Stanford CS347 Guest Lecture: Apache Spark
- 1. Stanford CS347 Guest Lecture Spark Reynold Xin @rxin Guest lecture, May 18, 2015, Stanford
- 2. Who am I? Reynold Xin Spark PMC member Databricks cofounder & architect UC Berkeley AMPLab PhD (on leave) 2
- 3. Agenda 1. MapReduce Review 2. Introduction to Spark and RDDs 3. Generality of RDDs (e.g. streaming, ML) 4. DataFrames 5. Internals (time permitting) 3
- 4. Agenda 1. MapReduce Review 2. Introduction to Spark and RDDs 3. Generality of RDDs (e.g. streaming, ML) 4. DataFrames 5. Internals (time permitting) 4
- 5. Google Datacenter How do we program this thing? 5
- 6. Traditional Network Programming Message-passing between nodes (MPI, RPC, etc) Really hard to do at scale: • How to split problem across nodes? – Important to consider network and data locality • How to deal with failures? – If a typical server fails every 3 years, a 10,000-node cluster sees 10 faults/day! • Even without failures: stragglers (a node is slow) Almost nobody does this! 6
- 7. Data-Parallel Models Restrict the programming interface so that the system can do more automatically “Here’s an operation, run it on all of the data” • I don’t care where it runs (you schedule that) • In fact, feel free to run it twice on different nodes 7
- 8. MapReduce Programming Model Data type: key-value records Map function: (Kin, Vin) -> list(Kinter, Vinter) Reduce function: (Kinter, list(Vinter)) -> list(Kout, Vout) 8
- 9. MapReduce Programmability Most real applications require multiple MR steps • Google indexing pipeline: 21 steps • Analytics queries (e.g. count clicks & top K): 2 – 5 steps • Iterative algorithms (e.g. PageRank): 10’s of steps Multi-step jobs create spaghetti code • 21 MR steps -> 21 mapper and reducer classes • Lots of boilerplate code per step 9
- 10. 10
- 11. Problems with MapReduce MapReduce use cases showed two major limitations: 1. difficulty of programming directly in MR. 2. Performance bottlenecks In short, MR doesn’t compose well for large applications Therefore, people built high level frameworks and specialized systems. 11
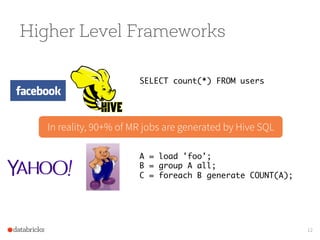
- 12. Higher Level Frameworks SELECT count(*) FROM users A = load 'foo'; B = group A all; C = foreach B generate COUNT(A); In reality, 90+% of MR jobs are generated by Hive SQL 12
- 13. Specialized Systems MapReduce General Batch Processing Specialized Systems: iterative, interactive, streaming, graph, etc. Pregel Giraph Dremel Drill Tez Impala GraphLab StormS4 F1 MillWheel 13
- 14. Agenda 1. MapReduce Review 2. Introduction to Spark and RDDs 3. Generality of RDDs (e.g. streaming, ML) 4. DataFrames 5. Internals (time permitting) 14
- 15. Spark: A Brief History 15 2002 2002 MapReduce @ Google 2004 MapReduce paper 2006 Hadoop @Yahoo! 2004 2006 2008 2010 2012 2014 2014 Apache Spark top-level 2010 Spark paper 2008 Hadoop Summit
- 16. Spark Summary Unlike the various specialized systems, Spark’s goal was to generalize MapReduce to support new apps Two small additions are enough: • fast data sharing • general DAGs More efficient engine, and simpler for the end users. 16
- 18. Note: not a scientific comparison.
