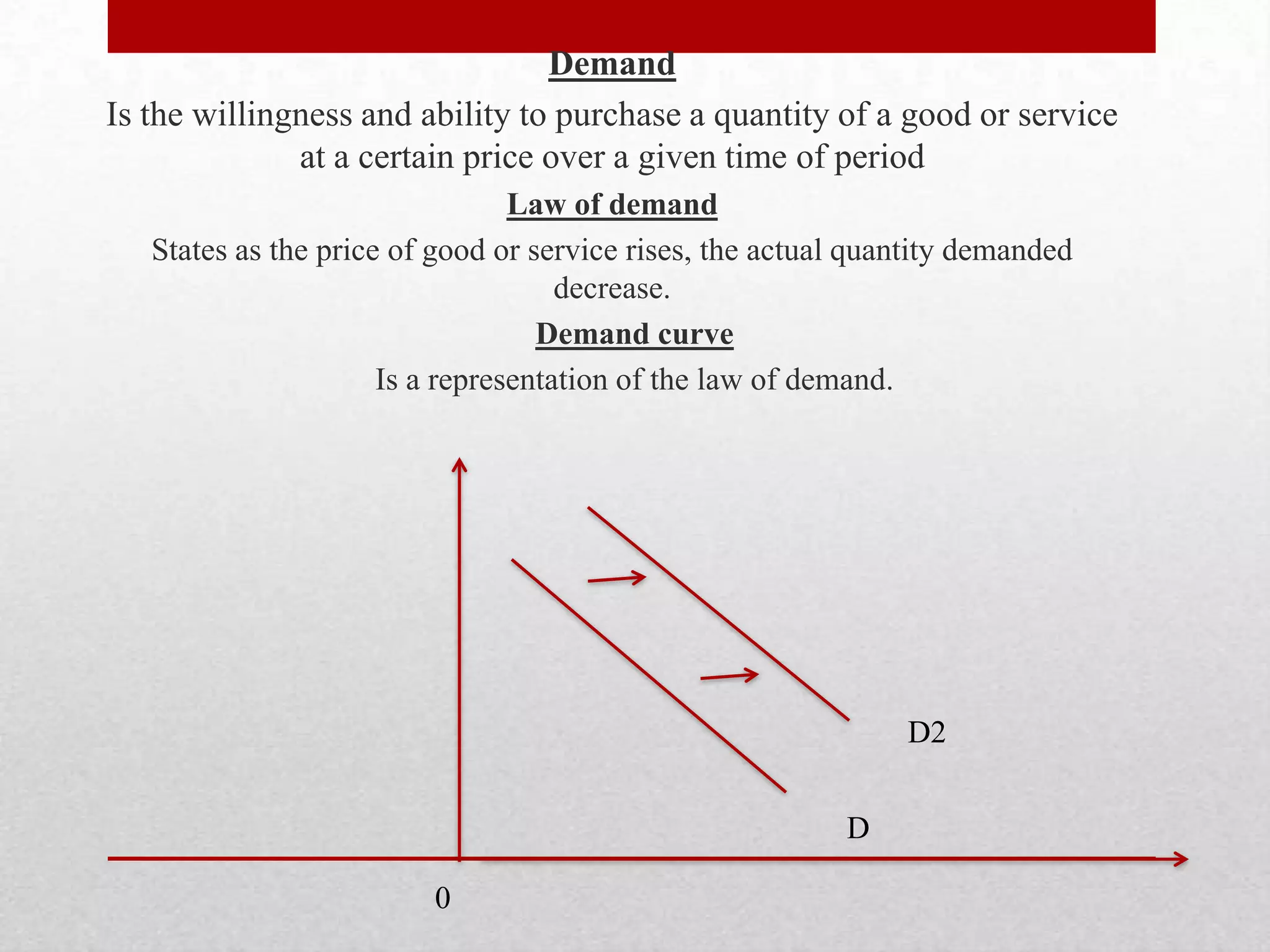
This document defines key economic terms across microeconomics and macroeconomics. It covers topics such as positive and normative economics, demand and supply, elasticities, costs of production, profit maximization, and market structures. Specifically, it defines scarcity, factors of production, the production possibility curve, economic growth, price ceilings and floors, income and cross elasticities, fixed and variable costs, short and long run periods, laws of returns, and revenues.