Telecom Roaming Overview
- 1. Telecom Roaming Overview Private & Confidential property of Shilpin Pvt. Ltd. www.shilpin.in
- 2. Objective Roaming Overview Entities Related to Roaming Service Home Network & Visited Network National, International, Inter-standard Roaming Inbound & Outbound Roaming Roaming Scenario’s Benefit of GSM technology in Roaming Jargon
- 3. Roaming Overview Roaming is an ability to access mobile data and voice services even if subscriber is outside the coverage area of HOME Network. It is possible via using VISITED Network services. To provide roaming facility to subscribers, operators should have roaming agreement with the other operators in different places.
- 4. Roaming Overview … City 1 (Home Area) Subscriber’s own area where they are using its own providers services Home Operator Hutch Area Visited Operator’s Area (Roaming Partner of Hutch) City 2 (Visited Area) Subscriber is on Roaming. Other operators Network Infrastructure Hutch Network Infrastructure Hutch Subscriber MSC MSC Switch Cell phone Switch Hutch Subscriber but using other operator services for Roaming purpose Cell phone Roaming Agreement Present between Hutch and other Operators
- 5. Entities Related to Roaming Service Home Network (HPMN) - Coverage area of subscribers own telecom operator. Visited Network (VPMN) – Coverage area of another operator which is providing telecom network access to home operator subscriber. Clearing House – Entity which is a mediator between home and visitor operator to interchange their data in specified format. Roaming Agreement – To provide roaming facility both the operators (Home and Visitor) should have agreement to use each others network infrastructure. Data Clearing – Facility to validate, filter and clear the data from one operator to another operator.
- 6. Home Network & Visited Network Operator1 & Operator2 have Roaming Aggrement Roaming Data from Operator2 for Operator1 Roaming Data from Clearing house to Operator1 Operator1 suscriber in Operator1 coverage area Clearing House Cell phone City NE Cell phone Visited Network NE Home Network Operator1 suscriber in Operator2 coverage area
- 7. National, International, Inter-standard Roaming National Roaming – If visited Network is in the same country, it is called National Roaming. International Roaming – If the visited Network is in the different country, It is called international or Global Roaming. Inter-standard roaming - If the visited network operates on a different technical standard than the home network, this is known as Interstandard roaming.
- 8. Inbound & Outbound Roaming Assuming – Airtel as a home operator Inbound Roaming – Customers of other operator roaming in Airtel area and using Airtel infrastructure then this activity is called inbound roaming. Only those customers can roam in Airtel network whose operator has Inbound Roaming agreement with Airtel. Outbound Roaming – Outbound Roaming refers to Airtel customers roaming in network of other operators area. Customers of Airtel can roam in network of other operators with whom Airtel has Outbound Roaming agreement.
- 9. Roaming Scenario’s Scenario 1 - When Roamer receives calls while on roaming, all his calls will reach the MSC of his Home Network in the first instance. He will be traced in his visited network and the calls are therefore forwarded there. City 1 (Home Area) Subscriber’s own area where they are using its own providers services Home Operator Hutch Area Hutch Network Infrastructure Visited Operator’s Area (Roaming Partner of Hutch) City 2 (Visited Area) Subscriber is on Roaming. Caller calling to Hutch Roamer MSC HUTCH MSC Other Operators NE Hutch NE Other operators Network Infrastructure Caller Roaming Agreement Present between Hutch and other Operators Reciever Hutch Subscriber but using other operator services for Roaming purpose
- 10. Roaming Scenario’s Scenario 2- When roamer makes calls to his Home Network (HPLMN), he obviously knows that he is temporarily out of his home network and thus his calls are routed through his temporary home network ie. visited network (VPLMN). City 1 (Home Area) Subscriber’s own area where they are using its own providers services Home Operator Hutch Area Hutch Network Infrastructure Visited Operator’s Area (Roaming Partner of Hutch) City 2 (Visited Area) Subscriber is on Roaming. Hutch User Receiving Hutch Roamer Call MSC Other Operators NE HUTCH MSC Hutch NE Other operators Network Infrastructure Receiver of Hutch Roaming Agreement Present between Hutch and other Operators Caller - Hutch Roamer Hutch Subscriber but using other operator services for Roaming purpose
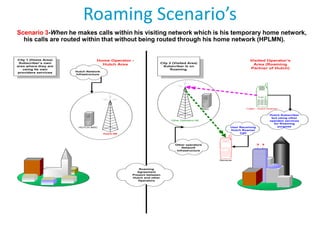
- 11. Roaming Scenario’s Scenario 3-When he makes calls within his visiting network which is his temporary home network, his calls are routed within that without being routed through his home network (HPLMN). City 1 (Home Area) Subscriber’s own area where they are using its own providers services Home Operator Hutch Area Hutch Network Infrastructure Visited Operator’s Area (Roaming Partner of Hutch) City 2 (Visited Area) Subscriber is on Roaming. Caller - Hutch Roamer MSC Other Operators NE User Receiving Hutch Roamer Call HUTCH MSC Hutch NE Other operators Network Infrastructure Reciever Roaming Agreement Present between Hutch and other Operators Hutch Subscriber but using other operator services for Roaming purpose
- 12. Roaming Scenario’s Scenario 4 - When he is making calls to networks other than his home network or the temporary home network, his calls are routed through the temporary home network only. City 1 (Home Area) Subscriber’s own area where they are using its own providers services City 2 (Visited Area) Subscriber is on Roaming. Hutch Network Infrastructure Home Operator Hutch Area Visited Operator’s Area (Roaming Partner of Hutch) City 3 (Receiver Area) City3 User Receiving Hutch Roamer Call Caller - Hutch Roamer Hutch Subscriber but using other operator services for Roaming purpose HUTCH MSC Reciever MSC Hutch NE Other Operators NE MSC Other operators Network Infrastructure Roaming Agreement Present between Hutch and other Operators City3 Operators NE Roaming Agreement Present between City2 & City3 Operators
- 13. Benefit of GSM technology in Roaming GSM Roaming, which involves roaming between GSM networks, offers the convenience of a single number, a single bill and a single phone with worldwide access to over 191 countries. The convenience of GSM Roaming has been a key driver behind the global success of the GSM Platform.
- 14. Jargon PLMN - Public Land Mobile Network. HPLMN - Home Public Land Mobile Network (Home Network ie. say the state of West Bengal) VPLMN - Visited Public Land Mobile Network (Visited Network - say the state where roaming - outside West Bengal) Notional TAX - The Trunk Auto Exchange of a particular State (say for West Bengal it is Asansol; for Orissa it is Cuttack and so on). Each state has a Level 1 TAX through which the calls for & from other states pass. PSTN Phone - Public Switched Telephone Network ie. a Landline Phone. PSTN Charges - The fixed line phone charges either Local Call Charges or STD Charges. Air Time - The duration of the call ie. during which time the call is there in the Air. POI - Point of Interconnect - This is where the mobile network is connected to the PSTN. SA - Service Area - The area served by a particular operator. Usual a state boundary. MSC - Mobile Switching Center ie. Mobile Exchange. BSC - Base Station Controller - It is an interface between the MSC on the one side and the BTS on the other. BTS - Base Transceiver Stations (Towers) Billing and Accounting for Roaming Group (BARG) - A subgroup of the GSM Association that focuses on the financial, administrative, and procedural issues related to roaming (visiting) customers.
- 15. THANKS