- 19. Programmability 19 WordCount in 50+ lines of Java MR WordCount in 3 lines of Spark
- 20. Performance Time to sort 100TB 2100 machines2013 Record: Hadoop 2014 Record: Spark Source: Daytona GraySort benchmark, sortbenchmark.org 72 minutes 207 machines 23 minutes Also sorted 1PB in 4 hours 20
- 21. RDD: Core Abstraction Resilient Distributed Datasets • Collections of objects spread across a cluster, stored in RAM or on Disk • Built through parallel transformations • Automatically rebuilt on failure Operations • Transformations (e.g. map, filter, groupBy) • Actions (e.g. count, collect, save) Write programs in terms of distributed datasets and operations on them
- 22. RDD Resilient Distributed Datasets are the primary abstraction in Spark – a fault-tolerant collection of elements that can be operated on in parallel Two types: • parallelized collections – take an existing single-node collection and parallel it • Hadoop datasets: files on HDFS or other compatible storage 22
- 23. Operations on RDDs Transformations f(RDD) => RDD § Lazy (not computed immediately) § E.g. “map” Actions: § Triggers computation § E.g. “count”, “saveAsTextFile” 23
- 24. Working With RDDs RDD textFile = sc.textFile(”SomeFile.txt”)!
- 25. Working With RDDs RDD RDD RDD RDD Transformations linesWithSpark = textFile.filter(lambda line: "Spark” in line)! textFile = sc.textFile(”SomeFile.txt”)!
- 26. Working With RDDs RDD RDD RDD RDD Transformations Action Value linesWithSpark = textFile.filter(lambda line: "Spark” in line)! linesWithSpark.count()! 74! ! linesWithSpark.first()! # Apache Spark! textFile = sc.textFile(”SomeFile.txt”)!
- 27. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns
- 28. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns Worker Worker Worker Driver
- 29. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns Worker Worker Worker Driver lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
- 30. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns Worker Worker Worker Driver lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) Base RDD
- 31. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) Worker Worker Worker Driver
- 32. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) Worker Worker Worker Driver Transformed RDD
- 33. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker Driver messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
- 34. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker Driver messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Ac5on
- 35. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker Driver messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3
- 36. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Driver tasks tasks tasks
- 37. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Driver Read HDFS Block Read HDFS Block Read HDFS Block
- 38. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Driver Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 Process & Cache Data Process & Cache Data Process & Cache Data
- 39. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Driver Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 results results results
- 40. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Driver Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()
- 41. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count() tasks tasks tasks Driver
- 42. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count() Driver Process from Cache Process from Cache Process from Cache
- 43. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count() Driver results results results
- 44. Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count() Driver Cache your data è Faster Results Full-text search of Wikipedia • 60GB on 20 EC2 machines • 0.5 sec from mem vs. 20s for on-disk
- 45. Language Support Standalone Programs Python, Scala, & Java Interactive Shells Python & Scala Performance Java & Scala are faster due to static typing …but Python is often fine Python lines = sc.textFile(...) lines.filter(lambda s: “ERROR” in s).count() Scala val lines = sc.textFile(...) lines.filter(x => x.contains(“ERROR”)).count() Java JavaRDD<String> lines = sc.textFile(...); lines.filter(new Function<String, Boolean>() { Boolean call(String s) { return s.contains(“error”); } }).count();
- 48. Fault Recovery RDDs track lineage information that can be used to efficiently reconstruct lost partitions Ex: messages = textFile(...).filter(_.startsWith(“ERROR”)) .map(_.split(‘t’)(2)) HDFS File Filtered RDD Mapped RDD filter (func = _.contains(...)) map (func = _.split(...))
