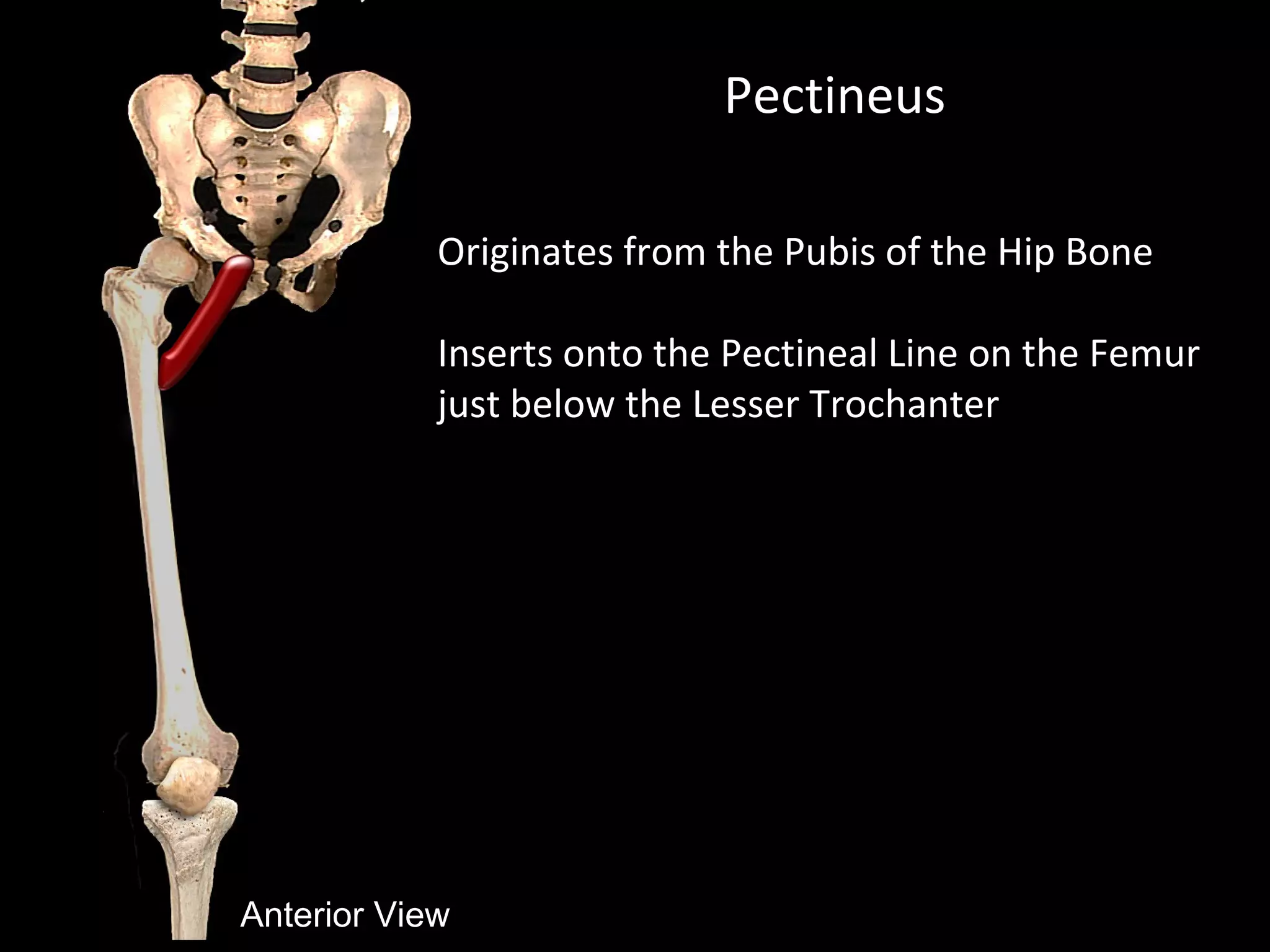
The document discusses the anatomical divisions of the thigh, specifically focusing on the three functional compartments: anterior (extensor), medial (adductor), and posterior (flexor). It details the muscles located within the adductor compartment, including the gracilis, adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus, and pectineus, along with their origins, insertions, actions, and nerve supplies. Additionally, it briefly mentions the hamstring muscles found in the posterior compartment.