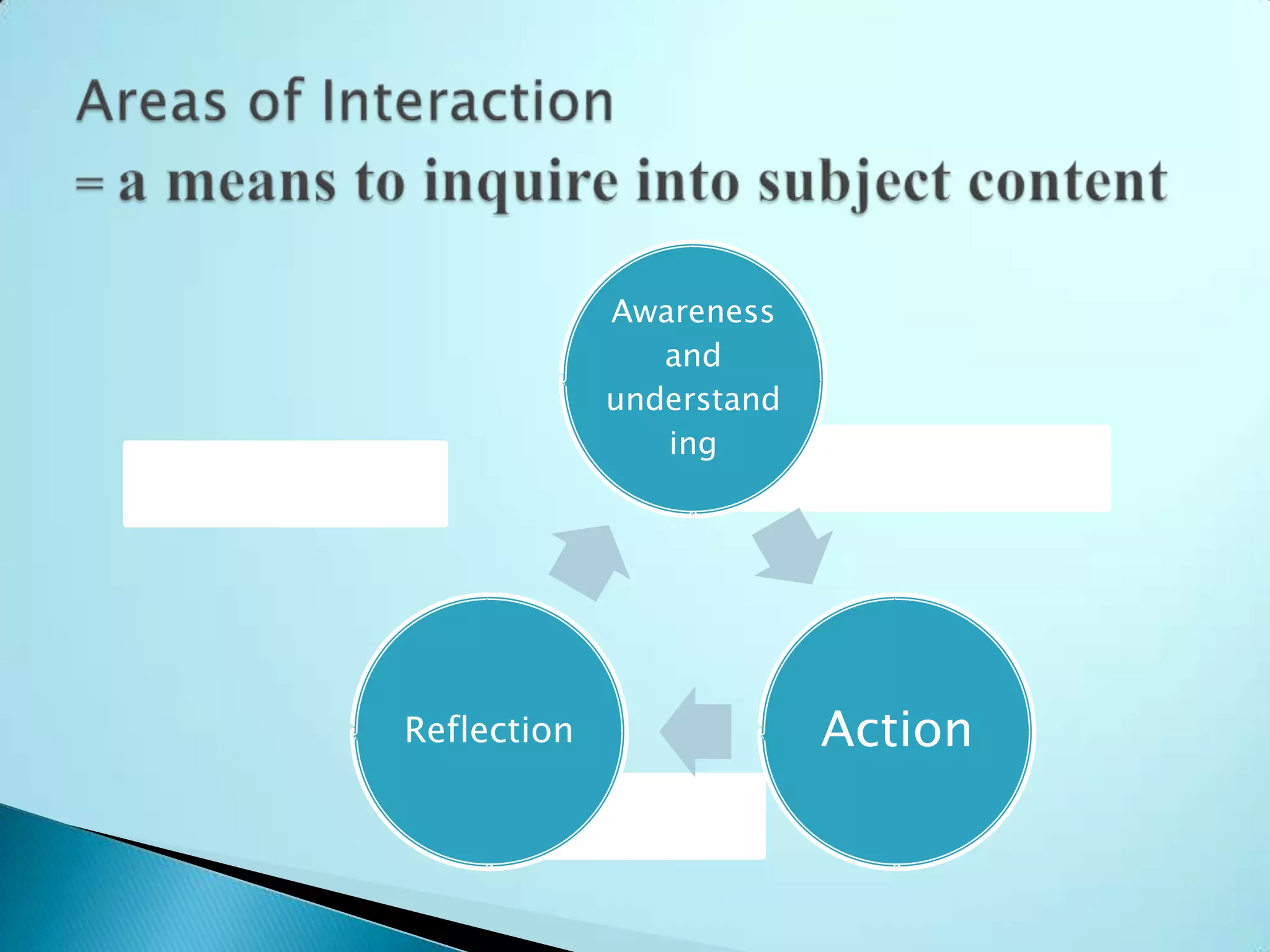
The document discusses the International Baccalaureate (IB) Middle Years Programme (MYP). It provides an overview of the MYP framework which focuses on global contexts for learning, approaches to teaching, areas of interaction and learner profile attributes. It emphasizes developing students as inquirers, knowledgeable, thinkers, communicators, principled, open-minded, caring, risk-takers, balanced, and reflective. Assessment in the MYP aims to support and encourage student learning through various strategies and tasks.