- 49. Fault Recovery Results 119 57 56 58 58 81 57 59 57 59 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Iteratrion time (s) Iteration Failure happens
- 50. Example: Logistic Regression Goal: find best line separating two sets of points + – + + + + + + + + – – – – – – – – + target – random initial line
- 51. Example: Logistic Regression val data = spark.textFile(...).map(readPoint).cache() var w = Vector.random(D) for (i <- 1 to ITERATIONS) { val gradient = data.map(p => (1 / (1 + exp(-p.y*(w dot p.x))) - 1) * p.y * p.x ).reduce(_ + _) w -= gradient } println("Final w: " + w) w automa5cally shipped to cluster
- 52. LR/K-Means Performance 0.96 110 0 25 50 75 100 125 Logistic Regression 4.1 155 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 K-Means Clustering Hadoop MR Spark Time per Iteration (s) 10B points
- 53. Agenda 1. MapReduce Review 2. Introduction to Spark and RDDs 3. Generality of RDDs (e.g. streaming, ML) 4. DataFrames 5. Internals (time permitting) 53
- 54. Generality of RDDs Spark Spark Streaming real-‐time Spark SQL SQL GraphX graph MLLib machine learning …
- 55. Generality of RDDs Spark RDDs, Transformations, and Actions Spark Streaming real-‐time Spark SQL GraphX graph MLLib machine learning DStream’s: Streams of RDD’s SchemaRDD’s RDD-‐Based Matrices RDD-‐Based Graphs
- 56. Many important apps must process large data streams at second-scale latencies • Site statistics, intrusion detection, online ML To build and scale these apps users want: • Integration: with offline analytical stack • Fault-tolerance: both for crashes and stragglers • Efficiency: low cost beyond base processing Spark Streaming: Motivation
- 57. Discretized Stream Processing t = 1: t = 2: stream 1 stream 2 batch opera5on pull input … … input immutable dataset (stored reliably) immutable dataset (output or state); stored in memory as RDD …
- 58. Programming Interface Simple functional API views = readStream("http:...", "1s") ones = views.map(ev => (ev.url, 1)) counts = ones.runningReduce(_ + _) Interoperates with RDDs ! // Join stream with static RDD counts.join(historicCounts).map(...) ! // Ad-hoc queries on stream state counts.slice(“21:00”,“21:05”).topK(10) t = 1: t = 2: views ones counts map reduce . . . = RDD = partition
- 59. Inherited “for free” from Spark RDD data model and API Data partitioning and shuffles Task scheduling Monitoring/instrumentation Scheduling and resource allocation
- 60. 0 20000 40000 60000 80000 100000 120000 140000 Hadoop MapReduce Storm (Streaming) Impala (SQL) Giraph (Graph) Spark non-test, non-example source lines Powerful Stack – Agile Development
- 61. 0 20000 40000 60000 80000 100000 120000 140000 Hadoop MapReduce Storm (Streaming) Impala (SQL) Giraph (Graph) Spark non-test, non-example source lines Streaming Powerful Stack – Agile Development
- 62. 0 20000 40000 60000 80000 100000 120000 140000 Hadoop MapReduce Storm (Streaming) Impala (SQL) Giraph (Graph) Spark non-test, non-example source lines SparkSQL Streaming Powerful Stack – Agile Development
- 63. Powerful Stack – Agile Development 0 20000 40000 60000 80000 100000 120000 140000 Hadoop MapReduce Storm (Streaming) Impala (SQL) Giraph (Graph) Spark non-test, non-example source lines GraphX Streaming SparkSQL
- 64. Powerful Stack – Agile Development 0 20000 40000 60000 80000 100000 120000 140000 Hadoop MapReduce Storm (Streaming) Impala (SQL) Giraph (Graph) Spark non-test, non-example source lines GraphX Streaming SparkSQL Your App?
- 65. Benefits for Users High performance data sharing • Data sharing is the bottleneck in many environments • RDD’s provide in-place sharing through memory Applications can compose models • Run a SQL query and then PageRank the results • ETL your data and then run graph/ML on it Benefit from investment in shared functionality • E.g. re-usable components (shell) and performance optimizations
- 66. Agenda 1. MapReduce Review 2. Introduction to Spark and RDDs 3. Generality of RDDs (e.g. streaming, ML) 4. DataFrames 5. Internals (time permitting) 66
- 67. From MapReduce to Spark 67
- 68. Beyond Hadoop Users 68 Spark early adopters Data Engineers Data Scientists Statisticians R users PyData … Users Understands MapReduce & functional APIs
- 69. 69
- 70. DataFrames in Spark Distributed collection of data grouped into named columns (i.e. RDD with schema) DSL designed for common tasks • Metadata • Sampling • Project, filter, aggregation, join, … • UDFs Available in Python, Scala, Java, and R (via SparkR) 70
