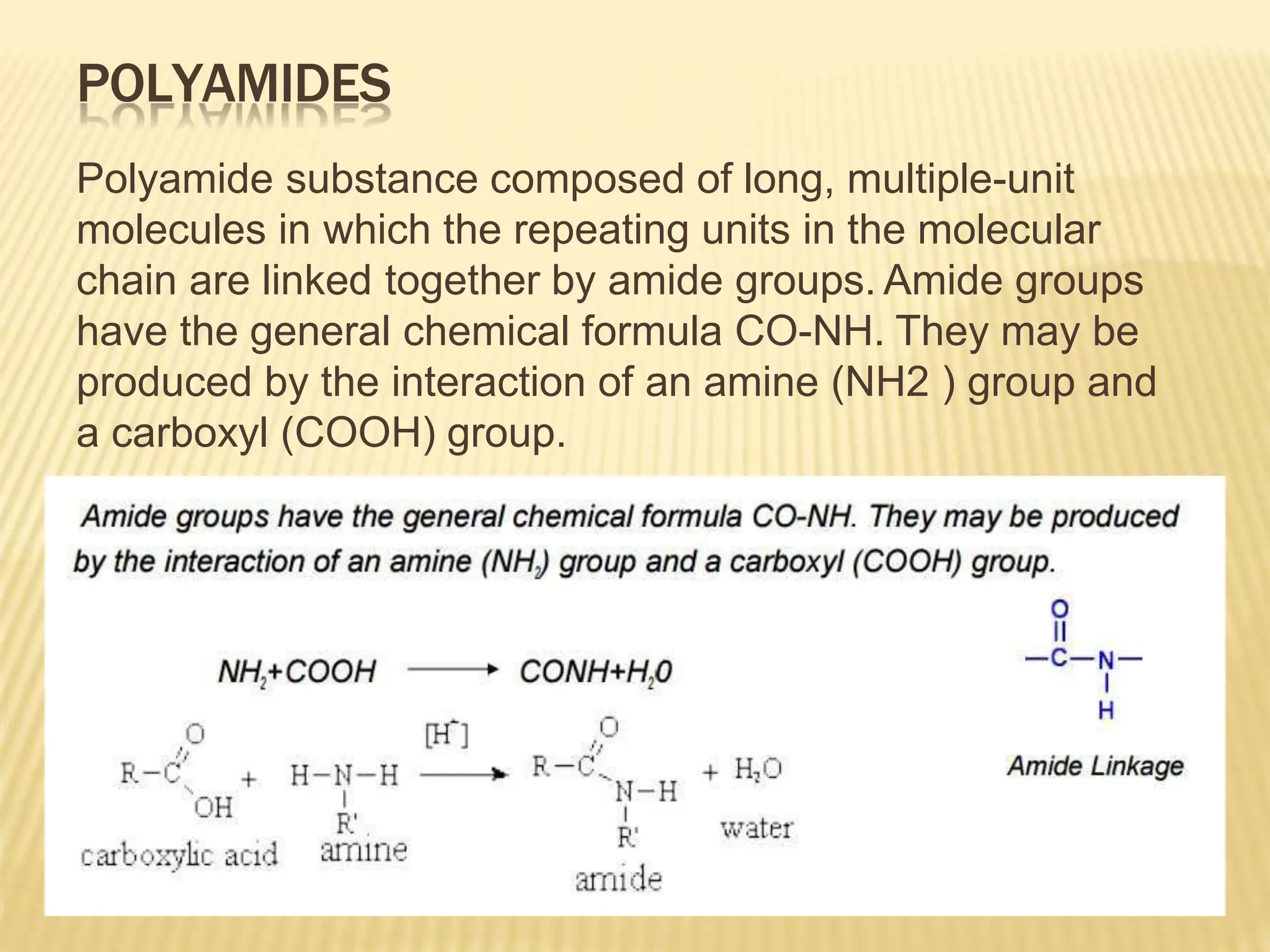
The document provides an in-depth overview of textile fibers, detailing classifications such as natural and man-made fibers. Key examples include cotton, rayon, silk, wool, polyamides, polyester, and acrylic, each described with their properties, manufacturing processes, and applications. It highlights important characteristics like elasticity, absorbency, and resilience that influence their use in textiles.