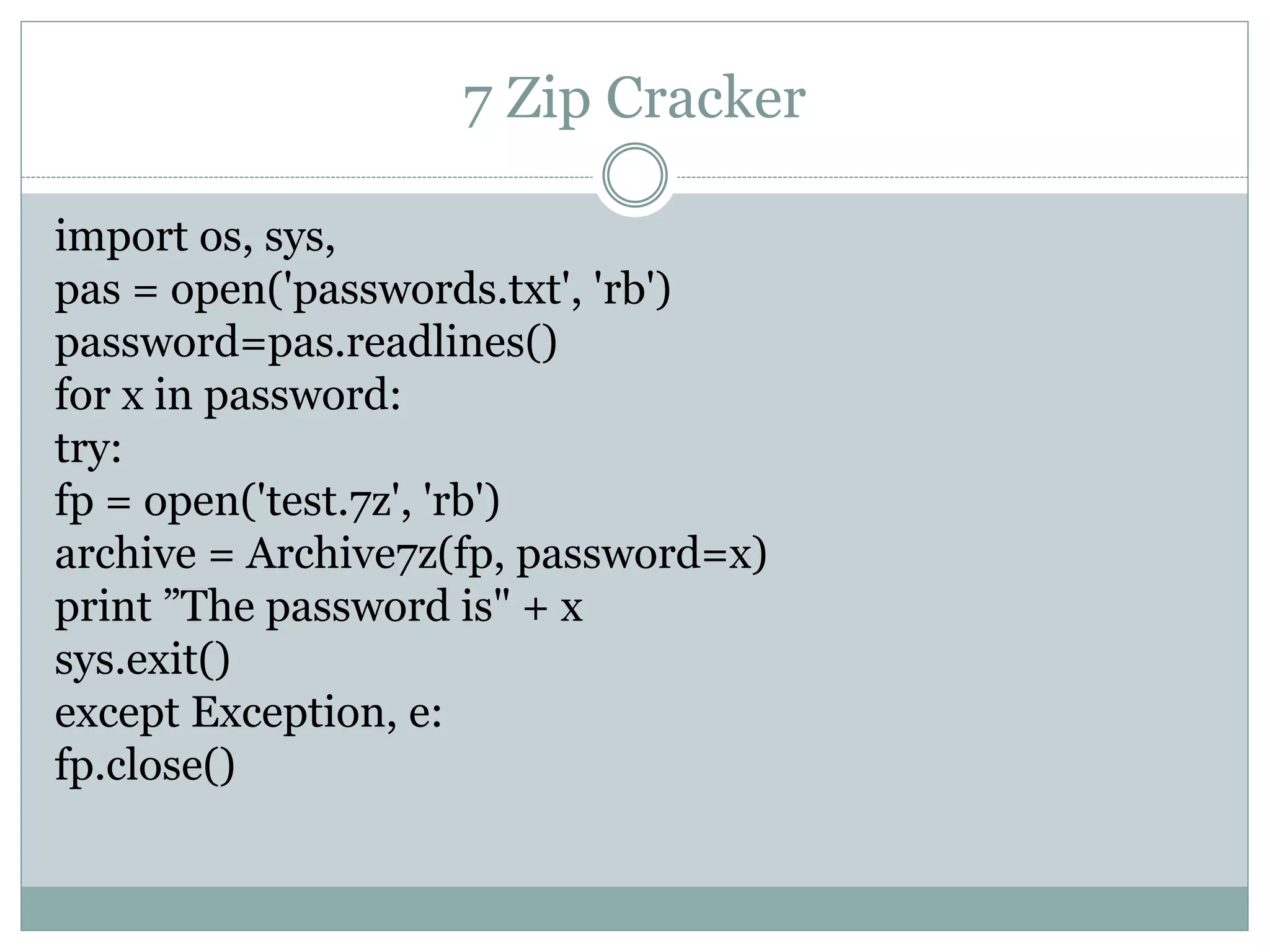
This document provides an overview of Python pen-testing techniques. It discusses why Python is useful for pen testing due to its ease of use, large library of modules, and multiplatform support. A brief history of Python and examples of common data types, code snippets, libraries like urllib2 and win32com, and techniques like fuzzing, encoding, password cracking, and WMI are also presented.



![Data Types
Data types:
Strings - “Hello”
Numbers – 123
Lists – [‘hello’,’2’,’1’]
Tuples - (‘1’,’2’,’3’) (immutable)
Dictionaries – d = {‘key1’:’dog’,’key2’:’cat’}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pentestusingpython-150111234148-conversion-gate01/75/Penetration-testing-using-python-6-2048.jpg)