The document provides an extensive overview of Python programming basics, including its features such as being interpreted, interactive, and object-oriented. It covers the Python interpreter, modes of operation, data types, variables, and operators, along with examples of how to manipulate strings, lists, and tuples. Additional topics include comments, expressions, statements, input/output functions, and type conversion.


















![Indexing
String A H E L L 0
Positive Index 0 1 2 3 4
Negative Index -5 -4 -3 -2 -1
Example: A[0] or A[-5] will display “H”
Example: A[1] or A[-4] will display “E”
Str=‘Python Program’
Str[-3]
Str[3]
Str[6]
Str[7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u2-241127050436-7296f597/85/Python-unit-2-is-added-Has-python-related-programming-content-19-320.jpg)




![• str='hello w'
• print(len(str))
• 7
• print(str[:])
• hello w
• print(str[::2])
• Hlow
• print(str[::-1])
• w olleh](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u2-241127050436-7296f597/85/Python-unit-2-is-added-Has-python-related-programming-content-24-320.jpg)
![Example
• Consider the string S=“Python Programming”
• Predict the output:
• s[-1]
• S[6:12]
• S[:4]
• S[:]
• S[5:5] , s[9:] ,s[0:5] , len(s)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u2-241127050436-7296f597/85/Python-unit-2-is-added-Has-python-related-programming-content-25-320.jpg)



![Lists
• List is an ordered sequence of items. Values in the list
are called elements / items.
• It can be written as a list of comma-separated items
(values) between square brackets[ ].
• Items in the lists can be of different data types.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u2-241127050436-7296f597/85/Python-unit-2-is-added-Has-python-related-programming-content-29-320.jpg)





























![Membership Operators
• Evaluates to find a value or a variable is in the specified sequence
of string, list, tuple, dictionary or not.
• Let, x=[5,3,6,4,1]. To check particular item in list or not, in and not in
operators are used.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u2-241127050436-7296f597/85/Python-unit-2-is-added-Has-python-related-programming-content-60-320.jpg)




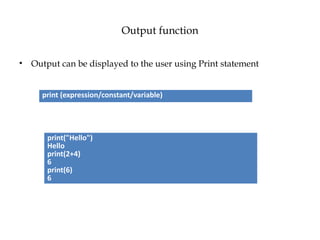





![• Celsius to Fahrenheit:
F = [(C*9/5) +32]
• convert kilometers to miles
Miles=0.62*km](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u2-241127050436-7296f597/85/Python-unit-2-is-added-Has-python-related-programming-content-71-320.jpg)