- 71. Not Just Less Code: Faster Implementations 0 2 4 6 8 10 RDD Scala RDD Python DataFrame Scala DataFrame Python DataFrame SQL Time to Aggregate 10 million int pairs (secs)
- 72. DataFrame Internals Represented internally as a “logical plan” Execution is lazy, allowing it to be optimized by a query optimizer 72
- 73. Plan Optimization & Execution 73 DataFrames and SQL share the same optimization/execution pipeline Maximize code reuse & share optimization efforts
- 74. 74 joined = users.join(events, users.id == events.uid) filtered = joined.filter(events.date >= ”2015-01-01”) this join is expensive à logical plan filter join scan (users) scan (events) physical plan join scan (users) filter scan (events)
- 75. Data Sources supported by DataFrames 75 built-in external { JSON } JDBC and more …
- 76. More Than Naïve Scans Data Sources API can automatically prune columns and push filters to the source • Parquet: skip irrelevant columns and blocks of data; turn string comparison into integer comparisons for dictionary encoded data • JDBC: Rewrite queries to push predicates down 76
- 77. 77 joined = users.join(events, users.id == events.uid) filtered = joined.filter(events.date > ”2015-01-01”) logical plan filter join scan (users) scan (events) optimized plan join scan (users) filter scan (events) optimized plan with intelligent data sources join scan (users) filter scan (events)
- 78. Our Experience So Far SQL is wildly popular and important • 100% of Databricks customers use some SQL Schema is very useful • Most data pipelines, even the ones that start with unstructured data, end up having some implicit structure • Key-value too limited • That said, semi-/un-structured support is paramount Separation of logical vs physical plan • Important for performance optimizations (e.g. join selection)
- 79. Machine Learning Pipelines tokenizer = Tokenizer(inputCol="text", outputCol="words”) hashingTF = HashingTF(inputCol="words", outputCol="features”) lr = LogisticRegression(maxIter=10, regParam=0.01) pipeline = Pipeline(stages=[tokenizer, hashingTF, lr]) df = sqlCtx.load("/path/to/data") model = pipeline.fit(df) df0 df1 df2 df3tokenizer hashingTF lr.model lr Pipeline Model
- 80. 80 R Interface (SparkR) Spark 1.4 (June) Exposes DataFrames, and ML library in R df = jsonFile(“tweets.json”) summarize( group_by( df[df$user == “matei”,], “date”), sum(“retweets”))
- 81. Data Science at Scale Higher level interfaces in Scala, Java, Python, R Drastically easier to program Big Data • With APIs similar to single-node tools 81
- 82. 82 {JSON} Data Sources Spark Core DataFrames ML Pipelines Spark Streaming Spark SQL MLlib GraphX
- 83. 83 Goal: unified engine across data sources, workloads and environments
- 84. Agenda 1. MapReduce Review 2. Introduction to Spark and RDDs 3. Generality of RDDs (e.g. streaming, ML) 4. DataFrames 5. Internals (time permitting) 84
- 85. Spark Application sc = new SparkContext f = sc.textFile(“…”)" " f.filter(…)" .count()" " ... Your program (JVM / Python) Spark driver" (app master) Spark executor (multiple of them) HDFS, HBase, … Block manager Task threads RDD graph Scheduler Block tracker Shuffle tracker Cluster" manager A single application often contains multiple actions
- 86. RDD is an interface 1. Set of partitions (“splits” in Hadoop) 2. List of dependencies on parent RDDs 3. Function to compute a partition (as an Iterator) given its parent(s) 4. (Optional) partitioner (hash, range) 5. (Optional) preferred location(s) for each partition “lineage” op5mized execu5on
- 87. Example: HadoopRDD partitions = one per HDFS block dependencies = none compute(part) = read corresponding block preferredLocations(part) = HDFS block location partitioner = none
- 88. Example: Filtered RDD partitions = same as parent RDD dependencies = “one-to-one” on parent compute(part) = compute parent and filter it preferredLocations(part) = none (ask parent) partitioner = none
- 89. RDD Graph (DAG of tasks) HadoopRDD" path = hdfs://... FilteredRDD" func = _.contains(…)" shouldCache = true file: errors: Partition-level view: Dataset-level view: Task1 Task2 ...
- 90. Example: JoinedRDD partitions = one per reduce task dependencies = “shuffle” on each parent compute(partition) = read and join shuffled data preferredLocations(part) = none partitioner = HashPartitioner(numTasks) Spark will now know this data is hashed!
