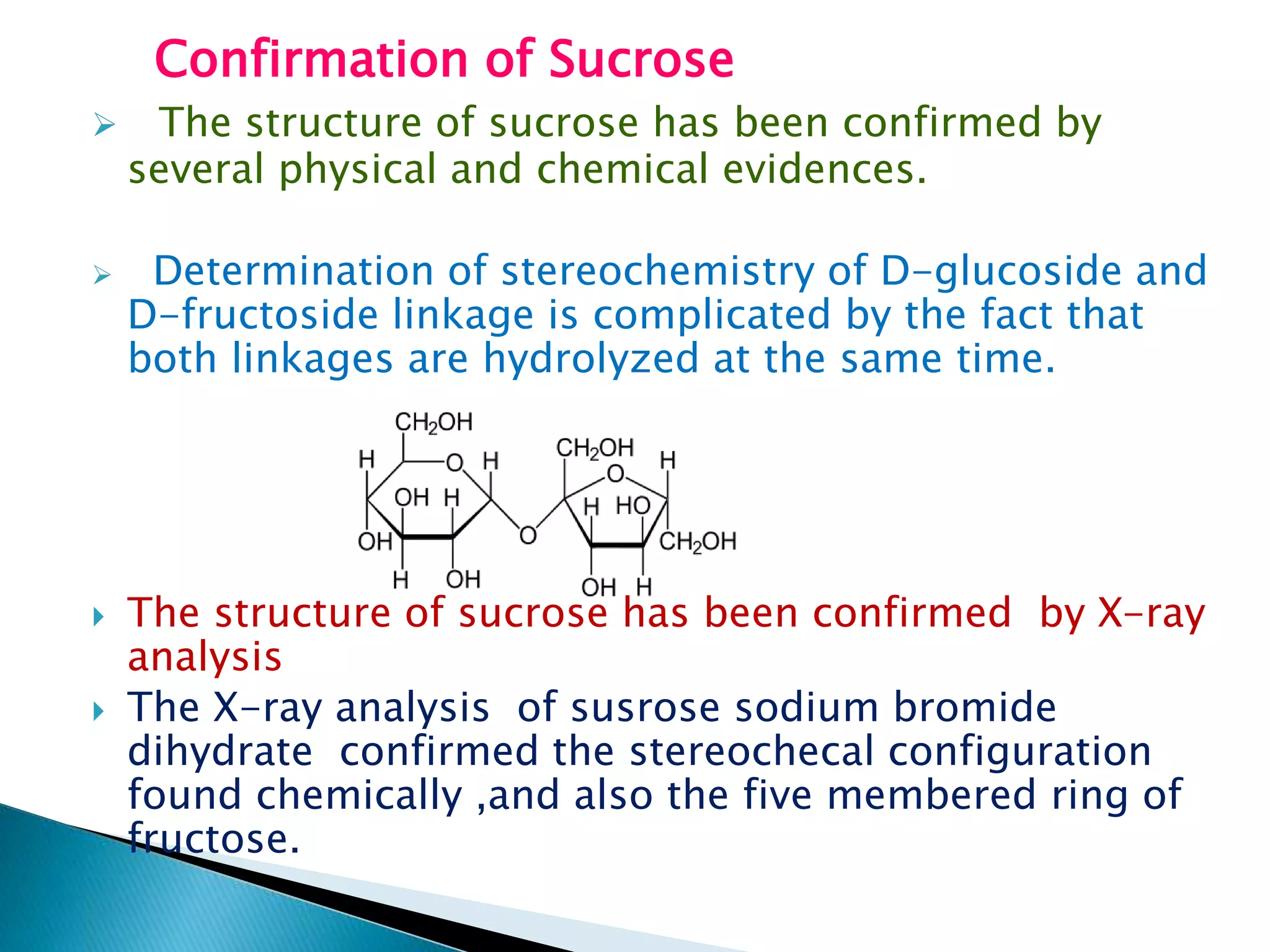
Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose units linked together. It is commonly found in sugar cane, sugar beets, maple sap, honey, and fruit juices. When hydrolyzed with acids or enzymes, sucrose breaks down into equal parts glucose and fructose. Structural analysis through techniques like periodate oxidation and X-ray crystallography confirm that sucrose contains an alpha-D-glucose unit linked via its 1 position to the 2 position of a beta-D-fructofuranose unit.