- 91. Dependency Types union groupByKey on" non-partitioned data join with inputs not" co-partitioned join with inputs co-partitioned map, filter “Narrow” (pipeline-able) “Wide” (shuffle)
- 92. Execution Process rdd1.join(rdd2) .groupBy(…) .filter(…) RDD Objects build operator DAG DAG Scheduler split graph into stages of tasks submit each stage as ready DAG Task Scheduler TaskSet launch tasks via cluster manager retry failed or straggling tasks Cluster manager Worker execute tasks store and serve blocks Block manager Threads Task
- 93. DAG Scheduler Input: RDD and partitions to compute Output: output from actions on those partitions Roles: • Build stages of tasks • Submit them to lower level scheduler (e.g. YARN, Mesos, Standalone) as ready • Lower level scheduler will schedule data based on locality • Resubmit failed stages if outputs are lost
- 94. Job Scheduler Captures RDD dependency graph Pipelines functions into “stages” Cache-aware for data reuse & locality Partitioning-aware to avoid shuffles join union groupBy map Stage 3 Stage 1 Stage 2 A: B: C: D: E: F: G: = cached partition
- 95. 95 {JSON} Data Sources Spark Core DataFrames ML Pipelines Spark Streaming Spark SQL MLlib GraphX
- 96. 96 Goal: unified engine across data sources, workloads and environments































![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
Driver
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-33-320.jpg)
![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
Driver
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Ac5on](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-34-320.jpg)
![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
Driver
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block
1
Block
2
Block
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-35-320.jpg)
![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block
1
Block
2
Block
3
Driver
tasks
tasks
tasks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-36-320.jpg)
![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block
1
Block
2
Block
3
Driver
Read
HDFS
Block
Read
HDFS
Block
Read
HDFS
Block](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-37-320.jpg)
![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block
1
Block
2
Block
3
Driver
Cache
1
Cache
2
Cache
3
Process
&
Cache
Data
Process
&
Cache
Data
Process
&
Cache
Data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-38-320.jpg)
![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block
1
Block
2
Block
3
Driver
Cache
1
Cache
2
Cache
3
results
results
results](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-39-320.jpg)
![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block
1
Block
2
Block
3
Driver
Cache
1
Cache
2
Cache
3
messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-40-320.jpg)
![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block
1
Block
2
Block
3
Cache
1
Cache
2
Cache
3
messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()
tasks
tasks
tasks
Driver](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-41-320.jpg)
![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block
1
Block
2
Block
3
Cache
1
Cache
2
Cache
3
messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()
Driver
Process
from
Cache
Process
from
Cache
Process
from
Cache](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-42-320.jpg)
![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block
1
Block
2
Block
3
Cache
1
Cache
2
Cache
3
messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()
Driver
results
results
results](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-43-320.jpg)
![Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block
1
Block
2
Block
3
Cache
1
Cache
2
Cache
3
messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()
Driver
Cache your data è Faster Results
Full-text search of Wikipedia
• 60GB on 20 EC2 machines
• 0.5 sec from mem vs. 20s for on-disk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-44-320.jpg)


































![Machine Learning Pipelines
tokenizer
=
Tokenizer(inputCol="text",
outputCol="words”)
hashingTF
=
HashingTF(inputCol="words",
outputCol="features”)
lr
=
LogisticRegression(maxIter=10,
regParam=0.01)
pipeline
=
Pipeline(stages=[tokenizer,
hashingTF,
lr])
df
=
sqlCtx.load("/path/to/data")
model
=
pipeline.fit(df)
df0 df1 df2 df3tokenizer hashingTF lr.model
lr
Pipeline Model](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-79-320.jpg)
![80
R Interface (SparkR)
Spark 1.4 (June)
Exposes DataFrames,
and ML library in R
df = jsonFile(“tweets.json”)
summarize(
group_by(
df[df$user == “matei”,],
“date”),
sum(“retweets”))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-05-18cs347-stanford-150519052758-lva1-app6891/85/Stanford-CS347-Guest-Lecture-Apache-Spark-80-320.jpg)









































































































